- 每道题控制一下时间,如果时间过了很久没思路,直接看题解,然后手敲,如果中途依然没思路,继续手敲;
- 分析执行结果,时间复杂度+空间复杂度,要求必须100%打败对手,写完之后看评论,学习更多的思路,做到一题多解;
- 代码中写清楚注释;
- 写过的代码一定要保存在github上面 【平常写的代码等文件一定要保存好】;
- 刷了大概几百到题;
- 大厂面试至少80%都是原题;
- 刷力扣+剑指offer;
- 多刷+狂刷
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(head!=null){
stack.push(head);
head=head.next;
}
if(stack.isEmpty())
return null;
ListNode node=stack.pop();
ListNode res=node;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
node.next=stack.pop();
node=node.next;
}
node.next=null;
return res;
}
}BM2 链表内指定区间反转
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int m, int n) {
ListNode virHead = new ListNode(-1);
virHead.next=head;
// 一定要加这句!!
ListNode pre = virHead;
for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode rightNode = pre;
for (int i = 0; i < n - m + 1; i++) {
rightNode = rightNode.next;
}
ListNode leftNode = pre.next;
ListNode cur = rightNode.next;
pre.next = null;
rightNode.next = null;
reverseLinekedList(leftNode);
pre.next = rightNode;
leftNode.next = cur;
return virHead.next;
}
private void reverseLinekedList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode cur_next = cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre = cur;
cur = cur_next;
}
}
}BM3 链表中的节点每k个一组翻转
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode tail = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if (tail == null)
// 如果数量不够k个,那么直接返回子链表的头指针即可,自动返回整个链表
return head;
tail = tail.next;
}
ListNode newHead = reverse(head, tail);
head.next = reverseKGroup(tail, k);
return newHead;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head, ListNode tail) {
ListNode next = null;
ListNode pre = null;
while (head != tail) {
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
BM4 合并两个排序的链表
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// 开始节点
ListNode resList = new ListNode(0);
// 将首指针赋给node链表
ListNode res=resList;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
resList.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
resList.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
resList = resList.next;
}
while (list1 != null) {
resList.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
resList = resList.next;
}
while (list2 != null) {
resList.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
resList = resList.next;
}
return res.next;
// return resList;
}
}
BM5 合并k个已排序的链表
// 分治思想
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ArrayList<ListNode> lists) {
return mergeList(lists,0,lists.size()-1);
}
// 合并列表
public ListNode mergeList(ArrayList<ListNode> lists, int left, int right) {
// 如果只有一个链表,则从数组中取出该数组!!
if(left==right) return lists.get(left);
if(left>right) return null;
int mid=left+(right-left)/2;
return merge(mergeList(lists,left,mid),mergeList(lists,mid+1,right));
}
// 就是简单的两个链表合并
public ListNode merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// 开始节点
ListNode resList = new ListNode(1);
// 将首指针赋给node链表
ListNode res = resList;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
resList.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
resList.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
resList = resList.next;
}
while (list1 != null) {
resList.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
resList = resList.next;
}
while (list2 != null) {
resList.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
resList = resList.next;
}
return res.next;
}
}import java.util.HashSet;
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode pos = head;
HashSet<ListNode> visitedNode = new HashSet<>();
while (pos != null) {
if (visitedNode.contains(pos)) {
return true;
}
visitedNode.add(pos);
pos = pos.next;
}
return false;
}
}// 1 栈 时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(1)。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode pHead, int k) {
if(pHead==null || k==0 )
return null;
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode node = new ListNode(0);
while (pHead != null) {
stack.push(pHead);
pHead = pHead.next;
}
if (stack.size() < k)
return null;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
node = stack.pop();
}
return node;
}
}
// 2 快慢指针 时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(n)。import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* @param head ListNode类
* @param n int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) {
// head是空的头指针,不带数据
ListNode pos = head;
// 此处必须将head赋值给q
ListNode q = head;
int len = 0;
while (head != null) {
len++;
head = head.next;
}
if (n == len) {
return q.next;
}
// for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// i++;
// if (i == len - n) {
// pos.next = pos.next.next;
// }
// pos = pos.next;
// }
int i = 0;
while (pos != null) {
i++;
if (i == len - n) {
pos.next = pos.next.next;
}
pos = pos.next;
}
return q;
}
}
BM10 两个链表的第一个公共结点
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
ListNode p1=pHead1;
ListNode p2=pHead2;
while(p1!=p2){
p1=(p1!=null)?p1.next:pHead2;
p2=(p2!=null)?p2.next:pHead1;
}
return p1;
}
}
BM11 链表相加(二)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head1 ListNode类
* @param head2 ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode addInList (ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
if(head1==null)
return head2;
if(head2==null)
return head1;
head1 = reverse(head1);
head2 = reverse(head2);
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode newHead = head;
// 注意此处进位是全局变量!!
int tmp = 0;
while (head1 != null || head2 != null) {
int val = tmp;
if (head1 != null) {
val += head1.val;
head1 = head1.next;
}
if (head2 != null) {
val += head2.val;
head2 = head2.next;
}
tmp = val / 10;
newHead.next = new ListNode(val % 10);
newHead = newHead.next;
}
// 注意此处最后进位的处理
if (tmp > 0) {
newHead.next = new ListNode(tmp);
}
return reverse(head.next);
}
ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode tail = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tail;
}
// 注意此处返回值
return pre;
}
}BM12 单链表的排序
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) {
ArrayList tmpArr = new ArrayList();
while (head != null) {
tmpArr.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
Collections.sort(tmpArr);
ListNode tmp = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode res = tmp;
// foreach循环
for (Object i : tmpArr) {
tmp.next = new ListNode(Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(i)));
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return res.next;
}
}BM13 判断一个链表是否为回文结构
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean isPail (ListNode head) {
// 复制原链表
ListNode tmp_head = head;
ListNode oldHeadList = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode oldHead= oldHeadList;
while (tmp_head != null) {
oldHead.next=new ListNode(tmp_head.val);
// 这样改变指针还是引用,并没有进行新的创建
// oldHead.next=tmp_head;
tmp_head=tmp_head.next;
oldHead=oldHead.next;
}
ListNode res = reverseList(head);
while (oldHeadList.next != null && res != null) {
if (oldHeadList.next.val != res.val)
return false;
oldHeadList = oldHeadList.next;
res = res.next;
}
return true;
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null, cur = head, next = null;
while (cur != null ) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
BM14 链表的奇偶重排
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList (ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode Node1 = head;
ListNode node1 = head;
ListNode Node2 = head.next;
ListNode node2 = head.next;
while (node1.next != null && node2.next != null) {
node1.next = node2.next;
node1=node1.next;
node2.next = node1.next;
node2=node2.next;
}
node1.next = Node2;
return Node1;
}
}
BM15 删除有序链表中重复的元素-I
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) {
// write code here
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode cur = head;
// 操作时对cur进行操作
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.val == cur.next.val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}
}
思想:
-
要求:空间复杂度 O(n)O(n),时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
增加辅助空间set,然后遍历原链表,构建新的链表即可
-
进阶:空间复杂度 O(1)O(1),时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) {
// write code here
if (head == null)
return head;
Set set = new HashSet();
ListNode cur = new ListNode(-1);
cur.next = head;
ListNode p = cur;
ListNode tmp = head;
while (tmp.next != null) {
if (tmp.val == tmp.next.val) {
set.add(tmp.val);
} else
tmp = tmp.next;
}
p = cur;
while (p.next != null) {
if (set.contains(p.next.val)) {
p.next = p.next.next;
} else
p = p.next;
}
return cur.next;
}
}
==O(logn)== 【重要!!】
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int search (int[] nums, int target) {
// write code here
int low=0,high=nums.length-1;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
int mid=(low+high)/2;
if(target<nums[mid]){
high=mid-1;
}
else if(target>nums[mid]){
low=mid+1;
}else{
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
public class Solution {
public boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) {
int m=array.length;
if(m==0)
return false;
int n=array[0].length;
if(n==0)
return false;
int row=0,columm=n-1;
while(row<m && columm>=0){
if(target==array[row][columm])
return true;
else if(target>array[row][columm]){
row++;
}
else
columm--;
}
return false;
}
}
BM19 寻找峰值
复杂度:o(n)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int findPeakElement (int[] nums) {
// write code here
if (nums.length == 2 && nums[0] > nums[1]) {
return 0;
} else if (nums.length == 2 && nums[0] < nums[1]) {
return 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1] && nums[i] > nums[i + 1])
return i;
else if (nums[nums.length - 1] > nums[nums.length - 2])
return nums.length - 1;
}
return 0;
}
}O(logN)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int findPeakElement (int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 1)
return 0;
if (n == 2 ) {
int peek = nums[0] > nums[1] ? 0 : 1;
return peek;
}
int low = 0, high = n - 1, mid = 0;
while (low < high) {
mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
// 峰值在右侧
if (nums[mid] < nums[mid + 1]) {
low = mid + 1;
}
//峰值在左侧
else if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]) {
high = mid;
}
}
return low;
}
}【存在一定的问题!】
归并算法 O(nlogn)
「归并排序」与「逆序对」是息息相关的。归并排序体现了 “分而治之” 的算法思想,具体为:
分: 不断将数组从中点位置划分开(即二分法),将整个数组的排序问题转化为子数组的排序问题; 治: 划分到子数组长度为 1 时,开始向上合并,不断将 较短排序数组 合并为 较长排序数组,直至合并至原数组时完成排序;
public class Solution {
// 这个思想一定要结合左侧的图示
int count = 0;
public int InversePairs(int [] array) {
if (array.length < 2)
return 0;
mergeSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
return count;
}
public void mergeSort(int [] array, int left, int right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (left < right) {
// 先分
mergeSort(array, left, mid);
mergeSort(array, mid + 1, right);
// 后合
merge(array, left, mid, right);
}
}
public void merge(int [] array, int left, int mid, int right) {
int[] arr = new int[right - left + 1];
int l = left;
int r = mid + 1;
int c = 0;
//注意此处s的取值
int s = left;
while (l <= mid && r <= right) {
if (array[l] < array[r]) {
arr[c++] = array[l++];
//没有重复数字所以可以这样!!
} else {
arr[c++] = array[r++];
//这个条件不会写?
//左右两侧都是升序,所以mid右侧是右侧序列最小值,因此可以这样计算
count += mid + 1 - l;
count %= 1000000007;
}
}
while (l <= mid)
arr[c++] = array[l++];
while (r <= right)
arr[c++] = array[r++];
for (int num : arr) {
array[s++] = num;
}
}
}import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int [] array) {
if (array.length == 0) return 0;
int low = 0, high = array.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
// 终止条件
if (array[low] < array[high]) {
return array[low];
}
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (array[mid] > array[high])
low = mid + 1;
else if (array[mid] < array[high]) {
high = mid ;
} else {
high--;
}
}
return array[low];
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int compare (String version1, String version2) {
// 注意转义处理
String[] str1 = version1.split("\\.");
String[] str2 = version2.split("\\.");
int i;
int maxLen = (str1.length > str1.length) ? str1.length : str2.length;
for ( i = 0; i < str1.length || i < str1.length; i++) {
int x = 0, y = 0;
if (i < str1.length) {
x = Integer.parseInt(str1[i]);
}
if (i < str2.length) {
y = Integer.parseInt(str2[i]);
}
if (x > y) {
return 1;
}
if (x < y) {
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
BM23 二叉树的前序遍历
定义 preorder(root) 表示当前遍历到 ==root 节点==的答案。按照定义,我们只要首先将 root 节点的值加入答案,然后递归调用 ==preorder(root.left) 来遍历 root 节点的左子树,最后递归调用 preorder(root.right) 来遍历 root 节点的右子树即可==,递归终止的条件为==碰到空节点==。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
preorder ( root, list);
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
res[i] = list.get(i);
}
return res;
}
public void preorder (TreeNode root, ArrayList list) {
if (root != null) {
list.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left, list);
preorder(root.right, list);
}
}
}
BM24 二叉树的中序遍历
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public int[] inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
// write code here
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(list, root);
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
res[i] = list.get(i);
}
return res;
}
public void dfs(List list, TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
dfs(list, root.left);
list.add(root.val);
dfs(list, root.right);
}
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return res;
//队列作用:遍历所有元素
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null)
queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
queue.offer(node.right);
}
res.add(list);
}
return res;
}
}方法一:层序遍历 + 双端队列(奇偶层逻辑分离) 方法一代码简短、容易实现;但需要判断每个节点的所在层奇偶性,即冗余了 NN 次判断。 通过将奇偶层逻辑拆分,可以消除冗余的判断。 算法流程:
BFS 循环: 循环打印奇 / 偶数层,当 deque 为空时跳出; 奇数层: 队首出节点,队尾先加左节点后加右节点 偶数层: 队尾出节点,队首先加右节点后加左节点
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(pRoot==null)
return res;
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(pRoot);
int level = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (level % 2 != 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.pollFirst();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null)
queue.addLast(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
queue.addLast(node.right);
} else {
TreeNode node = queue.pollLast();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.right != null)
queue.addFirst(node.right);
if (node.left != null)
queue.addFirst(node.left);
}
}
level++;
res.add(list);
}
return res;
}
}
方法二:层序遍历 + 双端队列 利用双端队列的两端皆可添加元素的特性,设打印列表(双端队列) tmp ,并规定: 奇数层 则添加至 tmp 尾部 , 偶数层 则添加至 tmp 头部 。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null) queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
LinkedList<Integer> tmp = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = queue.size(); i > 0; i--) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
// 偶数层 -> 队列头部
if(res.size() % 2 == 0) tmp.addLast(node.val);
// 奇数层 -> 队列尾部
else tmp.addFirst(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
}要求:空间复杂度 O(n),时间复杂度 O(n)
进阶:空间复杂度 O(树的高度)O(树的高度),时间复杂度 O(n)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null)
return false;
return hasPath(root, sum,0);
}
public boolean hasPath(TreeNode root, int sum,int res){
if (root == null)
return false;
// 要对累加值进行处理,否则递归错误
res += root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && res == sum)
return true;
return hasPath(root.left,sum,res) || hasPath(root.right,sum,res);
}
}==【看到二叉搜索树一定要想到中序遍历!!!】==
要求:空间复杂度O(1)(即在原树上操作),时间复杂度 O(n)
因此二叉搜索树的==中序遍历==就是一个递增序列,我们只要对它中序遍历就可以组装称为递增双向链表。
1、特殊情况,二叉树为空,则直接返回 null
2、创建 保留上一个结点 pre,返回链表结点 root
3、递归遍历左子树;root = pRootOfTree
4、遍历当前结点,并修改为双向链表 pRootOfTree.left=pre; pre.right=pRootOfTree;
5、更新 pre = pRootOfTree
6、递归遍历右子树
7、递归结束返回 root
public class Solution {
TreeNode cur = null, head = null;
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if (pRootOfTree == null)
return pRootOfTree;
Convert( pRootOfTree.left);
if (cur == null) {
cur = pRootOfTree;
head = pRootOfTree;
} else {
cur.right=pRootOfTree;
pRootOfTree.left=cur;
cur=pRootOfTree;
}
Convert( pRootOfTree.right);
return head;
}
}可以用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题
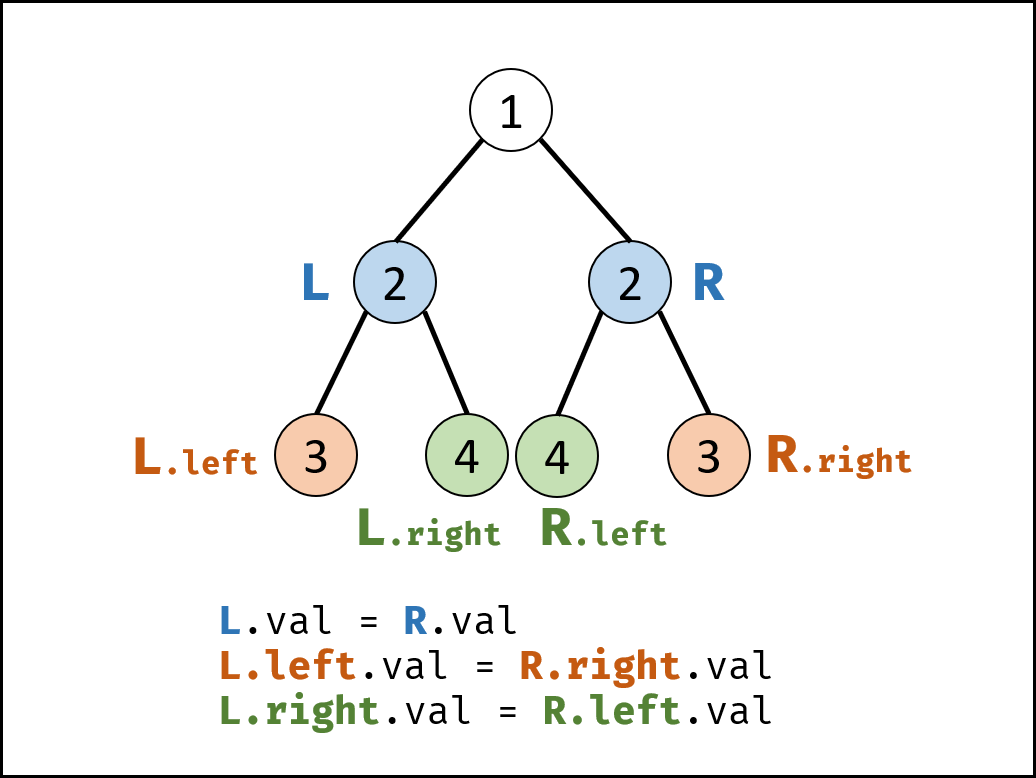
解题思路: 对称二叉树定义: 对于树中 任意两个对称节点 LL 和 RR ,一定有: L.val=R.val :即此两对称节点值相等。 L.left.val=R.right.val :即 LL 的 左子节点 和 RR 的 右子节点 对称; L.right.val = R.left.val :即 LL 的 右子节点 和 RR 的 左子节点 对称。
根据以上规律,考虑从顶至底递归,判断每对节点是否对称,从而判断树是否为对称二叉树。
算法流程: isSymmetric(root) :
特例处理: 若根节点 root 为空,则直接返回 truetrue 。 返回值: 即 recur(root.left, root.right) ; recur(L, R) :
终止条件: 当 LL 和 RR 同时越过叶节点: 此树从顶至底的节点都对称,因此返回 true ; 当 LL 或 RR 中只有一个越过叶节点: 此树不对称,因此返回 false ; 当节点 LL 值 不等于节点 RR 值: 此树不对称,因此返回 false ; 递推工作: 判断两节点 L.left和 R.right是否对称,即 recur(L.left, R.right) ; 判断两节点 L.right 和 R.left是否对称,即 recur(L.right, R.left) ; 返回值: 两对节点都对称时,才是对称树,因此用与逻辑符 && 连接。
public class Solution {
boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) {
return pRoot==null?true:recur(pRoot.left,pRoot.right);
}
boolean recur(TreeNode L,TreeNode R){
// 终止条件
if( L==null && R==null) return true;
// 注意或的条件顺序!!
if(L==null || R==null || L.val!=R.val) return false;
// 递推公式
return recur( L.left, R.right) && recur( L.right, R.left);
}
}进阶:空间复杂度 O(1),时间复杂度 O(n)
递归
时间复杂度:O(N) 空间复杂度:O(N)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
//终止条件
if (t1 == null) return t2;
if (t2 == null) return t1;
//递推工作
//合并根节点
t1.val = t1.val + t2.val;
//合并左子树
t1.left = mergeTrees ( t1.left, t2.left);
//合并右子树
t1.right = mergeTrees ( t1.right, t2.right);
return t1;
}
}要求: 空间复杂度 O(n) 。
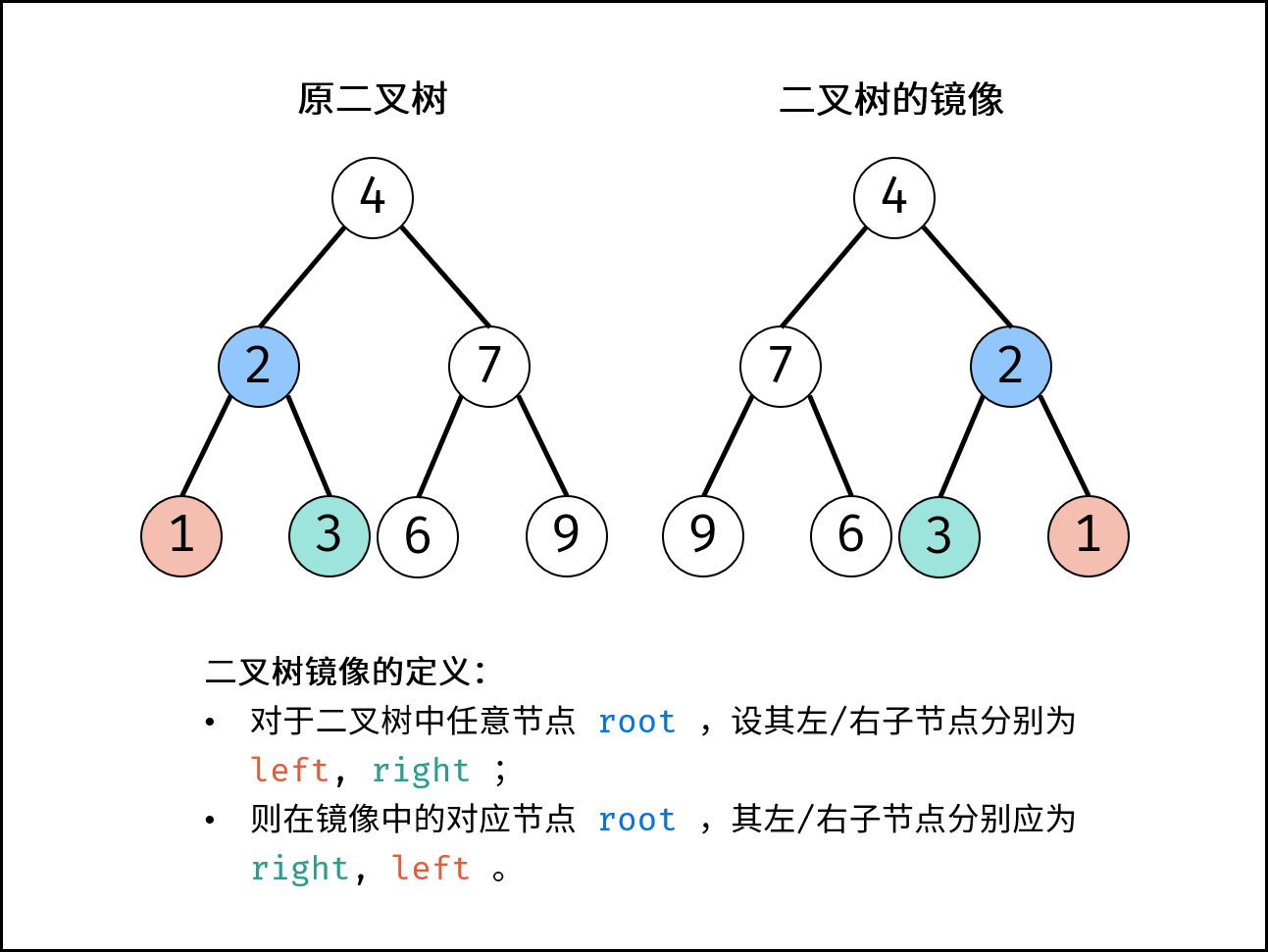
本题也有原地操作,即空间复杂度 O(1)的解法,时间复杂度 O(n)
二叉树镜像定义: 对于二叉树中任意节点 root ,设其左 / 右子节点分别为 left, rightleft,right ;则在二叉树的镜像中的对应 rootroot 节点,其左 / 右子节点分别为 right, leftright,left 。
方法一:递归法 根据二叉树镜像的定义,考虑递归遍历(dfs)二叉树,交换每个节点的左 / 右子节点,即可生成二叉树的镜像。 递归解析 终止条件:
当节点 root 为空时(即越过叶节点),则返回 null ; 递推工作: 初始化节点 tmp ,用于暂存 root 的左子节点; 开启递归 右子节点 mirrorTree(root.right),并将返回值作为 root的 左子节点 。 开启递归 左子节点 mirrorTree(tmp) ,并将返回值作为 root 的 右子节点 。 返回值:
返回当前节点 root ;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode Mirror (TreeNode pRoot) {
// 终止条件
if (pRoot == null) return null;
// 递推工作
TreeNode tmp = pRoot.left;
pRoot.left = pRoot.right;
pRoot.right = tmp;
pRoot.left = Mirror (pRoot.left);
pRoot.right = Mirror (pRoot.right);
return pRoot;
}
}是否要增加新的recur函数取决于,原函数的参数是否够用,如果不够用,则要新开辟函数!!
方法一:中序遍历
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**中序遍历得到list,然后遍历list比较前后的值*/
public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
inOrder(list, root);
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < list.size() - 1; i++) {
if (list.get(i) >= list.get(i + 1))
return false;
}
return true;
}
public void inOrder(List list, TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
dfs(list, root.left);
list.add(root.val);
dfs(list, root.right);
}
}
}方法二:递归
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) {
return recur(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
public boolean recur (TreeNode root, long min, long max) {
// 终止条件
if (root == null) return true;
if (root.val <= min || root.val >= max) return false;
return recur (root.left, min, root.val) && recur (root.right, root.val, max);
}
}思想:层序遍历
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean isCompleteTree (TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return false;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
boolean flag = false;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node == null)
flag = true;
else {
if (!queue.isEmpty() && flag) {
return false;
}
queue.offer(node.left);
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
return true;
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
return depth(root) != -1;
}
// 求二叉树的最大高度:自底向上
public int depth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
int ldep = depth(root.left);
if (ldep == -1) return -1;
int rdep = depth(root.right);
if (rdep == -1) return -1;
int sub = Math.abs(ldep - rdep);
if (sub > 1) return -1;
return Math.max(ldep, rdep) + 1;
}
}
方法二:一次遍历 思路与算法
在方法一中,我们对从根节点开始,通过遍历找出到达节点 pp 和 qq 的路径,一共需要两次遍历。我们也可以考虑将这两个节点放在一起遍历。
整体的遍历过程与方法一中的类似:
我们从根节点开始遍历;
如果当前节点的值大于 pp 和 qq 的值,说明 pp 和 qq 应该在当前节点的左子树,因此将当前节点移动到它的左子节点;
如果当前节点的值小于 pp 和 qq 的值,说明 pp 和 qq 应该在当前节点的右子树,因此将当前节点移动到它的右子节点;
如果当前节点的值不满足上述两条要求,那么说明当前节点就是「分岔点」。此时,pp 和 qq 要么在当前节点的不同的子树中,要么其中一个就是当前节点。
可以发现,如果我们将这两个节点放在一起遍历,我们就省去了存储路径需要的空间。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int p, int q) {
TreeNode ancestor = root;
while (true) {
if (ancestor.val > p && ancestor.val > q)
ancestor = ancestor.left;
else if (ancestor.val < p && ancestor.val < q)
ancestor = ancestor.right;
else
return ancestor.val;
}
}
}
根据以上定义,若 rootroot 是 p, qp,q 的 最近公共祖先 ,则只可能为以下情况之一:
pp 和 qq 在 rootroot 的子树中,且分列 rootroot 的 异侧(即分别在左、右子树中); p = root,且 qq 在 rootroot 的左或右子树中; q = root,且 pp 在 rootroot 的左或右子树中;
考虑通过递归对二叉树进行先序遍历,当遇到节点 pp 或 qq 时返回。从底至顶回溯,当节点 p, qp,q 在节点 rootroot 的异侧时,节点 rootroot 即为最近公共祖先,则向上返回 rootroot 。
递归解析: 终止条件: 当越过叶节点,则直接返回 null ; 当 rootroot 等于 p, q,则直接返回 root ; 递推工作: 3.若不为1, 2中情况,说明需要继续处理: 对左子树进行递归,返回值记为 t1 对右子树进行递归,返回值记位 t2 t1 ,t2 存在以下几种情况:
【处理技巧!!】
【123按照异常情况处理】
①. 当t1, t2都为空时,说明root的左右子树中都不存在o1, o2, 返回空 ②. 当t1为空且t2不为空时,说明左子树找不到 o1, o2,所以返回 t2 ③. 当t2为空且t1不为空时,说明右子树找不到 o1, o2,所以返回 t1
【4按正常情况处理】
④. 当t1, t2都不为空时,说明o1, o2分别位于root的左右子树中,既root为答案,返回root
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int o1, int o2) {
if (root == null)
return -1;
if (root.val == o1 || root.val == o2)
return root.val;
// 1结果在左子树中
int left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, o1, o2);
// 2结果在右子树中
int right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, o1, o2);
if (left == -1)
return right;
if (right == -1)
return left;
// 3根节点是祖先
return root.val;
}
}要求:序列化和反序列化都是空间复杂度 O(n)O(n),时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
通常使用的前序、中序、后序、层序遍历记录的二叉树的信息不完整,即唯一的输出序列可能对应着多种二叉树可能性。题目要求的 序列化 和 反序列化 是 可逆操作 。因此,序列化的字符串应携带 完整的二叉树信息 。
序列化 使用==层序遍历==实现。反序列化 通过以上递推公式反推各节点在序列中的索引,进而实现。
反序列化 Deserialize : 基于本文开始推出的 node , node.left , node.right 在序列化列表中的位置关系,可实现反序列化。
利用==队列按层构建二叉树==,借助一个指针 i 指向节点 node 的左、右子节点,每==构建一个 node 的左、右子节点==,指针 i 就向右移动 11 位。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
String Serialize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return "";
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
// 注意这块!!
if (node != null) {
res.append(node.val + ",");
queue.offer(node.left);
queue.offer(node.right);
} else {
res.append("null,");
}
}
return res.toString();
}
TreeNode Deserialize(String str) {
if (str.equals("")) return null;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
String[] res = str.split(",");
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(res[0]));
queue.offer(root);
int i = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
// 注意这块!!
if (!res[i].equals("null")) {
node.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(res[i]));
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (!res[i + 1].equals("null")) {
node.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(res[i + 1]));
queue.offer(node.right);
}
i = i + 2;
}
return root;
}
}分治算法解析: 递推参数:
==根节点在前序遍历的索引 root 、子树在中序遍历的左边界 left 、子树在中序遍历的右边界 right ;==
终止条件: 当 left > right ,代表已经越过叶节点,此时返回 nullnull ;
递推工作:
-
建立根节点 node : 节点值为 preorder[root] ;
-
划分左右子树: 查找根节点在中序遍历 inorder 中的索引 i ;
-
构建左右子树: 开启左右子树递归;
根节点索引 中序遍历左边界 中序遍历右边界 左子树 root + 1 left i - 1 右子树 i - left + root + 1 i + 1 right TIPS: i - left + root + 1含义为 根节点索引 + 左子树长度 + 1
返回值: 回溯返回 node ,作为上一层递归中根节点的左 / 右子节点;
import java.util.*;
// 思想:根据前序找到根节点,然后在中序中划分出左右子树
public class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> dic = new HashMap<>();
int[] pre1;
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre, int [] vin) {
pre1 = pre;
for (int i = 0; i < vin.length; i++) {
dic.put(vin[i], i);
}
return recur(0, 0, vin.length - 1);
}
TreeNode recur(int root, int left, int right) {
if (left > right)
return null;
// 根节点
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(pre1[root]);
// 划分左右子树
int pos = dic.get(pre1[root]);
node.left = recur(root+1,left,pos-1);
// 右子树的根节点=root+左子树的长度
node.right = recur(root+pos-left+1,pos+1,right);
return node;
}
}import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> dic = new HashMap<>();
int[] pre1;
public int[] solve (int[] xianxu, int[] zhongxu) {
pre1 = xianxu;
for (int i = 0; i < zhongxu.length; i++) {
dic.put(zhongxu[i], i);
}
TreeNode root=recur(0, 0, zhongxu.length - 1);
int[] tmp = new int[xianxu.length];
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int j=0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (i == size - 1) {
tmp[j++] = node.val;
}
if (node.left != null)
queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
int[] res = new int[j];
for(int p=0;p<j;p++){
res[p]=tmp[p];
}
return res;
}
TreeNode recur(int root, int left, int right) {
if (left > right)
return null;
// 根节点
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(pre1[root]);
// 划分左右子树
int pos = dic.get(pre1[root]);
node.left = recur(root + 1, left, pos - 1);
// 右子树的根节点=root+左子树的长度
node.right = recur(root + pos - left + 1, pos + 1, right);
return node;
}
}
BM42 用两个栈实现队列
import java.util.Stack;
// 当插入时,直接插入 stack1
// 当弹出时,当 stack2 不为空,弹出 stack2 栈顶元素,
// 如果 stack2 为空,将 stack1 中的全部数逐个出栈入栈 stack2,
// 再弹出 stack2 栈顶元素
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
BM43 包含min函数的栈
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> minStack = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack.push(node);
if (minStack.empty())
minStack.push(node);
else {
if (node < minStack.peek() ) {
minStack.push(node);
} else {
minStack.push(minStack.peek());
}
}
}
public void pop() {
stack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
BM44 有效括号序列
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean isValid (String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
switch (s.charAt(i)) {
case '[':
case '{':
case '(':
stack.push(s.charAt(i));
break;
// 此处||两边的表达式位置会对结果有影响!!
case ']':
if ( stack.empty() || stack.peek() != '[' )
return false;
stack.pop();
break;
case '}':
if ( stack.empty() || stack.peek() != '{' )
return false;
stack.pop();
break;
case ')':
if (stack.empty() || stack.peek() != '(' )
return false;
stack.pop();
break;
}
}
return stack.empty() ? true : false;
}
}
除了由Vector定义的所有方法,自己也定义了一些方法:
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | boolean ==empty()== 测试堆栈是否为空。 |
| 2 | Object ==peek( )== 查看堆栈顶部的对象,但不从堆栈中移除它。 |
| 3 | Object pop( ) 移除堆栈顶部的对象,并作为此函数的值返回该对象。 |
| 4 | Object push(Object element) 把项压入堆栈顶部。 |
| 5 | int search(Object element) 返回对象在堆栈中的位置,以 1 为基数。 |
【双端队列】
要求:空间复杂度 O(n)O(n),时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
- 遍历数组的每一个元素,
- 如果容器为空,则直接将当前元素==加入==到容器中。
- 如果容器不为空,则让当前元素和容器的==最后一个元素比较==,如果大于,则将容器的最后一个元素删除,然后继续讲当前元素和容器的最后一个元素比较
- 如果当前元素小于容器的最后一个元素,则直接将当前元素加入到容器的末尾
- 如果容器头部的元素已经不属于当前窗口的边界,则应该将头部元素删除
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int [] num, int size) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (size == 0 || size > num.length) return res;
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
while (!deque.isEmpty() && num[deque.peekLast()] < num[i] ) {
deque.pollLast();
}
deque.offerLast(i);
// 如果容器头部的元素已经不属于当前窗口的边界,则应该将头部元素删除
if (deque.peekFirst() <= i - size) {
deque.pollFirst();
}
if (i + 1 >= size) {
res.add(num[ deque.peekFirst()]);
}
}
return res;
}
}
双端队列的方法
由于Deque继承了Queue接口,因此它继承了Queue接口的所有方法。
除了Queue接口中可用的方法之外,Deque界面还包括以下方法:
- addFirst() - 在双端队列的开头添加指定的元素。如果双端队列已满,则引发异常。
- addLast() - 在双端队列的末尾添加指定的元素。如果双端队列已满,则引发异常。
- offerFirst() - 在双端队列的开头添加指定的元素。如果双端队列已满,则返回false。
- offerLast() - 在双端队列的末尾添加指定的元素。如果双端队列已满,则返回false。
- getFirst() - 返回双端队列的第一个元素。如果双端队列为空,则引发异常。
- getLast() - 返回双端队列的最后一个元素。如果双端队列为空,则引发异常。
- peekFirst() - 返回双端队列的==第一个元素==。如果双端队列为空,则返回null。
- peekLast() - 返回双端队列的==最后一个元素==。如果双端队列为空,则返回null。
- removeFirst() - 返回并删除双端队列的第一个元素。如果双端队列为空,则引发异常。
- removeLast() - 返回并删除双端队列的最后一个元素。如果双端队列为空,则引发异常。
- pollFirst() - 返回并删除双端队列的第一个元素。如果双端队列为空,则返回null。
- pollLast() - 返回并删除双端队列的最后一个元素。如果双端队列为空,则返回null。
【快排】
要求:空间复杂度 O(n)O(n) ,时间复杂度 O(nlogn)O(nlogn)
==时间复杂度 O(Nlog N): 库函数、快排等排序算法的平均时间复杂度为 O(N log N)== 空间复杂度 O(N) : 快速排序的递归深度最好(平均)为 O(\log N)O(logN) ,最差情况(即输入数组完全倒序)为 O(N)O(N)。
import java.util.*;
// 思想:先进行排序(快排),然后直接取前k个元素
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (k == 0)
return res;
if (k >= input.length) {
for (int i : input)
res.add(i);
return res;
}
int[] resArr = quickSort(input, 0, input.length - 1, k);
for (int i : resArr) {
res.add(i);
}
return res;
}
// 快速排序
public int[] quickSort(int [] input, int l, int h, int k) {
int pivot = input[l];
int low = l, high = h;
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && input[high] >= pivot)
--high;
input[low] = input[high];
while (low < high && input[low] <= pivot)
++low;
input[high] = input[low];
}
input[low] = pivot;
if (low + 1 > k)
return quickSort(input, l, low - 1, k);
if (low + 1 < k)
return quickSort(input, low + 1, h, k);
// 数组的复制
return Arrays.copyOf(input, k);
}
}
-
boolean equals(int[] a,int[] b) 判断两个数组是否相等。 2 String toString(int[] a) 输出数组信息。 3 void fill(int[] a,int val) 将指定值填充到数组之中。【全部元素被替换成val】 4 void sort(int[] a) 对数组进行排序。【原数组被改变了】
-
int binarySearch(int[] a,int key) 对排序后的数组进行二分法检索指定的值。 【返回负数表示未找到指定值!!】
-
==Arrays.asList(num[k], num[i], num[j]))== 该方法是将数组转化为list
已经知道之所以asList 方法产生的 ArrayList 不能修改大小,==是因为这个 ArrayList 并不是“货真价实”的 ArrayList== ,那我们就自行创建一个真正的 ArrayList :
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] myArray = { "Apple", "Banana", "Orange" };
List<String> myList = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(myArray));
myList.add("Guava");
}
}
- copyOfRange(int []original,int from,int to),original为原始的int型数组,from为开始角标值,to为终止角标值。(其中包括from角标,不包括to角标。即处于[from,to)状态)
【力扣已通过!!】
【快排】
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int findKth(int[] a, int n, int K) {
return quickSort(a, 0, n - 1, K);
}
// 快排,从大到小排序
public int quickSort(int[] a, int l, int h, int K) {
int pivot = a[l];
int low = l, high = h;
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && a[high] <= pivot)
high--;
a[low] = a[high];
while (low < high && a[low] >= pivot)
low++;
a[high] = a[low];
}
a[low] = pivot;
if(low==K-1)
return a[low];
else if(low<K-1){
return quickSort(a,low+1,h, K);
}else
return quickSort(a,l,low-1, K);
}
}
【优先队列 / 堆】
进阶: 空间复杂度 O(n) *O*(n) , 时间复杂度 O(nlogn) *O*(nlogn)
平衡堆:大顶堆+小顶堆(参考k神)
`即“大顶堆的堆顶”与“小顶堆的堆顶”就是排序数据流的两个中位数。
大顶堆 n 小顶堆 m=n+1
【规定奇数时,小顶堆个数多!】
findMedian(): 1.当m+n为偶数时,中位数=(A堆顶元素+B堆顶元素)/2.0 2.当m+n为奇数时,中位数=A堆顶元素 **addNum(int num):**其目的是使得两个堆平衡(数目差0或1)
当两堆总大小为偶数时,即两堆大小相等,先将新元素插入maxHeap,重新排序后将新的最值拿出并插入到minHeap; 当两堆总大小为奇数时,即两堆大小不等,先将新元素插入minHeap,重新排序后将新的最值拿出并插入到maxHeap;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
Queue<Integer> A=new PriorityQueue<>(); //小顶堆
Queue<Integer> B=new PriorityQueue<>((x,y)->(y-x)); //大顶堆
public void Insert(Integer num) {
if(A.size()!=B.size()){
A.offer(num);
B.offer(A.poll());
}else{
B.offer(num);
A.offer(B.poll());
}
}
public Double GetMedian() {
return A.size()!=B.size()?(double)A.peek():(double)(A.peek()+B.peek())/2;
}
}import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
List<Integer> save = new ArrayList<>();
public void Insert(Integer num) {
save.add(num);
Collections.sort(save);
}
public Double GetMedian() {
int len = save.size();
if(len == 0){
return null;
}
if(len % 2 == 0){
int first = save.get(len/2-1);
int second = save.get(len/2);
return (double)(first+second)/2;
}else{
return (double)save.get(len/2);
}
}
}要求:空间复杂度: O(n)O(n),时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
BM52 数组中只出现一次的两个数字
要求:空间复杂度 O(N),时间复杂度 O(n)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] FindNumsAppearOnce (int[] array) {
int len = array.length;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(array[i])) {
map.put(array[i], map.get(array[i]) + 1);
} else {
map.put(array[i], 1);
}
}
int[] res = new int[len];
Set set = map.keySet();
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
int i = 0;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
int key = Integer.parseInt(iterator.next().toString());
int value = map.get(key);
if (value == 1) {
res[i++] = key;
}
}
int[] tmp = Arrays.copyOf(res, i);
Arrays.sort(tmp);
return tmp;
}
}
进阶: 空间复杂度 O(1),时间复杂度 O(n)
方法三:将数组视为哈希表
要找的数一定在==[1,N+1]==之间 **思想:**遍历一次数组把>1的和<length的值放到原数组对应位置;然后再遍历一次数组查当前下标是否和值对应,如果不对应那这个下标就是答案,否则遍历完都没出现那么答案就是数组长度加1。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int minNumberDisappeared (int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (nums[i] >= 0 && nums[i] <= n && nums[nums[i] - 1]!=nums[i] ) {
int tmp = nums[nums[i] - 1];
nums[nums[i] - 1] = nums[i];
nums[i] = tmp;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != i + 1)
return i + 1;
}
return n+1;
}
}空间复杂度:O(n^2),时间复杂度 O(n^2)
解题思路: 双指针法铺垫: 先将给定 nums 排序,复杂度为 O(NlogN) 双指针法思路: 固定 3 个指针中最左(最小)数字的指针 k,双指针 i,j 分设在数组索引 (k, len(nums))两端,通过双指针交替向中间移动,记录对于每个固定指针 k 的所有满足 nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j] == 0 的 i,j 组合:
- 当 nums[k] > 0 时直接break跳出:因为 nums[j] >= nums[i] >= nums[k] > 0,即 33 个数字都大于 00 ,在此固定指针 k 之后不可能再找到结果了。
- 当 k > 0且nums[k] == nums[k - 1]时即跳过此元素nums[k]:因为已经将 nums[k - 1] 的所有组合加入到结果中,本次双指针搜索只会得到重复组合。
- i,j 分设在数组索引 (k, len(nums)) 两端,当i < j时循环计算s = nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j],并按照以下规则执行双指针移动:
- 当s < 0时,i += 1并跳过所有重复的nums[i];
- 当s > 0时,j -= 1并跳过所有重复的nums[j];
- 当s == 0时,记录组合[k, i, j]至res,执行i += 1和j -= 1并跳过所有重复的nums[i]和nums[j],防止记录到重复组合。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
// 思想:双指针法
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> threeSum(int[] num) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 此时原数组已经被修改
Arrays.sort(num);
for (int k = 0; k < num.length - 2; k++) {
if (num[k] > 0) break;
if (k > 0 && num[k] == num[k - 1]) continue;
int i = k + 1, j = num.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
int sum = num[k] + num[i] + num[j];
if (sum < 0) {
// 注意i++和++i的区别
while (i < j && num[i] == num[++i]);
//为什么不对???这样写??
//while (i < j && num[i] == num[i+1]) i++;
} else if (sum > 0) {
while (i < j && num[j] == num[--j]);
} else {
// 技巧:如何将一个数组添加到另一个数组中!!
res.add(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(num[k], num[i], num[j])));
// 这一步也很重要,思想技巧
while (i < j && num[i] == num[++i]);
while (i < j && num[j] == num[--j]);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}BM55 没有重复项数字的全排列
要求:空间复杂度 O(n!)O(n!) ,时间复杂度 O(n!)O(n!)
import java.util.*;
// 典型的回溯类题目
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
int n = num.length;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// ArrayList<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
int[] visted = new int[n];
// 进行回溯
backTrack(num, visted, new ArrayList<Integer>(), res);
return res;
}
public void backTrack(int[] num, int[] visted, ArrayList<Integer> tmp,
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res) {
if (tmp.size() == num.length) {
//问题???注意此处的写法
res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (visted[i] == 1) continue;
visted[i] = 1;
tmp.add(num[i]);
backTrack(num, visted, tmp, res);
visted[i] = 0;
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
}BM56 有重复项数字的全排列
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] num) {
Arrays.sort(num);
int n = num.length;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int[] visted = new int[n];
// 进行回溯
backTrack(num, visted, new ArrayList<Integer>(), res);
return res;
}
public void backTrack(int[] num, int[] visted, ArrayList<Integer> tmp,
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res) {
if (tmp.size() == num.length && !res.contains(new ArrayList<>(tmp))) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (visted[i] == 1) continue;
visted[i] = 1;
tmp.add(num[i]);
backTrack(num, visted, tmp, res);
visted[i] = 0;
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
【递归】
思路一:深度优先遍历DFS 目标是找到矩阵中 “岛屿的数量” ,上下左右相连的 1 都被认为是连续岛屿。 dfs方法:
设目前指针指向一个岛屿中的某一点 (i, j),寻找包括此点的岛屿边界。 从 (i, j) 向此点的上下左右 (i+1,j),(i-1,j),(i,j+1),(i,j-1) 做深度搜索。 终止条件: (i, j) 越过矩阵边界; grid[i][j] == 0,代表此分支已越过岛屿边界。 搜索岛屿的同时,执行 grid[i][j] = '0',即将岛屿所有节点删除,以免之后重复搜索相同岛屿。 主循环: 遍历整个矩阵,当遇到 grid[i][j] == '1' 时,从此点开始做深度优先搜索 dfs,岛屿数 count + 1 且在深度优先搜索中删除此岛屿。 最终返回岛屿数 count 即可。
class Solution {
// 深度优先遍历
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){
if(grid[i][j]=='1'){
dfs(grid,i,j);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
private void dfs(char[][] grid,int i,int j){
if(i<0 || j<0 || i>=grid.length || j>=grid[0].length || grid[i][j]=='0')
return ;
grid[i][j]='0';
dfs(grid,i+1,j);
dfs(grid,i,j+1);
dfs(grid,i-1,j);
dfs(grid,i,j-1);
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder();
public ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) {
// Arrays.sort(str);
int n = str.length();
int[] visted=new int[n];
backTrack(str, visted);
return res;
}
public void backTrack(String str, int[] visted) {
if (tmp.length()==str.length() && !res.contains(tmp.toString()) ) {
res.add(tmp.toString());
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if(visted[i]==1) continue;
visted[i]=1;
tmp.append(str.charAt(i));
backTrack(str,visted);
visted[i]=0;
tmp.deleteCharAt(tmp.length()-1);
}
}
}
4.StringBuffer、StringBuilder中的常用方法 【掌握!】 增:append(xxx) ==删:delete(int start,int end)== 【凡是涉及开始和结束的索引,都是左闭右开!!】 改:setCharAt(int n ,char ch) 【修改一个字符】 / replace(int start, int end, String str) 查:charAt(int n ) 插:insert(int offset, xxx) 长度:length(); 遍历:for() + charAt() / toString()
反转:reverse()
- 以上是排列的解决方案,55,56,58,三道题都是一个模板;
BM60 括号生成
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
// 思想:如果左括号数量不大于 n,我们可以放一个左括号。
// 如果右括号数量小于左括号的数量,我们可以放一个右括号。
ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder( );
public ArrayList<String> generateParenthesis (int n) {
backTrack(n, 0, 0);
return res;
}
public void backTrack(int n, int left, int right) {
//注意终止条件
if (tmp.length()==2*n) {
res.add(tmp.toString());
return;
}
if(left<n){
tmp.append('(');
backTrack(n,left+1,right);
//注意此处!!
tmp.deleteCharAt(tmp.length()-1);
}
if(right<left){
tmp.append(')');
backTrack(n,left,right+1);
tmp.deleteCharAt(tmp.length()-1);
}
}
}
进阶:空间复杂度 O(nm)O(n**m) ,时间复杂度 O(nm)O(n**m)
【递归】
import java.util.*;
// 所有数据为开始节点进行查找
// 思想:深度优先搜索,由于序列递增,因此无需回溯。
public class Solution {
int m, n,res;
int
public int solve (int[][] matrix) {
m = matrix.length;
n = matrix[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
dfs(matrix, i, j, 0, -1);
}
}
return res;
}
public void dfs(int[][] matrix, int i, int j, int tmp, int pre) {
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= m || j >= n || matrix[i][j] <= pre) {
res = Math.max(res, tmp);
return;
}
dfs(matrix, i - 1, j, tmp + 1, matrix[i][j]);
dfs(matrix, i, j + 1, tmp + 1, matrix[i][j]);
dfs(matrix, i + 1, j, tmp + 1, matrix[i][j]);
dfs(matrix, i, j - 1, tmp + 1, matrix[i][j]);
}
}
BM63 跳台阶
public class Solution {
public int jumpFloor(int target) {
// 递归方式
// if (target <= 2) return target;
// return jumpFloor(target-1)+jumpFloor(target-2);
// 迭代方式
if (target <= 2) return target;
int res = 0, m = 1, n = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= target; i++) {
res = m + n;
m = n;
n = res;
}
return res;
}
}请你计算并返回达到==楼梯顶部==的最低花费。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int minCostClimbingStairs (int[] cost) {
//方式一 代码随想录
// if(cost.length==0)
// return 0;
// if(cost.length==1)
// return cost[0];
// int sum=0,m=cost[0],n=cost[1];
// for(int i=2;i<cost.length;i++){
// sum=Math.min(m,n)+cost[i];
// m=n;
// n=sum;
// }
// return Math.min(m,n);
// }
//方式二
public int minCostClimbingStairs(int[] cost) {
if (cost == null || cost.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (cost.length == 1) {
return cost[0];
}
int[] dp = new int[cost.length];
dp[0] = cost[0];
dp[1] = cost[1];
for (int i = 2; i < cost.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2]) + cost[i];
}
//最后一步,如果是由倒数第二步爬,则最后一步的体力花费可以不用算
return Math.min(dp[cost.length - 1], dp[cost.length - 2]);
}
//方式三 官网方法
int n=cost.length;
int[] dp=new int[n+1];
dp[0]=dp[1]=0;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
dp[i]=Math.min(dp[i-1]+cost[i-1],dp[i-2]+cost[i-2]);
}
return dp[n];
}
}BM65 最长公共子序列(二)
要求:空间复杂度 O(n^2),时间复杂度 O(n^2)
最长公共子序列问题是典型的二维动态规划问题。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public String LCS (String s1, String s2) {
int m = s1.length();
int n = s2.length();
if(m==0 || n==0) return "-1";
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=1;i<m+1;i++){
for(int j=1;j<n+1;j++){
if(s1.charAt(i-1)==s2.charAt(j-1)){
//注意此处
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
}else{
dp[i][j]=Math.max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
int len1=m,len2=n;
while(len1>0 && len2>0){
if(s1.charAt(len1-1)==s2.charAt(len2-1)){
res.append(s1.charAt(len1-1));
len1--;
len2--;
}else{
if(dp[len1-1][len2]>dp[len1][len2-1])
len1--;
else
len2--;
}
}
if(res.length()==0) return "-1";
return res.reverse().toString();
}
}BM66 最长公共子串
要求: 空间复杂度 O(n^2)O(n2),时间复杂度 O(n^2)O(n2)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
// maxLastInx
public String LCS (String s1, String s2) {
int m = s1.length();
int n = s2.length();
int maxLen = 0, maxLastInx = 0;
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 1; i < m + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n + 1; j++) {
if (s1.charAt(i - 1) == s2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
if (maxLen < dp[i][j]) {
maxLen = dp[i][j];
maxLastInx = i;
}
} else {
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// 注意substring范围?
return s1.substring(maxLastInx - maxLen, maxLastInx);
}
}
BM67 不同路径的数目(一)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param m int整型
* @param n int整型
* @return int整型
*/
// 思想:dp[i][j]表示到[i,j]点共有多少条路径,第一行和第一列的位置,只有一条路径;
// 其余位置,dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];只考虑前一步的状态即可,不用考虑其他状态
public int uniquePaths (int m, int n) {
int[][] dp=new int[m+1][n+1];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
dp[i][0]=1;
}
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
dp[0][j]=1;
}
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}
BM68 矩阵的最小路径和
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int minPathSum (int[][] matrix) {
int m=matrix.length,n=matrix[0].length;
int[][] dp=new int[m][n];
dp[0][0]=matrix[0][0];
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0]+matrix[i][0];
}
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
dp[0][j]=dp[0][j-1]+matrix[0][j];
}
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
dp[i][j]=Math.min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1])+matrix[i][j];
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}
BM69 把数字翻译成字符串
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int solve (String nums) {
int length = nums.length();
if(length==0||nums.charAt(0)=='0')
return 0;
int[] dp = new int[length];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
if(nums.charAt(i)!='0'){
dp[i] = dp[i-1];
}
int num = (nums.charAt(i-1)-'0')*10+(nums.charAt(i)-'0');
if(num>=10&&num<=26){
if(i==1){
dp[i] += 1;
}else if(num>=10&&num<=26){
dp[i] += dp[i-2];
}
}
}
return dp[length-1];
}
}
-
原地 算法找未出现的第一个正整数
-
二维矩阵每个维度有序,查找目标值
-
大数相乘;
-
链表按指定规则重新排列。
-
求二叉树的最大宽度
-
L474零和一
-
二维01背包
-
找到第K小的数剑指 Offer 40. 最小的k个数,秒
-
无重复的最长字串3. 无重复字符的最长子串,秒
-
道滑动窗口题,注意回滚
-
lc 76 hard 滑窗 难点在左边界的移动
-
输入几个区间数组,输出覆盖的最大长度,题目难度算是mid吧,参考lc上的各种数组区间问题,可以在找区间过程中就进行统计,举例:[[1.0, 2.3], [4, 6], [5.5, 7], [5.5, 9], [12, 22]],输出16.3 = (2.3 - 1.0) + (9 - 4) + (22 - 12)
-
给定一个长为m的字符串s1,s1中的所有字符都不重复,给定一个长为n的字符串s2,能否在s2中找到仅有s1字符组成的字串(顺序任意),返回起始位置,未找到返回-1,举例,s1 = "abcd",s2 = "tbcacbdata",res = 3
一个m大小的窗口向右移动就完了。。我直接用了一面算法题的思路写复杂了,喜提加面
-
lc 33 搜索旋转排序数组
lc 143 重排链表
HJ8 合并表记录
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
// 不指定初始化的大小,有bug???
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(n);
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
int key = scanner.nextInt();
int value = scanner.nextInt();
if (!map.containsKey(key)) {
map.put(key, value);
} else {
map.put(key, map.get(key) + value);
}
}
for (int key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + " " + map.get(key));
}
}
}