diff --git a/.github/CONTRIBUTING.md b/.github/CONTRIBUTING.md
index e5d00c17b..29f4ca7e1 100644
--- a/.github/CONTRIBUTING.md
+++ b/.github/CONTRIBUTING.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ Want to help out with the Swift Algorithm Club? Great! While we don't have stric
Our repo is all about learning. The `README` file is the cake, and the sample code is the cherry on top. A good contribution has succinct explanations supported by diagrams. Code is best introduced in chunks, weaved into the explanations where relevant.
-> When choosing between brievity and performance, err to the side of brievity as long as the time complexity of the particular implementation is the same. You can make a note afterwards suggesting a more performant way of doing things.
+> When choosing between brevity and performance, err to the side of brevity as long as the time complexity of the particular implementation is the same. You can make a note afterwards suggesting a more performant way of doing things.
**API Design Guidelines**
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ We follow the following Swift [style guide](https://github.com/raywenderlich/swi
Unit tests. Fixes for typos. No contribution is too small. :-)
-The repository has over 100 different data structures and algorithms. We're always interested in improvements to existing implementations and better explanations. Suggestions for making the code more Swift-like or to make it fit better with the standard library is most welcomed.
+The repository has over 100 different data structures and algorithms. We're always interested in improvements to existing implementations and better explanations. Suggestions for making the code more Swift-like or to make it fit better with the standard library are most welcome.
### New Contributions
diff --git a/.travis.yml b/.travis.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index 5d2a05848..000000000
--- a/.travis.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
-language: objective-c
-osx_image: xcode9
-# sudo: false
-
-install:
-
-# - ./install_swiftlint.sh
-
-script:
-
-- xcodebuild test -project ./All-Pairs\ Shortest\ Paths/APSP/APSP.xcodeproj -scheme APSPTests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Array2D/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./AVL\ Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Binary\ Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Boyer-Moore-Horspool/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Binary\ Search\ Tree/Solution\ 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Bloom\ Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Bounded\ Priority\ Queue/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Breadth-First\ Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Bucket\ Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Comb\ Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Convex\ Hull/Convex\ Hull.xcodeproj -scheme Tests -destination 'platform=iOS Simulator,name=iPhone 7,OS=11.0'
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Counting\ Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Depth-First\ Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Graph/Graph.xcodeproj -scheme GraphTests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Heap\ Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Insertion\ Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./K-Means/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Linked\ List/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Singly\ Linked\ List/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Longest\ Common\ Subsequence/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Minimum\ Spanning\ Tree\ \(Unweighted\)/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Priority\ Queue/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Queue/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Quicksort/Tests/Tests-Quicksort.xcodeproj -scheme Tests-Quicksort
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Radix\ Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Rootish\ Array\ Stack/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Select\ Minimum\ Maximum/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Selection\ Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Shell\ Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Shortest\ Path\ \(Unweighted\)/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Single-Source\ Shortest\ Paths\ \(Weighted\)/SSSP.xcodeproj -scheme SSSPTests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Stack/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Topological\ Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Treap/Treap/Treap.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Palindromes/Test/Test.xcodeproj -scheme Test
-- xcodebuild test -project ./Ternary\ Search\ Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj -scheme Tests
diff --git a/3Sum and 4Sum/3Sum.playground/Contents.swift b/3Sum and 4Sum/3Sum.playground/Contents.swift
index 2581da6e7..d172aed1f 100644
--- a/3Sum and 4Sum/3Sum.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/3Sum and 4Sum/3Sum.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,3 +1,7 @@
+// last checked with Xcode 10.1
+#if swift(>=4.2)
+print("Hello, Swift 4.2!")
+#endif
extension Collection where Element: Equatable {
diff --git a/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata b/3Sum and 4Sum/3Sum.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
similarity index 100%
rename from Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
rename to 3Sum and 4Sum/3Sum.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
diff --git a/3Sum and 4Sum/3Sum.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/3Sum and 4Sum/3Sum.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/3Sum and 4Sum/3Sum.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/3Sum and 4Sum/4Sum.playground/Contents.swift b/3Sum and 4Sum/4Sum.playground/Contents.swift
index 86b530224..37f75918c 100644
--- a/3Sum and 4Sum/4Sum.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/3Sum and 4Sum/4Sum.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,3 +1,8 @@
+// last checked with Xcode 10.1
+#if swift(>=4.2)
+print("Hello, Swift 4.2!")
+#endif
+
extension Collection where Element: Equatable {
/// In a sorted collection, replaces the given index with a successor mapping to a unique element.
diff --git a/Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata b/3Sum and 4Sum/4Sum.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
similarity index 100%
rename from Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
rename to 3Sum and 4Sum/4Sum.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
diff --git a/3Sum and 4Sum/4Sum.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/3Sum and 4Sum/4Sum.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/3Sum and 4Sum/4Sum.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/A-Star/AStar.swift b/A-Star/AStar.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..41a9fac6c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/AStar.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
+// Written by Alejandro Isaza.
+
+import Foundation
+
+public protocol Graph {
+ associatedtype Vertex: Hashable
+ associatedtype Edge: WeightedEdge where Edge.Vertex == Vertex
+
+ /// Lists all edges going out from a vertex.
+ func edgesOutgoing(from vertex: Vertex) -> [Edge]
+}
+
+public protocol WeightedEdge {
+ associatedtype Vertex
+
+ /// The edge's cost.
+ var cost: Double { get }
+
+ /// The target vertex.
+ var target: Vertex { get }
+}
+
+public final class AStar {
+ /// The graph to search on.
+ public let graph: G
+
+ /// The heuristic cost function that estimates the cost between two vertices.
+ ///
+ /// - Note: The heuristic function needs to always return a value that is lower-than or equal to the actual
+ /// cost for the resulting path of the A* search to be optimal.
+ public let heuristic: (G.Vertex, G.Vertex) -> Double
+
+ /// Open list of nodes to expand.
+ private var open: HashedHeap>
+
+ /// Closed list of vertices already expanded.
+ private var closed = Set()
+
+ /// Actual vertex cost for vertices we already encountered (refered to as `g` on the literature).
+ private var costs = Dictionary()
+
+ /// Store the previous node for each expanded node to recreate the path.
+ private var parents = Dictionary()
+
+ /// Initializes `AStar` with a graph and a heuristic cost function.
+ public init(graph: G, heuristic: @escaping (G.Vertex, G.Vertex) -> Double) {
+ self.graph = graph
+ self.heuristic = heuristic
+ open = HashedHeap(sort: <)
+ }
+
+ /// Finds an optimal path between `source` and `target`.
+ ///
+ /// - Precondition: both `source` and `target` belong to `graph`.
+ public func path(start: G.Vertex, target: G.Vertex) -> [G.Vertex] {
+ open.insert(Node(vertex: start, cost: 0, estimate: heuristic(start, target)))
+ while !open.isEmpty {
+ guard let node = open.remove() else {
+ break
+ }
+ costs[node.vertex] = node.cost
+
+ if (node.vertex == target) {
+ let path = buildPath(start: start, target: target)
+ cleanup()
+ return path
+ }
+
+ if !closed.contains(node.vertex) {
+ expand(node: node, target: target)
+ closed.insert(node.vertex)
+ }
+ }
+
+ // No path found
+ return []
+ }
+
+ private func expand(node: Node, target: G.Vertex) {
+ let edges = graph.edgesOutgoing(from: node.vertex)
+ for edge in edges {
+ let g = cost(node.vertex) + edge.cost
+ if g < cost(edge.target) {
+ open.insert(Node(vertex: edge.target, cost: g, estimate: heuristic(edge.target, target)))
+ parents[edge.target] = node.vertex
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ private func cost(_ vertex: G.Edge.Vertex) -> Double {
+ if let c = costs[vertex] {
+ return c
+ }
+
+ let node = Node(vertex: vertex, cost: Double.greatestFiniteMagnitude, estimate: 0)
+ if let index = open.index(of: node) {
+ return open[index].cost
+ }
+
+ return Double.greatestFiniteMagnitude
+ }
+
+ private func buildPath(start: G.Vertex, target: G.Vertex) -> [G.Vertex] {
+ var path = Array()
+ path.append(target)
+
+ var current = target
+ while current != start {
+ guard let parent = parents[current] else {
+ return [] // no path found
+ }
+ current = parent
+ path.append(current)
+ }
+
+ return path.reversed()
+ }
+
+ private func cleanup() {
+ open.removeAll()
+ closed.removeAll()
+ parents.removeAll()
+ }
+}
+
+private struct Node: Hashable, Comparable {
+ /// The graph vertex.
+ var vertex: V
+
+ /// The actual cost between the start vertex and this vertex.
+ var cost: Double
+
+ /// Estimated (heuristic) cost betweent this vertex and the target vertex.
+ var estimate: Double
+
+ public init(vertex: V, cost: Double, estimate: Double) {
+ self.vertex = vertex
+ self.cost = cost
+ self.estimate = estimate
+ }
+
+ static func < (lhs: Node, rhs: Node) -> Bool {
+ return lhs.cost + lhs.estimate < rhs.cost + rhs.estimate
+ }
+
+ static func == (lhs: Node, rhs: Node) -> Bool {
+ return lhs.vertex == rhs.vertex
+ }
+
+ var hashValue: Int {
+ return vertex.hashValue
+ }
+}
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/graph.dot b/A-Star/Images/graph.dot
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..941d66232
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Images/graph.dot
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+digraph G {
+ rankdir=LR;
+ { A [ label = "h = 3" ] }
+ { rank = same; B [ label = "h = 2" ]; C [ label = "h = 2" ]; D [ label = "h = 2" ] }
+ { rank = same; E [ label = "h = 1" ]; F [ label = "h = 1" ]; G [ label = "h = 1" ] }
+ { H [ label = "h = 0", style = filled, color = green ] }
+ A -> { B C D }
+ B -> E
+ E -> F
+ D -> G
+ G -> H
+}
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/graph.png b/A-Star/Images/graph.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c0a4b1cc8
Binary files /dev/null and b/A-Star/Images/graph.png differ
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step1.dot b/A-Star/Images/step1.dot
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5785aea4c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Images/step1.dot
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+digraph G {
+ rankdir=LR;
+ { A [ label = "g = 0\nh = 3", style = filled, color = deepskyblue1 ] }
+ { rank = same; B [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightgrey ]; C [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightgrey ]; D [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightgrey ] }
+ { rank = same; E [ label = "g = \?\nh = 1" ]; F [ label = "g = \?\nh = 1" ]; G [ label = "g = \?\nh = 1" ] }
+ { H [ label = "g = \?\nh = 0" ] }
+ A -> { B C D }
+ B -> E
+ E -> F
+ D -> G
+ G -> H
+}
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step1.png b/A-Star/Images/step1.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a983033a2
Binary files /dev/null and b/A-Star/Images/step1.png differ
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step2.dot b/A-Star/Images/step2.dot
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0c8a9d53d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Images/step2.dot
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+digraph G {
+ rankdir=LR;
+ { A [ label = "g = 0\nh = 3", style = filled, color = lightblue ] }
+ { rank = same; B [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = deepskyblue1 ]; C [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightgrey ]; D [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightgrey ] }
+ { rank = same; E [ label = "g = 2\nh = 1", style = filled, color = lightgrey ]; F [ label = "g = \?\nh = 1" ]; G [ label = "g = \?\nh = 1" ] }
+ { H [ label = "g = \?\nh = 0" ] }
+ A -> { B C D }
+ B -> E
+ E -> F
+ D -> G
+ G -> H
+}
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step2.png b/A-Star/Images/step2.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..10b4300f4
Binary files /dev/null and b/A-Star/Images/step2.png differ
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step3.dot b/A-Star/Images/step3.dot
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..32a75891d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Images/step3.dot
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+digraph G {
+ rankdir=LR;
+ { A [ label = "g = 0\nh = 3", style = filled, color = lightblue ] }
+ { rank = same; B [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ]; C [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = deepskyblue1 ]; D [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightgrey ] }
+ { rank = same; E [ label = "g = 2\nh = 1", style = filled, color = lightgrey ]; F [ label = "g = \?\nh = 1" ]; G [ label = "g = \?\nh = 1" ] }
+ { H [ label = "g = \?\nh = 0" ] }
+ A -> { B C D }
+ B -> E
+ E -> F
+ D -> G
+ G -> H
+}
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step3.png b/A-Star/Images/step3.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e195e7e8e
Binary files /dev/null and b/A-Star/Images/step3.png differ
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step4.dot b/A-Star/Images/step4.dot
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..16db76796
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Images/step4.dot
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+digraph G {
+ rankdir=LR;
+ { A [ label = "g = 0\nh = 3", style = filled, color = lightblue ] }
+ { rank = same; B [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ]; C [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ]; D [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = deepskyblue1 ] }
+ { rank = same; E [ label = "g = 2\nh = 1", style = filled, color = lightgrey ]; F [ label = "g = \?\nh = 1" ]; G [ label = "g = 2\nh = 1", style = filled, color = lightgrey ] }
+ { H [ label = "g = \?\nh = 0" ] }
+ A -> { B C D }
+ B -> E
+ E -> F
+ D -> G
+ G -> H
+}
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step4.png b/A-Star/Images/step4.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c07f34c80
Binary files /dev/null and b/A-Star/Images/step4.png differ
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step5.dot b/A-Star/Images/step5.dot
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2986b6a90
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Images/step5.dot
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+digraph G {
+ rankdir=LR;
+ { A [ label = "g = 0\nh = 3", style = filled, color = lightblue ] }
+ { rank = same; B [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ]; C [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ]; D [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ] }
+ { rank = same; E [ label = "g = 2\nh = 1", style = filled, color = deepskyblue1 ]; F [ label = "g = 3\nh = 1", style = filled, color = lightgrey ]; G [ label = "g = 2\nh = 1", style = filled, color = lightgrey ] }
+ { H [ label = "g = \?\nh = 0" ] }
+ A -> { B C D }
+ B -> E
+ E -> F
+ D -> G
+ G -> H
+}
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step5.png b/A-Star/Images/step5.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..40a7008da
Binary files /dev/null and b/A-Star/Images/step5.png differ
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step6.dot b/A-Star/Images/step6.dot
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b5e3179b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Images/step6.dot
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+digraph G {
+ rankdir=LR;
+ { A [ label = "g = 0\nh = 3", style = filled, color = lightblue ] }
+ { rank = same; B [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ]; C [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ]; D [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ] }
+ { rank = same; E [ label = "g = 2\nh = 1", style = filled, color = lightblue ]; F [ label = "g = 3\nh = 1", style = filled, color = lightgrey ]; G [ label = "g = 2\nh = 1", style = filled, color = deepskyblue1 ] }
+ { H [ label = "g = 3\nh = 0", style = filled, color = lightgrey ] }
+ A -> { B C D }
+ B -> E
+ E -> F
+ D -> G
+ G -> H
+}
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step6.png b/A-Star/Images/step6.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..9e7baef26
Binary files /dev/null and b/A-Star/Images/step6.png differ
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step7.dot b/A-Star/Images/step7.dot
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c5b26b6b3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Images/step7.dot
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+digraph G {
+ rankdir=LR;
+ { A [ label = "g = 0\nh = 3", style = filled, color = lightblue ] }
+ { rank = same; B [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ]; C [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ]; D [ label = "g = 1\nh = 2", style = filled, color = lightblue ] }
+ { rank = same; E [ label = "g = 2\nh = 1", style = filled, color = lightblue ]; F [ label = "g = 3\nh = 1", style = filled, color = lightgrey ]; G [ label = "g = 2\nh = 1", style = filled, color = lightblue ] }
+ { H [ label = "g = 3\nh = 0", style = filled, color = deepskyblue1 ] }
+ A -> { B C D }
+ B -> E
+ E -> F
+ D -> G
+ G -> H
+}
diff --git a/A-Star/Images/step7.png b/A-Star/Images/step7.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0eedd638f
Binary files /dev/null and b/A-Star/Images/step7.png differ
diff --git a/A-Star/README.md b/A-Star/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b373d25fc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+# A*
+
+A* (pronounced "ay star") is a heuristic best-first search algorithm. A* minimizes node expansions, therefore minimizing the search time, by using a heuristic function. The heuristic function gives an estimate of the distance between two vertices. For instance if you are searching for a path between two points in a city, you can estimate the actual street distance with the straight-line distance.
+
+A* works by expanding the most promising nodes first, according to the heuristic function. In the city example it would choose streets which go in the general direction of the target first and, only if those are dead ends, backtrack and try other streets. This speeds up search in most sitations.
+
+A* is optimal (it always find the shortest path) if the heuristic function is admissible. A heuristic function is admissible if it never overestimates the cost of reaching the goal. In the extreme case of the heuristic function always retuning `0` A* acts exactly the same as [Dijkstra's Algorithm](../Dijkstra). The closer the heuristic function is to the actual distance the faster the search.
+
+## Example
+
+Let's run through an example on this simple directed graph. We are going to assume that all edges have a cost of 1 and the heuristic function is going to be the column starting at goal and going back:
+
+
+
+On the first step we expand the root node on the left (blue). We set the cost `g` to zero and add all neighbors to the open list (grey).
+
+
+
+We put the first node in the closed list (light blue) so that we don't try expanding it again if there were to be loops in the graph. Next we take the node on the open list with the smallest value of `g + h` where `g` is the current cost (0) plus the edge cost (1). Since all nodes in the open list have the same value we choose the top one.
+
+
+
+We repeat the process and pick the next node from the open list. In this case there are no new nodes to add to the open list.
+
+
+
+We expand the next node. One more node on the open list, but nothing exciting yet.
+
+
+
+Sicne the top and the bottom nodes have the same value we choose the top one. This is not a great choice but we could do better if we had a better heuristic function.
+
+
+
+Now we expand the bottom node because it has a smaller value than the middle node (2 + 1 < 3 + 1).
+
+
+
+And we finally reach the goal! We never even expanded that middle node. We didn't have to because its value is 4, which is equal to the total lenght of our solution and therefore guaranteed to not be part of the optimal solution.
+
+
+
+The final step is to backtrack from the goal node to buld the optimal path.
diff --git a/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.swift b/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.swift
new file mode 100755
index 000000000..87f674cd5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+import Foundation
+import XCTest
+
+struct GridGraph: Graph {
+ struct Vertex: Hashable {
+ var x: Int
+ var y: Int
+
+ static func == (lhs: Vertex, rhs: Vertex) -> Bool {
+ return lhs.x == rhs.x && lhs.y == rhs.y
+ }
+
+ public var hashValue: Int {
+ return x.hashValue ^ y.hashValue
+ }
+ }
+
+ struct Edge: WeightedEdge {
+ var cost: Double
+ var target: Vertex
+ }
+
+ func edgesOutgoing(from vertex: Vertex) -> [Edge] {
+ return [
+ Edge(cost: 1, target: Vertex(x: vertex.x - 1, y: vertex.y)),
+ Edge(cost: 1, target: Vertex(x: vertex.x + 1, y: vertex.y)),
+ Edge(cost: 1, target: Vertex(x: vertex.x, y: vertex.y - 1)),
+ Edge(cost: 1, target: Vertex(x: vertex.x, y: vertex.y + 1)),
+ ]
+ }
+}
+
+class AStarTests: XCTestCase {
+ func testSameStartAndEnd() {
+ let graph = GridGraph()
+ let astar = AStar(graph: graph, heuristic: manhattanDistance)
+ let path = astar.path(start: GridGraph.Vertex(x: 0, y: 0), target: GridGraph.Vertex(x: 0, y: 0))
+ XCTAssertEqual(path.count, 1)
+ XCTAssertEqual(path[0].x, 0)
+ XCTAssertEqual(path[0].y, 0)
+ }
+
+ func testDiagonal() {
+ let graph = GridGraph()
+ let astar = AStar(graph: graph, heuristic: manhattanDistance)
+ let path = astar.path(start: GridGraph.Vertex(x: 0, y: 0), target: GridGraph.Vertex(x: 10, y: 10))
+ XCTAssertEqual(path.count, 21)
+ XCTAssertEqual(path[0].x, 0)
+ XCTAssertEqual(path[0].y, 0)
+ XCTAssertEqual(path[20].x, 10)
+ XCTAssertEqual(path[20].y, 10)
+ }
+
+ func manhattanDistance(_ s: GridGraph.Vertex, _ t: GridGraph.Vertex) -> Double {
+ return Double(abs(s.x - t.x) + abs(s.y - t.y))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..cacd1e5ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -0,0 +1,291 @@
+// !$*UTF8*$!
+{
+ archiveVersion = 1;
+ classes = {
+ };
+ objectVersion = 46;
+ objects = {
+
+/* Begin PBXBuildFile section */
+ 611D099C1F8978AB00C7092B /* AStarTests.swift in Sources */ = {isa = PBXBuildFile; fileRef = 611D099B1F8978AB00C7092B /* AStarTests.swift */; };
+ 611D099E1F8978BC00C7092B /* AStar.swift in Sources */ = {isa = PBXBuildFile; fileRef = 611D099D1F8978BB00C7092B /* AStar.swift */; };
+ 611D09A01F89795100C7092B /* HashedHeap.swift in Sources */ = {isa = PBXBuildFile; fileRef = 611D099F1F89795100C7092B /* HashedHeap.swift */; };
+/* End PBXBuildFile section */
+
+/* Begin PBXFileReference section */
+ 611D099B1F8978AB00C7092B /* AStarTests.swift */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; fileEncoding = 4; lastKnownFileType = sourcecode.swift; path = AStarTests.swift; sourceTree = ""; };
+ 611D099D1F8978BB00C7092B /* AStar.swift */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; fileEncoding = 4; lastKnownFileType = sourcecode.swift; name = AStar.swift; path = ../AStar.swift; sourceTree = ""; };
+ 611D099F1F89795100C7092B /* HashedHeap.swift */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; fileEncoding = 4; lastKnownFileType = sourcecode.swift; name = HashedHeap.swift; path = "../../Hashed Heap/HashedHeap.swift"; sourceTree = ""; };
+ 7B2BBC801C779D720067B71D /* AStarTests.xctest */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; explicitFileType = wrapper.cfbundle; includeInIndex = 0; path = AStarTests.xctest; sourceTree = BUILT_PRODUCTS_DIR; };
+ 7B2BBC941C779E7B0067B71D /* Info.plist */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; fileEncoding = 4; lastKnownFileType = text.plist.xml; path = Info.plist; sourceTree = SOURCE_ROOT; };
+/* End PBXFileReference section */
+
+/* Begin PBXFrameworksBuildPhase section */
+ 7B2BBC7D1C779D720067B71D /* Frameworks */ = {
+ isa = PBXFrameworksBuildPhase;
+ buildActionMask = 2147483647;
+ files = (
+ );
+ runOnlyForDeploymentPostprocessing = 0;
+ };
+/* End PBXFrameworksBuildPhase section */
+
+/* Begin PBXGroup section */
+ 7B2BBC681C779D710067B71D = {
+ isa = PBXGroup;
+ children = (
+ 7B2BBC831C779D720067B71D /* Tests */,
+ 7B2BBC721C779D710067B71D /* Products */,
+ );
+ sourceTree = "";
+ };
+ 7B2BBC721C779D710067B71D /* Products */ = {
+ isa = PBXGroup;
+ children = (
+ 7B2BBC801C779D720067B71D /* AStarTests.xctest */,
+ );
+ name = Products;
+ sourceTree = "";
+ };
+ 7B2BBC831C779D720067B71D /* Tests */ = {
+ isa = PBXGroup;
+ children = (
+ 611D099F1F89795100C7092B /* HashedHeap.swift */,
+ 611D099D1F8978BB00C7092B /* AStar.swift */,
+ 611D099B1F8978AB00C7092B /* AStarTests.swift */,
+ 7B2BBC941C779E7B0067B71D /* Info.plist */,
+ );
+ name = Tests;
+ sourceTree = "";
+ };
+/* End PBXGroup section */
+
+/* Begin PBXNativeTarget section */
+ 7B2BBC7F1C779D720067B71D /* AStarTests */ = {
+ isa = PBXNativeTarget;
+ buildConfigurationList = 7B2BBC8C1C779D720067B71D /* Build configuration list for PBXNativeTarget "AStarTests" */;
+ buildPhases = (
+ 7B2BBC7C1C779D720067B71D /* Sources */,
+ 7B2BBC7D1C779D720067B71D /* Frameworks */,
+ 7B2BBC7E1C779D720067B71D /* Resources */,
+ );
+ buildRules = (
+ );
+ dependencies = (
+ );
+ name = AStarTests;
+ productName = TestsTests;
+ productReference = 7B2BBC801C779D720067B71D /* AStarTests.xctest */;
+ productType = "com.apple.product-type.bundle.unit-test";
+ };
+/* End PBXNativeTarget section */
+
+/* Begin PBXProject section */
+ 7B2BBC691C779D710067B71D /* Project object */ = {
+ isa = PBXProject;
+ attributes = {
+ LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0720;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 0900;
+ ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Swift Algorithm Club";
+ TargetAttributes = {
+ 7B2BBC7F1C779D720067B71D = {
+ CreatedOnToolsVersion = 7.2;
+ LastSwiftMigration = 0900;
+ };
+ };
+ };
+ buildConfigurationList = 7B2BBC6C1C779D710067B71D /* Build configuration list for PBXProject "AStarTests" */;
+ compatibilityVersion = "Xcode 3.2";
+ developmentRegion = English;
+ hasScannedForEncodings = 0;
+ knownRegions = (
+ en,
+ Base,
+ );
+ mainGroup = 7B2BBC681C779D710067B71D;
+ productRefGroup = 7B2BBC721C779D710067B71D /* Products */;
+ projectDirPath = "";
+ projectRoot = "";
+ targets = (
+ 7B2BBC7F1C779D720067B71D /* AStarTests */,
+ );
+ };
+/* End PBXProject section */
+
+/* Begin PBXResourcesBuildPhase section */
+ 7B2BBC7E1C779D720067B71D /* Resources */ = {
+ isa = PBXResourcesBuildPhase;
+ buildActionMask = 2147483647;
+ files = (
+ );
+ runOnlyForDeploymentPostprocessing = 0;
+ };
+/* End PBXResourcesBuildPhase section */
+
+/* Begin PBXSourcesBuildPhase section */
+ 7B2BBC7C1C779D720067B71D /* Sources */ = {
+ isa = PBXSourcesBuildPhase;
+ buildActionMask = 2147483647;
+ files = (
+ 611D099C1F8978AB00C7092B /* AStarTests.swift in Sources */,
+ 611D099E1F8978BC00C7092B /* AStar.swift in Sources */,
+ 611D09A01F89795100C7092B /* HashedHeap.swift in Sources */,
+ );
+ runOnlyForDeploymentPostprocessing = 0;
+ };
+/* End PBXSourcesBuildPhase section */
+
+/* Begin XCBuildConfiguration section */
+ 7B2BBC871C779D720067B71D /* Debug */ = {
+ isa = XCBuildConfiguration;
+ buildSettings = {
+ ALWAYS_SEARCH_USER_PATHS = NO;
+ CLANG_CXX_LANGUAGE_STANDARD = "gnu++0x";
+ CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
+ CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
+ CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
+ CODE_SIGN_IDENTITY = "-";
+ COPY_PHASE_STRIP = NO;
+ DEBUG_INFORMATION_FORMAT = dwarf;
+ ENABLE_STRICT_OBJC_MSGSEND = YES;
+ ENABLE_TESTABILITY = YES;
+ GCC_C_LANGUAGE_STANDARD = gnu99;
+ GCC_DYNAMIC_NO_PIC = NO;
+ GCC_NO_COMMON_BLOCKS = YES;
+ GCC_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = 0;
+ GCC_PREPROCESSOR_DEFINITIONS = (
+ "DEBUG=1",
+ "$(inherited)",
+ );
+ GCC_WARN_64_TO_32_BIT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_ABOUT_RETURN_TYPE = YES_ERROR;
+ GCC_WARN_UNDECLARED_SELECTOR = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_UNINITIALIZED_AUTOS = YES_AGGRESSIVE;
+ GCC_WARN_UNUSED_FUNCTION = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_UNUSED_VARIABLE = YES;
+ MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET = 10.11;
+ MTL_ENABLE_DEBUG_INFO = YES;
+ ONLY_ACTIVE_ARCH = YES;
+ SDKROOT = macosx;
+ SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Onone";
+ SWIFT_SWIFT3_OBJC_INFERENCE = Default;
+ };
+ name = Debug;
+ };
+ 7B2BBC881C779D720067B71D /* Release */ = {
+ isa = XCBuildConfiguration;
+ buildSettings = {
+ ALWAYS_SEARCH_USER_PATHS = NO;
+ CLANG_CXX_LANGUAGE_STANDARD = "gnu++0x";
+ CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
+ CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
+ CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
+ CODE_SIGN_IDENTITY = "-";
+ COPY_PHASE_STRIP = NO;
+ DEBUG_INFORMATION_FORMAT = "dwarf-with-dsym";
+ ENABLE_NS_ASSERTIONS = NO;
+ ENABLE_STRICT_OBJC_MSGSEND = YES;
+ GCC_C_LANGUAGE_STANDARD = gnu99;
+ GCC_NO_COMMON_BLOCKS = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_64_TO_32_BIT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_ABOUT_RETURN_TYPE = YES_ERROR;
+ GCC_WARN_UNDECLARED_SELECTOR = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_UNINITIALIZED_AUTOS = YES_AGGRESSIVE;
+ GCC_WARN_UNUSED_FUNCTION = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_UNUSED_VARIABLE = YES;
+ MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET = 10.11;
+ MTL_ENABLE_DEBUG_INFO = NO;
+ SDKROOT = macosx;
+ SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Owholemodule";
+ SWIFT_SWIFT3_OBJC_INFERENCE = Default;
+ };
+ name = Release;
+ };
+ 7B2BBC8D1C779D720067B71D /* Debug */ = {
+ isa = XCBuildConfiguration;
+ buildSettings = {
+ CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
+ COMBINE_HIDPI_IMAGES = YES;
+ INFOPLIST_FILE = Info.plist;
+ LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
+ PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
+ PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
+ SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Onone";
+ SWIFT_SWIFT3_OBJC_INFERENCE = Default;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ };
+ name = Debug;
+ };
+ 7B2BBC8E1C779D720067B71D /* Release */ = {
+ isa = XCBuildConfiguration;
+ buildSettings = {
+ CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
+ COMBINE_HIDPI_IMAGES = YES;
+ INFOPLIST_FILE = Info.plist;
+ LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
+ PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
+ PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
+ SWIFT_SWIFT3_OBJC_INFERENCE = Default;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ };
+ name = Release;
+ };
+/* End XCBuildConfiguration section */
+
+/* Begin XCConfigurationList section */
+ 7B2BBC6C1C779D710067B71D /* Build configuration list for PBXProject "AStarTests" */ = {
+ isa = XCConfigurationList;
+ buildConfigurations = (
+ 7B2BBC871C779D720067B71D /* Debug */,
+ 7B2BBC881C779D720067B71D /* Release */,
+ );
+ defaultConfigurationIsVisible = 0;
+ defaultConfigurationName = Release;
+ };
+ 7B2BBC8C1C779D720067B71D /* Build configuration list for PBXNativeTarget "AStarTests" */ = {
+ isa = XCConfigurationList;
+ buildConfigurations = (
+ 7B2BBC8D1C779D720067B71D /* Debug */,
+ 7B2BBC8E1C779D720067B71D /* Release */,
+ );
+ defaultConfigurationIsVisible = 0;
+ defaultConfigurationName = Release;
+ };
+/* End XCConfigurationList section */
+ };
+ rootObject = 7B2BBC691C779D710067B71D /* Project object */;
+}
diff --git a/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata b/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6c0ea8493
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/AStarTests.xcscheme b/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/AStarTests.xcscheme
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5473b4c0c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Tests/AStarTests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/AStarTests.xcscheme
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/A-Star/Tests/Info.plist b/A-Star/Tests/Info.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ba72822e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/A-Star/Tests/Info.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+
+
+
+
+ CFBundleDevelopmentRegion
+ en
+ CFBundleExecutable
+ $(EXECUTABLE_NAME)
+ CFBundleIdentifier
+ $(PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER)
+ CFBundleInfoDictionaryVersion
+ 6.0
+ CFBundleName
+ $(PRODUCT_NAME)
+ CFBundlePackageType
+ BNDL
+ CFBundleShortVersionString
+ 1.0
+ CFBundleSignature
+ ????
+ CFBundleVersion
+ 1
+
+
diff --git a/AVL Tree/AVLTree.playground/Contents.swift b/AVL Tree/AVLTree.playground/Contents.swift
index 04ef78d07..34c1e6ddd 100644
--- a/AVL Tree/AVLTree.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/AVL Tree/AVLTree.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,9 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
let tree = AVLTree()
diff --git a/AVL Tree/README.markdown b/AVL Tree/README.markdown
index e7515d99f..4e974ba71 100644
--- a/AVL Tree/README.markdown
+++ b/AVL Tree/README.markdown
@@ -88,4 +88,4 @@ The interesting bits are in the `balance()` method which is called after inserti
AVL tree was the first self-balancing binary tree. These days, the [red-black tree](../Red-Black%20Tree/) seems to be more popular.
-*Written for Swift Algorithm Club by Mike Taghavi and Matthijs Hollemans*
+*Written for Swift Algorithm Club by [Mike Taghavi](https://github.com/mitghi) and [Matthijs Hollemans](https://github.com/hollance)*
diff --git a/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.playground/Contents.swift b/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.playground/Contents.swift
index b1b499b39..24c27cac8 100644
--- a/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,10 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
import Graph
import APSP
diff --git a/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.playground/contents.xcplayground b/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.playground/contents.xcplayground
index 06828af92..d5a8d0e3f 100644
--- a/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.playground/contents.xcplayground
+++ b/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.playground/contents.xcplayground
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index 78df3fb76..dc8e509a1 100644
--- a/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -187,16 +187,16 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0730;
- LastUpgradeCheck = 0820;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1010;
ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Swift Algorithm Club";
TargetAttributes = {
493D8DDF1CDD2A1C0089795A = {
CreatedOnToolsVersion = 7.3;
- LastSwiftMigration = 0820;
+ LastSwiftMigration = 1010;
};
493D8DF01CDD5B960089795A = {
CreatedOnToolsVersion = 7.3;
- LastSwiftMigration = 0820;
+ LastSwiftMigration = 1010;
};
};
};
@@ -302,14 +302,22 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -349,14 +357,22 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -388,7 +404,7 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = "com.swift-algorithm-club.APSPTests";
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -400,7 +416,7 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = "com.swift-algorithm-club.APSPTests";
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
@@ -420,7 +436,7 @@
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = "com.swift-algorithm-club.APSP";
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
SKIP_INSTALL = YES;
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
VERSIONING_SYSTEM = "apple-generic";
VERSION_INFO_PREFIX = "";
};
@@ -442,7 +458,7 @@
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = "com.swift-algorithm-club.APSP";
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
SKIP_INSTALL = YES;
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
VERSIONING_SYSTEM = "apple-generic";
VERSION_INFO_PREFIX = "";
};
diff --git a/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/APSP.xcscheme b/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/APSP.xcscheme
index e313c4b88..944957d8f 100644
--- a/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/APSP.xcscheme
+++ b/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSP.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/APSP.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSPTests/APSPTests.swift b/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSPTests/APSPTests.swift
index c2f64e239..ce0dfcf32 100644
--- a/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSPTests/APSPTests.swift
+++ b/All-Pairs Shortest Paths/APSP/APSPTests/APSPTests.swift
@@ -19,14 +19,6 @@ struct TestCase where T: Hashable {
}
class APSPTests: XCTestCase {
-
- func testSwift4() {
- // last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
- #if swift(>=4.0)
- print("Hello, Swift 4!")
- #endif
- }
-
/**
See Figure 25.1 of “Introduction to Algorithms” by Cormen et al, 3rd ed., pg 690
*/
diff --git a/Array2D/Array2D.playground/Contents.swift b/Array2D/Array2D.playground/Contents.swift
index 77c0b364c..d31d77540 100644
--- a/Array2D/Array2D.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Array2D/Array2D.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,8 +1,3 @@
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
/*
Two-dimensional array with a fixed number of rows and columns.
This is mostly handy for games that are played on a grid, such as chess.
diff --git a/Array2D/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Array2D/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index a0fb1480b..af9b7c3b8 100644
--- a/Array2D/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Array2D/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -226,7 +226,7 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -238,7 +238,7 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/B-Tree/BTree.playground/Contents.swift b/B-Tree/BTree.playground/Contents.swift
index a0643586f..f6325513a 100644
--- a/B-Tree/BTree.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/B-Tree/BTree.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -2,10 +2,7 @@
import Foundation
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
+// last checked with Xcode 10.0
let bTree = BTree(order: 1)!
diff --git a/B-Tree/BTree.playground/Sources/BTree.swift b/B-Tree/BTree.playground/Sources/BTree.swift
index 2693eb308..2ed0b2593 100644
--- a/B-Tree/BTree.playground/Sources/BTree.swift
+++ b/B-Tree/BTree.playground/Sources/BTree.swift
@@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ extension BTreeNode {
}
}
-// MARK: BTreeNode extension: Travelsals
+// MARK: BTreeNode extension: Traversals
extension BTreeNode {
@@ -443,7 +443,7 @@ public class BTree {
}
}
-// MARK: BTree extension: Travelsals
+// MARK: BTree extension: Traversals
extension BTree {
/**
diff --git a/B-Tree/BTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/B-Tree/BTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/B-Tree/BTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/B-Tree/README.md b/B-Tree/README.md
index f6924aadc..10a06853e 100644
--- a/B-Tree/README.md
+++ b/B-Tree/README.md
@@ -133,7 +133,7 @@ Else:

-####Merging two nodes
+#### Merging two nodes
Let's say we want to merge the child `c1` at index `i` in its parent's children array.
diff --git a/B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index 3e12b9ac3..66eb85190 100644
--- a/B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -85,12 +85,12 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0730;
- LastUpgradeCheck = 0800;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1000;
ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Viktor Szilárd Simkó";
TargetAttributes = {
C66702771D0EEE25008CD769 = {
CreatedOnToolsVersion = 7.3.1;
- LastSwiftMigration = 0800;
+ LastSwiftMigration = 1000;
};
};
};
@@ -144,14 +144,22 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -192,14 +200,22 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -234,7 +250,7 @@
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = viktorsimko.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Onone";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -247,7 +263,7 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = viktorsimko.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
index 9d6c542ae..d1555acfb 100644
--- a/B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/B-Tree/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
= 1 else { return }
if n > 1 {
- solveHanoi(n: n - 1, from: from, to: spare, spare: to)
- } else {
- solveHanoi(n: n - 1, from: spare, to: to, spare: from)
+ solveHanoi(n: n - 1, from: from, to: spare, spare: to)
+ solveHanoi(n: n - 1, from: spare, to: to, spare: from)
}
}
```
@@ -132,9 +136,9 @@ Below are some examples for each category of performance:
The most trivial example of function that takes O(n!) time is given below.
```swift
- func nFacFunc(n: Int) {
+ func nFactFunc(n: Int) {
for i in stride(from: 0, to: n, by: 1) {
- nFactFunc(n - 1)
+ nFactFunc(n: n - 1)
}
}
```
diff --git a/Binary Search Tree/README.markdown b/Binary Search Tree/README.markdown
index 1d9321591..57d1f4bff 100644
--- a/Binary Search Tree/README.markdown
+++ b/Binary Search Tree/README.markdown
@@ -268,7 +268,7 @@ If there are no more nodes to look at -- when `left` or `right` is nil -- then w
Searching is a recursive process, but you can also implement it with a simple loop instead:
```swift
- public func search(value: T) -> BinarySearchTree? {
+ public func search(_ value: T) -> BinarySearchTree? {
var node: BinarySearchTree? = self
while let n = node {
if value < n.value {
@@ -375,7 +375,7 @@ As an exercise, see if you can implement filter and reduce.
We can make the code more readable by defining some helper functions.
```swift
- private func reconnectParentToNode(node: BinarySearchTree?) {
+ private func reconnectParentTo(node: BinarySearchTree?) {
if let parent = parent {
if isLeftChild {
parent.left = node
@@ -557,7 +557,7 @@ As a result, doing `tree.search(100)` gives nil.
You can check whether a tree is a valid binary search tree with the following method:
```swift
- public func isBST(minValue minValue: T, maxValue: T) -> Bool {
+ public func isBST(minValue: T, maxValue: T) -> Bool {
if value < minValue || value > maxValue { return false }
let leftBST = left?.isBST(minValue: minValue, maxValue: value) ?? true
let rightBST = right?.isBST(minValue: value, maxValue: maxValue) ?? true
@@ -615,8 +615,8 @@ This implementation is recursive, and each case of the enum will be treated diff
public var height: Int {
switch self {
- case .Empty: return 0
- case .Leaf: return 1
+ case .Empty: return -1
+ case .Leaf: return 0
case let .Node(left, _, right): return 1 + max(left.height, right.height)
}
}
diff --git a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/BinarySearchTree.playground/Contents.swift b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/BinarySearchTree.playground/Contents.swift
index 8c06ae9e1..ec9902283 100644
--- a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/BinarySearchTree.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/BinarySearchTree.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,10 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
let tree = BinarySearchTree(value: 7)
tree.insert(value: 2)
tree.insert(value: 5)
diff --git a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/BinarySearchTree.playground/Sources/BinarySearchTree.swift b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/BinarySearchTree.playground/Sources/BinarySearchTree.swift
index 34ade3896..2d0eb7e57 100644
--- a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/BinarySearchTree.playground/Sources/BinarySearchTree.swift
+++ b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/BinarySearchTree.playground/Sources/BinarySearchTree.swift
@@ -235,7 +235,7 @@ extension BinarySearchTree {
/*
Finds the node whose value precedes our value in sorted order.
*/
- public func predecessor() -> BinarySearchTree? {
+ public func predecessor() -> BinarySearchTree? {
if let left = left {
return left.maximum()
} else {
@@ -251,7 +251,7 @@ extension BinarySearchTree {
/*
Finds the node whose value succeeds our value in sorted order.
*/
- public func successor() -> BinarySearchTree? {
+ public func successor() -> BinarySearchTree? {
if let right = right {
return right.minimum()
} else {
diff --git a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/BinarySearchTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/BinarySearchTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/BinarySearchTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index f4c3f65c7..d7c687e0c 100644
--- a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -83,12 +83,12 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0720;
- LastUpgradeCheck = 0720;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1000;
ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Swift Algorithm Club";
TargetAttributes = {
7B2BBC7F1C779D720067B71D = {
CreatedOnToolsVersion = 7.2;
- LastSwiftMigration = 0820;
+ LastSwiftMigration = 1000;
};
};
};
@@ -141,13 +141,23 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
CODE_SIGN_IDENTITY = "-";
@@ -185,13 +195,23 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
CODE_SIGN_IDENTITY = "-";
@@ -210,6 +230,7 @@
MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET = 10.11;
MTL_ENABLE_DEBUG_INFO = NO;
SDKROOT = macosx;
+ SWIFT_COMPILATION_MODE = wholemodule;
};
name = Release;
};
@@ -221,7 +242,8 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_SWIFT3_OBJC_INFERENCE = Default;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -233,7 +255,8 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_SWIFT3_OBJC_INFERENCE = Default;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
index 8ef8d8581..afd69e6a7 100644
--- a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 1/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
// Each time you insert something, you get back a completely new tree.
var tree = BinarySearchTree.leaf(7)
tree = tree.insert(newValue: 2)
diff --git a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 2/BinarySearchTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 2/BinarySearchTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 2/BinarySearchTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 2/BinarySearchTree.swift b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 2/BinarySearchTree.swift
index 272b86368..23b1c8aca 100644
--- a/Binary Search Tree/Solution 2/BinarySearchTree.swift
+++ b/Binary Search Tree/Solution 2/BinarySearchTree.swift
@@ -20,8 +20,8 @@ public enum BinarySearchTree {
/* Distance of this node to its lowest leaf. Performance: O(n). */
public var height: Int {
switch self {
- case .empty: return 0
- case .leaf: return 1
+ case .empty: return -1
+ case .leaf: return 0
case let .node(left, _, right): return 1 + max(left.height, right.height)
}
}
diff --git a/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/Contents.swift b/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/Contents.swift
index 715fb5dc2..f673f25c4 100644
--- a/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,10 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
// An unsorted array of numbers
let numbers = [11, 59, 3, 2, 53, 17, 31, 7, 19, 67, 47, 13, 37, 61, 29, 43, 5, 41, 23]
diff --git a/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/Sources/BinarySearch.swift b/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/Sources/BinarySearch.swift
deleted file mode 100644
index d6623e355..000000000
--- a/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/Sources/BinarySearch.swift
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
-/**
- Binary Search
-
- Recursively splits the array in half until the value is found.
-
- If there is more than one occurrence of the search key in the array, then
- there is no guarantee which one it finds.
-
- Note: The array must be sorted!
- **/
-
-import Foundation
-
-// The recursive version of binary search.
-
-public func binarySearch(_ a: [T], key: T, range: Range) -> Int? {
- if range.lowerBound >= range.upperBound {
- return nil
- } else {
- let midIndex = range.lowerBound + (range.upperBound - range.lowerBound) / 2
- if a[midIndex] > key {
- return binarySearch(a, key: key, range: range.lowerBound ..< midIndex)
- } else if a[midIndex] < key {
- return binarySearch(a, key: key, range: midIndex + 1 ..< range.upperBound)
- } else {
- return midIndex
- }
- }
-}
-
-/**
- The iterative version of binary search.
-
- Notice how similar these functions are. The difference is that this one
- uses a while loop, while the other calls itself recursively.
- **/
-
-public func binarySearch(_ a: [T], key: T) -> Int? {
- var lowerBound = 0
- var upperBound = a.count
- while lowerBound < upperBound {
- let midIndex = lowerBound + (upperBound - lowerBound) / 2
- if a[midIndex] == key {
- return midIndex
- } else if a[midIndex] < key {
- lowerBound = midIndex + 1
- } else {
- upperBound = midIndex
- }
- }
- return nil
-}
diff --git a/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/contents.xcplayground b/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/contents.xcplayground
index 06828af92..69d154d1e 100644
--- a/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/contents.xcplayground
+++ b/Binary Search/BinarySearch.playground/contents.xcplayground
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/Binary Search/README.markdown b/Binary Search/README.markdown
index 09b141e04..0cecce6cf 100644
--- a/Binary Search/README.markdown
+++ b/Binary Search/README.markdown
@@ -4,15 +4,15 @@ Goal: Quickly find an element in an array.
Let's say you have an array of numbers and you want to determine whether a specific number is in that array, and if so, at which index.
-In most cases, Swift's `indexOf()` function is good enough for that:
+In most cases, Swift's `Collection.index(of:)` function is good enough for that:
```swift
let numbers = [11, 59, 3, 2, 53, 17, 31, 7, 19, 67, 47, 13, 37, 61, 29, 43, 5, 41, 23]
-numbers.indexOf(43) // returns 15
+numbers.index(of: 43) // returns 15
```
-The built-in `indexOf()` function performs a [linear search](../Linear%20Search/). In code that looks something like this:
+The built-in `Collection.index(of:)` function performs a [linear search](../Linear%20Search/). In code that looks something like this:
```swift
func linearSearch(_ a: [T], _ key: T) -> Int? {
diff --git a/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.playground/Contents.swift b/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.playground/Contents.swift
index 9da194fed..b0bff577a 100644
--- a/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,10 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
public indirect enum BinaryTree {
case node(BinaryTree, T, BinaryTree)
case empty
diff --git a/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.playground/contents.xcplayground b/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.playground/contents.xcplayground
index 06828af92..69d154d1e 100644
--- a/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.playground/contents.xcplayground
+++ b/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.playground/contents.xcplayground
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.swift b/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.swift
index 102f23e06..6146880b4 100644
--- a/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.swift
+++ b/Binary Tree/BinaryTree.swift
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ extension BinaryTree: CustomStringConvertible {
}
extension BinaryTree {
- public func traverseInOrder(process: T -> Void) {
+ public func traverseInOrder(process: (T) -> Void) {
if case let .node(left, value, right) = self {
left.traverseInOrder(process: process)
process(value)
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ extension BinaryTree {
}
}
- public func traversePreOrder(process: T -> Void) {
+ public func traversePreOrder(process: (T) -> Void) {
if case let .node(left, value, right) = self {
process(value)
left.traversePreOrder(process: process)
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ extension BinaryTree {
}
}
- public func traversePostOrder(process: T -> Void) {
+ public func traversePostOrder(process: (T) -> Void) {
if case let .node(left, value, right) = self {
left.traversePostOrder(process: process)
right.traversePostOrder(process: process)
diff --git a/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/Contents.swift b/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/Contents.swift
index 95253ea27..70d5ca5e8 100644
--- a/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,10 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
// Create a bit set that stores 140 bits
var bits = BitSet(size: 140)
@@ -94,3 +89,23 @@ z.all1() // false
//var bigBits = BitSet(size: 10000)
//print(bigBits)
+
+var smallBitSet = BitSet(size: 16)
+smallBitSet[5] = true
+smallBitSet[10] = true
+print(smallBitSet >> 3)
+print(smallBitSet << 6) // one bit shifts off the end
+
+var bigBitSet = BitSet( size: 120 )
+bigBitSet[1] = true
+bigBitSet[3] = true
+bigBitSet[7] = true
+bigBitSet[32] = true
+bigBitSet[55] = true
+bigBitSet[64] = true
+bigBitSet[80] = true
+print(bigBitSet)
+print(bigBitSet << 32)
+print(bigBitSet << 64)
+print(bigBitSet >> 32)
+print(bigBitSet >> 64)
diff --git a/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/Sources/BitSet.swift b/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/Sources/BitSet.swift
index 59306f5a5..258bce457 100644
--- a/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/Sources/BitSet.swift
+++ b/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/Sources/BitSet.swift
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ public struct BitSet {
We store the bits in a list of unsigned 64-bit integers.
The first entry, `words[0]`, is the least significant word.
*/
- private let N = 64
+ fileprivate let N = 64
public typealias Word = UInt64
fileprivate(set) public var words: [Word]
@@ -221,6 +221,50 @@ prefix public func ~ (rhs: BitSet) -> BitSet {
return out
}
+// MARK: - Bit shift operations
+
+/*
+ Note: For bitshift operations, the assumption is that any bits that are
+ shifted off the end of the end of the declared size are not still set.
+ In other words, we are maintaining the original number of bits.
+ */
+
+public func << (lhs: BitSet, numBitsLeft: Int) -> BitSet {
+ var out = lhs
+ let offset = numBitsLeft / lhs.N
+ let shift = numBitsLeft % lhs.N
+ for i in 0..= 0) {
+ out.words[i] = lhs.words[i - offset] << shift
+ }
+ if (i - offset - 1 >= 0) {
+ out.words[i] |= lhs.words[i - offset - 1] >> (lhs.N - shift)
+ }
+ }
+
+ out.clearUnusedBits()
+ return out
+}
+
+public func >> (lhs: BitSet, numBitsRight: Int) -> BitSet {
+ var out = lhs
+ let offset = numBitsRight / lhs.N
+ let shift = numBitsRight % lhs.N
+ for i in 0..> shift
+ }
+ if (i + offset + 1 < lhs.words.count) {
+ out.words[i] |= lhs.words[i + offset + 1] << (lhs.N - shift)
+ }
+ }
+
+ out.clearUnusedBits()
+ return out
+}
+
// MARK: - Debugging
extension UInt64 {
diff --git a/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/contents.xcplayground b/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/contents.xcplayground
index 06828af92..69d154d1e 100644
--- a/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/contents.xcplayground
+++ b/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/contents.xcplayground
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Bit Set/BitSet.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Bit Set/BitSet.swift b/Bit Set/BitSet.swift
deleted file mode 100644
index cfe8517b5..000000000
--- a/Bit Set/BitSet.swift
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,248 +0,0 @@
-/*
- A fixed-size sequence of n bits. Bits have indices 0 to n-1.
- */
-public struct BitSet {
- /* How many bits this object can hold. */
- private(set) public var size: Int
-
- /*
- We store the bits in a list of unsigned 64-bit integers.
- The first entry, `words[0]`, is the least significant word.
- */
- private let N = 64
- public typealias Word = UInt64
- fileprivate(set) public var words: [Word]
-
- private let allOnes = ~Word()
-
- /* Creates a bit set that can hold `size` bits. All bits are initially 0. */
- public init(size: Int) {
- precondition(size > 0)
- self.size = size
-
- // Round up the count to the next multiple of 64.
- let n = (size + (N-1)) / N
- words = [Word](repeating: 0, count: n)
- }
-
- /* Converts a bit index into an array index and a mask inside the word. */
- private func indexOf(_ i: Int) -> (Int, Word) {
- precondition(i >= 0)
- precondition(i < size)
- let o = i / N
- let m = Word(i - o*N)
- return (o, 1 << m)
- }
-
- /* Returns a mask that has 1s for all bits that are in the last word. */
- private func lastWordMask() -> Word {
- let diff = words.count*N - size
- if diff > 0 {
- // Set the highest bit that's still valid.
- let mask = 1 << Word(63 - diff)
- // Subtract 1 to turn it into a mask, and add the high bit back in.
- return (Word)(mask | (mask - 1))
- } else {
- return allOnes
- }
- }
-
- /*
- If the size is not a multiple of N, then we have to clear out the bits
- that we're not using, or bitwise operations between two differently sized
- BitSets will go wrong.
- */
- fileprivate mutating func clearUnusedBits() {
- words[words.count - 1] &= lastWordMask()
- }
-
- /* So you can write bitset[99] = ... */
- public subscript(i: Int) -> Bool {
- get { return isSet(i) }
- set { if newValue { set(i) } else { clear(i) } }
- }
-
- /* Sets the bit at the specified index to 1. */
- public mutating func set(_ i: Int) {
- let (j, m) = indexOf(i)
- words[j] |= m
- }
-
- /* Sets all the bits to 1. */
- public mutating func setAll() {
- for i in 0.. Bool {
- let (j, m) = indexOf(i)
- words[j] ^= m
- return (words[j] & m) != 0
- }
-
- /* Determines whether the bit at the specific index is 1 (true) or 0 (false). */
- public func isSet(_ i: Int) -> Bool {
- let (j, m) = indexOf(i)
- return (words[j] & m) != 0
- }
-
- /*
- Returns the number of bits that are 1. Time complexity is O(s) where s is
- the number of 1-bits.
- */
- public var cardinality: Int {
- var count = 0
- for var x in words {
- while x != 0 {
- let y = x & ~(x - 1) // find lowest 1-bit
- x = x ^ y // and erase it
- count += 1
- }
- }
- return count
- }
-
- /* Checks if all the bits are set. */
- public func all1() -> Bool {
- for i in 0.. Bool {
- for x in words {
- if x != 0 { return true }
- }
- return false
- }
-
- /* Checks if none of the bits are set. */
- public func all0() -> Bool {
- for x in words {
- if x != 0 { return false }
- }
- return true
- }
-}
-
-// MARK: - Equality
-
-extension BitSet: Equatable {
-}
-
-public func == (lhs: BitSet, rhs: BitSet) -> Bool {
- return lhs.words == rhs.words
-}
-
-// MARK: - Hashing
-
-extension BitSet: Hashable {
- /* Based on the hashing code from Java's BitSet. */
- public var hashValue: Int {
- var h = Word(1234)
- for i in stride(from: words.count, to: 0, by: -1) {
- h ^= words[i - 1] &* Word(i)
- }
- return Int((h >> 32) ^ h)
- }
-}
-
-// MARK: - Bitwise operations
-
-extension BitSet {
- public static var allZeros: BitSet {
- return BitSet(size: 64)
- }
-}
-
-private func copyLargest(_ lhs: BitSet, _ rhs: BitSet) -> BitSet {
- return (lhs.words.count > rhs.words.count) ? lhs : rhs
-}
-
-/*
- Note: In all of these bitwise operations, lhs and rhs are allowed to have a
- different number of bits. The new BitSet always has the larger size.
- The extra bits that get added to the smaller BitSet are considered to be 0.
- That will strip off the higher bits from the larger BitSet when doing &.
- */
-
-public func & (lhs: BitSet, rhs: BitSet) -> BitSet {
- let m = max(lhs.size, rhs.size)
- var out = BitSet(size: m)
- let n = min(lhs.words.count, rhs.words.count)
- for i in 0.. BitSet {
- var out = copyLargest(lhs, rhs)
- let n = min(lhs.words.count, rhs.words.count)
- for i in 0.. BitSet {
- var out = copyLargest(lhs, rhs)
- let n = min(lhs.words.count, rhs.words.count)
- for i in 0.. BitSet {
- var out = BitSet(size: rhs.size)
- for i in 0.. String {
- var s = ""
- var n = self
- for _ in 1...64 {
- s += ((n & 1 == 1) ? "1" : "0")
- n >>= 1
- }
- return s
- }
-}
-
-extension BitSet: CustomStringConvertible {
- public var description: String {
- var s = ""
- for x in words {
- s += x.bitsToString() + " "
- }
- return s
- }
-}
-
diff --git a/Bit Set/README.markdown b/Bit Set/README.markdown
index 6bb6e7c89..365950d06 100644
--- a/Bit Set/README.markdown
+++ b/Bit Set/README.markdown
@@ -329,6 +329,90 @@ This is the original value but with the lowest 1-bit removed.
We keep repeating this process until the value consists of all zeros. The time complexity is **O(s)** where **s** is the number of 1-bits.
+## Bit Shift Operations
+
+Bit shifts are a common and very useful mechanism when dealing with bitsets. Here is the right-shift function:
+
+```
+public func >> (lhs: BitSet, numBitsRight: Int) -> BitSet {
+ var out = lhs
+ let offset = numBitsRight / lhs.N
+ let shift = numBitsRight % lhs.N
+ for i in 0..> shift
+ }
+
+ if (i + offset + 1 < lhs.words.count) {
+ out.words[i] |= lhs.words[i + offset + 1] << (lhs.N - shift)
+ }
+ }
+
+ out.clearUnusedBits()
+ return out
+}
+```
+
+Let's start with this line:
+
+```swift
+for i in 0..> 10
+
+I've grouped each part of the number by word to make it easier to see what happens. The for-loop goes from least significant word to most significant. So for index zero we're want to know what bits will make up our least significant word. Let's calculate our offset and shift values:
+
+ offset = 10 / 8 = 1 (remember this is integer division)
+ shift = 10 % 8 = 2
+
+So we consult the word at offset 1 to get some of our bits:
+
+ 11000000 >> 2 = 00110000
+
+And we get the rest of them from the word one further away:
+
+ 01000010 << (8 - 2) = 10000000
+
+And we bitwise OR these together to get our least significant term
+
+ 00110000
+ 10000000
+ -------- OR
+ 10110000
+
+We repeat this for the 2nd least significant term and obtain:
+
+ 00010000
+
+The last term can't get any bits because they are past the end of our number so those are all zeros. Our result is:
+
+ 00000000 00010000 10110000
+
## See also
[Bit Twiddling Hacks](http://graphics.stanford.edu/~seander/bithacks.html)
diff --git a/Bloom Filter/BloomFilter.playground/Contents.swift b/Bloom Filter/BloomFilter.playground/Contents.swift
index 9e4a89351..7a3719d57 100644
--- a/Bloom Filter/BloomFilter.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Bloom Filter/BloomFilter.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,8 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
+
public class BloomFilter {
fileprivate var array: [Bool]
private var hashFunctions: [(T) -> Int]
@@ -54,7 +51,7 @@ public class BloomFilter {
func djb2(x: String) -> Int {
var hash = 5381
- for char in x.characters {
+ for char in x {
hash = ((hash << 5) &+ hash) &+ char.hashValue
}
return Int(hash)
@@ -62,7 +59,7 @@ func djb2(x: String) -> Int {
func sdbm(x: String) -> Int {
var hash = 0
- for char in x.characters {
+ for char in x {
hash = char.hashValue &+ (hash << 6) &+ (hash << 16) &- hash
}
return Int(hash)
diff --git a/Bloom Filter/BloomFilter.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Bloom Filter/BloomFilter.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Bloom Filter/BloomFilter.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Bloom Filter/BloomFilter.playground/timeline.xctimeline b/Bloom Filter/BloomFilter.playground/timeline.xctimeline
deleted file mode 100644
index bf468afec..000000000
--- a/Bloom Filter/BloomFilter.playground/timeline.xctimeline
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,6 +0,0 @@
-
-
-
-
-
diff --git a/Bloom Filter/README.markdown b/Bloom Filter/README.markdown
index 3fff0a379..5f2ede069 100644
--- a/Bloom Filter/README.markdown
+++ b/Bloom Filter/README.markdown
@@ -100,4 +100,31 @@ public func query(_ value: T) -> Bool {
If you're coming from another imperative language, you might notice the unusual syntax in the `exists` assignment. Swift makes use of functional paradigms when it makes code more consise and readable, and in this case `reduce` is a much more consise way to check if all the required bits are `true` than a `for` loop.
-*Written for Swift Algorithm Club by Jamil Dhanani. Edited by Matthijs Hollemans.*
+## Another approach
+
+In the previous section, you learnt about how using multiple different hash functions can help reduce the chance of collisions in the bloom filter. However, good hash functions are difficult to design. A simple alternative to multiple hash functions is to use a set of random numbers.
+
+As an example, let's say a bloom filter wants to hash each element 15 times during insertion. Instead of using 15 different hash functions, you can rely on just one hash function. The hash value can then be combined with 15 different values to form the indices for flipping. This bloom filter would initialize a set of 15 random numbers ahead of time and use these values during each insertion.
+
+```
+hash("Hello world!") >> hash(987654321) // would flip bit 8
+hash("Hello world!") >> hash(123456789) // would flip bit 2
+```
+
+Since Swift 4.2, `Hasher` is now included in the Standard library, which is designed to reduce multiple hashes to a single hash in an efficient manner. This makes combining the hashes trivial.
+
+```
+private func computeHashes(_ value: T) -> [Int] {
+ return randomSeeds.map() { seed in
+ let hasher = Hasher()
+ hasher.combine(seed)
+ hasher.combine(value)
+ let hashValue = hasher.finalize()
+ return abs(hashValue % array.count)
+ }
+}
+```
+
+If you want to learn more about this approach, you can read about the [Hasher documentation](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/swift/hasher) or Soroush Khanlou's [Swift 4.2 Bloom filter](http://khanlou.com/2018/09/bloom-filters/) implementation.
+
+*Written for Swift Algorithm Club by Jamil Dhanani. Edited by Matthijs Hollemans. Updated by Bruno Scheele.*
diff --git a/Bloom Filter/Tests/BloomFilterTests.swift b/Bloom Filter/Tests/BloomFilterTests.swift
index 30df702a7..d88ec0a31 100644
--- a/Bloom Filter/Tests/BloomFilterTests.swift
+++ b/Bloom Filter/Tests/BloomFilterTests.swift
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ import XCTest
func djb2(_ x: String) -> Int {
var hash = 5381
- for char in x.characters {
+ for char in x {
hash = ((hash << 5) &+ hash) &+ char.hashValue
}
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ func djb2(_ x: String) -> Int {
func sdbm(_ x: String) -> Int {
var hash = 0
- for char in x.characters {
+ for char in x {
hash = char.hashValue &+ (hash << 6) &+ (hash << 16) &- hash
}
diff --git a/Bloom Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Bloom Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index 6493fd153..f0649ba26 100644
--- a/Bloom Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Bloom Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -83,12 +83,12 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0720;
- LastUpgradeCheck = 0800;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1000;
ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Swift Algorithm Club";
TargetAttributes = {
7B2BBC7F1C779D720067B71D = {
CreatedOnToolsVersion = 7.2;
- LastSwiftMigration = 0800;
+ LastSwiftMigration = 1000;
};
};
};
@@ -141,14 +141,22 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -188,14 +196,22 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -228,7 +244,7 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -240,7 +256,7 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/Bloom Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Bloom Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Bloom Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Bloom Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/Bloom Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
index 14f27f777..afd69e6a7 100644
--- a/Bloom Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/Bloom Filter/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
struct Message: Comparable, CustomStringConvertible {
let name: String
let priority: Int
diff --git a/Bounded Priority Queue/BoundedPriorityQueue.playground/contents.xcplayground b/Bounded Priority Queue/BoundedPriorityQueue.playground/contents.xcplayground
index 06828af92..69d154d1e 100644
--- a/Bounded Priority Queue/BoundedPriorityQueue.playground/contents.xcplayground
+++ b/Bounded Priority Queue/BoundedPriorityQueue.playground/contents.xcplayground
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/Bounded Priority Queue/BoundedPriorityQueue.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Bounded Priority Queue/BoundedPriorityQueue.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Bounded Priority Queue/BoundedPriorityQueue.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Bounded Priority Queue/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Bounded Priority Queue/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index 842c51695..11f907b47 100644
--- a/Bounded Priority Queue/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Bounded Priority Queue/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -86,7 +86,7 @@
TargetAttributes = {
B80004B21C83E342001FE2D7 = {
CreatedOnToolsVersion = 7.2.1;
- LastSwiftMigration = 0820;
+ LastSwiftMigration = 1000;
};
};
};
@@ -226,7 +226,7 @@
SDKROOT = macosx;
SWIFT_OBJC_BRIDGING_HEADER = "";
SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Onone";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -269,7 +269,7 @@
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
SDKROOT = macosx;
SWIFT_OBJC_BRIDGING_HEADER = "";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/Bounded Priority Queue/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Bounded Priority Queue/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Bounded Priority Queue/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.playground/Contents.swift b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.playground/Contents.swift
index e88a1b93d..933cbc4ac 100644
--- a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,10 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
- print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
/*
Boyer-Moore string search
@@ -16,13 +11,13 @@ extension String {
func index(of pattern: String, usingHorspoolImprovement: Bool = false) -> Index? {
// Cache the length of the search pattern because we're going to
// use it a few times and it's expensive to calculate.
- let patternLength = pattern.characters.count
- guard patternLength > 0, patternLength <= characters.count else { return nil }
+ let patternLength = pattern.count
+ guard patternLength > 0, patternLength <= self.count else { return nil }
// Make the skip table. This table determines how far we skip ahead
// when a character from the pattern is found.
var skipTable = [Character: Int]()
- for (i, c) in pattern.characters.enumerated() {
+ for (i, c) in pattern.enumerated() {
skipTable[c] = patternLength - i - 1
}
diff --git a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.playground/timeline.xctimeline b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.playground/timeline.xctimeline
index 89bc76f90..2688d72c1 100644
--- a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.playground/timeline.xctimeline
+++ b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.playground/timeline.xctimeline
@@ -3,17 +3,17 @@
version = "3.0">
diff --git a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.swift b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.swift
index af8aea9d9..481b7d483 100644
--- a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.swift
+++ b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/BoyerMooreHorspool.swift
@@ -9,13 +9,13 @@ extension String {
func index(of pattern: String, usingHorspoolImprovement: Bool = false) -> Index? {
// Cache the length of the search pattern because we're going to
// use it a few times and it's expensive to calculate.
- let patternLength = pattern.characters.count
- guard patternLength > 0, patternLength <= characters.count else { return nil }
-
+ let patternLength = pattern.count
+ guard patternLength > 0, patternLength <= self.count else { return nil }
+
// Make the skip table. This table determines how far we skip ahead
// when a character from the pattern is found.
var skipTable = [Character: Int]()
- for (i, c) in pattern.characters.enumerated() {
+ for (i, c) in pattern.enumerated() {
skipTable[c] = patternLength - i - 1
}
diff --git a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/README.markdown b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/README.markdown
index f5e21ea41..8879d8df6 100644
--- a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/README.markdown
+++ b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/README.markdown
@@ -38,13 +38,13 @@ extension String {
func index(of pattern: String) -> Index? {
// Cache the length of the search pattern because we're going to
// use it a few times and it's expensive to calculate.
- let patternLength = pattern.characters.count
- guard patternLength > 0, patternLength <= characters.count else { return nil }
+ let patternLength = pattern.count
+ guard patternLength > 0, patternLength <= count else { return nil }
// Make the skip table. This table determines how far we skip ahead
// when a character from the pattern is found.
var skipTable = [Character: Int]()
- for (i, c) in pattern.characters.enumerated() {
+ for (i, c) in pattern.enumerated() {
skipTable[c] = patternLength - i - 1
}
@@ -162,13 +162,13 @@ extension String {
func index(of pattern: String) -> Index? {
// Cache the length of the search pattern because we're going to
// use it a few times and it's expensive to calculate.
- let patternLength = pattern.characters.count
+ let patternLength = pattern.count
guard patternLength > 0, patternLength <= characters.count else { return nil }
// Make the skip table. This table determines how far we skip ahead
// when a character from the pattern is found.
var skipTable = [Character: Int]()
- for (i, c) in pattern.characters.enumerated() {
+ for (i, c) in pattern.enumerated() {
skipTable[c] = patternLength - i - 1
}
diff --git a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/Tests/BoyerMooreTests.swift b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/Tests/BoyerMooreTests.swift
index 9efe60874..436173127 100755
--- a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/Tests/BoyerMooreTests.swift
+++ b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/Tests/BoyerMooreTests.swift
@@ -26,8 +26,8 @@ class BoyerMooreTest: XCTestCase {
XCTAssertNotNil(index)
let startIndex = index!
- let endIndex = string.index(index!, offsetBy: pattern.characters.count)
- let match = string.substring(with: startIndex..
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
index 538a6f4fa..afd69e6a7 100644
--- a/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/Boyer-Moore-Horspool/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
func breadthFirstSearch(_ graph: Graph, source: Node) -> [String] {
var queue = Queue()
diff --git a/Breadth-First Search/BreadthFirstSearch.playground/Sources/Graph.swift b/Breadth-First Search/BreadthFirstSearch.playground/Sources/Graph.swift
index 87e21897c..0343120f8 100644
--- a/Breadth-First Search/BreadthFirstSearch.playground/Sources/Graph.swift
+++ b/Breadth-First Search/BreadthFirstSearch.playground/Sources/Graph.swift
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ public class Graph: CustomStringConvertible, Equatable {
self.nodes = []
}
- public func addNode(_ label: String) -> Node {
+ @discardableResult public func addNode(_ label: String) -> Node {
let node = Node(label)
nodes.append(node)
return node
diff --git a/Breadth-First Search/BreadthFirstSearch.playground/contents.xcplayground b/Breadth-First Search/BreadthFirstSearch.playground/contents.xcplayground
index 513c2e7e9..f635e9804 100644
--- a/Breadth-First Search/BreadthFirstSearch.playground/contents.xcplayground
+++ b/Breadth-First Search/BreadthFirstSearch.playground/contents.xcplayground
@@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
-
\ No newline at end of file
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/Breadth-First Search/BreadthFirstSearch.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Breadth-First Search/BreadthFirstSearch.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Breadth-First Search/BreadthFirstSearch.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Breadth-First Search/README.markdown b/Breadth-First Search/README.markdown
index b2298822f..097f4278d 100644
--- a/Breadth-First Search/README.markdown
+++ b/Breadth-First Search/README.markdown
@@ -151,7 +151,7 @@ This will output: `["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f", "g", "h"]`
Breadth-first search can be used to solve many problems. A small selection:
-* Computing the [shortest path](../Shortest%20Path/) between a source node and each of the other nodes (only for unweighted graphs).
+* Computing the [shortest path](../Shortest%20Path%20(Unweighted)/) between a source node and each of the other nodes (only for unweighted graphs).
* Calculating the [minimum spanning tree](../Minimum%20Spanning%20Tree%20(Unweighted)/) on an unweighted graph.
*Written by [Chris Pilcher](https://github.com/chris-pilcher) and Matthijs Hollemans*
diff --git a/Breadth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Breadth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index f86abf86e..a7f04e00a 100644
--- a/Breadth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Breadth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -59,7 +59,6 @@
7B2BBC941C779E7B0067B71D /* Info.plist */,
);
name = Tests;
- path = TestsTests;
sourceTree = "";
};
/* End PBXGroup section */
@@ -89,12 +88,12 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0720;
- LastUpgradeCheck = 0820;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1000;
ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Swift Algorithm Club";
TargetAttributes = {
7B2BBC7F1C779D720067B71D = {
CreatedOnToolsVersion = 7.2;
- LastSwiftMigration = 0820;
+ LastSwiftMigration = 1000;
};
};
};
@@ -149,13 +148,23 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
CODE_SIGN_IDENTITY = "-";
@@ -193,13 +202,23 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
CODE_SIGN_IDENTITY = "-";
@@ -218,6 +237,7 @@
MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET = 10.11;
MTL_ENABLE_DEBUG_INFO = NO;
SDKROOT = macosx;
+ SWIFT_COMPILATION_MODE = wholemodule;
};
name = Release;
};
@@ -231,7 +251,7 @@
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Onone";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -244,7 +264,7 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/Breadth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Breadth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Breadth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Breadth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/Breadth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
index dfcf6de42..afd69e6a7 100644
--- a/Breadth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/Breadth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
))
diff --git a/Bubble Sort/MyPlayground.playground/Sources/BubbleSort.swift b/Bubble Sort/MyPlayground.playground/Sources/BubbleSort.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..09e01542b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Bubble Sort/MyPlayground.playground/Sources/BubbleSort.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+//
+// BubbleSort.swift
+//
+// Created by Julio Brazil on 1/10/18.
+//
+// Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and
+// associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including
+// without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
+// copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the
+// following conditions:
+//
+// The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial
+// portions of the Software.
+//
+// THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT
+// LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO
+// EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
+// AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE
+// OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
+//
+
+import Foundation
+
+/// Performs the bubble sort algorithm in the array
+///
+/// - Parameter elements: a array of elements that implement the Comparable protocol
+/// - Returns: an array with the same elements but in order
+public func bubbleSort (_ elements: [T]) -> [T] where T: Comparable {
+ return bubbleSort(elements, <)
+}
+
+public func bubbleSort (_ elements: [T], _ comparison: (T,T) -> Bool) -> [T] {
+ var array = elements
+
+ for i in 0..
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/Ordered Set/OrderedSet.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata b/Bubble Sort/MyPlayground.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
similarity index 100%
rename from Ordered Set/OrderedSet.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
rename to Bubble Sort/MyPlayground.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
diff --git a/Bubble Sort/MyPlayground.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Bubble Sort/MyPlayground.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Bubble Sort/MyPlayground.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Bubble Sort/README.markdown b/Bubble Sort/README.markdown
index 93d370827..211a5aefa 100644
--- a/Bubble Sort/README.markdown
+++ b/Bubble Sort/README.markdown
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
# Bubble Sort
-Bubble sort is a sorting algorithm that is implemented by starting in the beginning of the array and swapping the first two elements only if the first element is greater than the second element. This comparison is then moved onto the next pair and so on and so forth. This is done until the array is completely sorted. The smaller items slowly “bubble” up to the beginning of the array.
+Bubble sort is a sorting algorithm that is implemented by starting in the beginning of the array and swapping the first two elements only if the first element is greater than the second element. This comparison is then moved onto the next pair and so on and so forth. This is done until the array is completely sorted. The smaller items slowly “bubble” up to the beginning of the array. Sometimes this algorithm is refered as Sinking sort, due to the larger, or heavier elements sinking to the end of the array.
##### Runtime:
- Average: O(N^2)
@@ -12,3 +12,116 @@ Bubble sort is a sorting algorithm that is implemented by starting in the beginn
### Implementation:
The implementation will not be shown as the average and worst runtimes show that this is a very inefficient algorithm. However, having a grasp of the concept will help you understand the basics of simple sorting algorithms.
+
+Bubble sort is a very simple sorting algorithm, it consists in comparing pairs of adjacent elements in the array, if the first element is larger, swap them, otherwise, you do nothing and go for the next comparison.
+This is accomplished by looking through the array `n` times, `n` being the amount of elements in the array.
+
+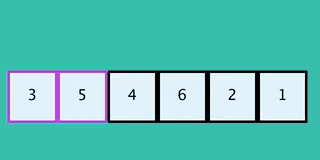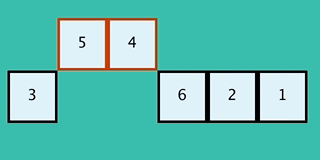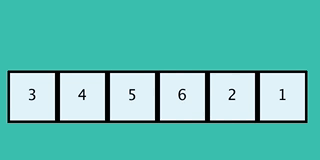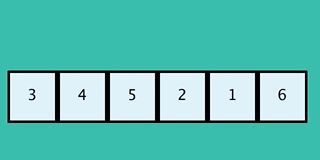
+
+This GIF shows a inverted implementation than
+
+#### Example
+Let us take the array `[5, 1, 4, 2, 8]`, and sort the array from lowest number to greatest number using bubble sort. In each step, elements written in bold are being compared. Three passes will be required.
+
+##### First Pass
+[ **5 1** 4 2 8 ] -> [ **1 5** 4 2 8 ], Here, algorithm compares the first two elements, and swaps since 5 > 1.
+
+[ 1 **5 4** 2 8 ] -> [ 1 **4 5** 2 8 ], Swap since 5 > 4
+
+[ 1 4 **5 2** 8 ] -> [ 1 4 **2 5** 8 ], Swap since 5 > 2
+
+[ 1 4 2 **5 8** ] -> [ 1 4 2 **5 8** ], Now, since these elements are already in order (8 > 5), algorithm does not swap them.
+
+##### Second Pass
+[ **1 4** 2 5 8 ] -> [ **1 4** 2 5 8 ]
+
+[ 1 **4 2** 5 8 ] -> [ 1 **2 4** 5 8 ], Swap since 4 > 2
+
+[ 1 2 **4 5** 8 ] -> [ 1 2 **4 5** 8 ]
+
+[ 1 2 4 **5 8** ] -> [ 1 2 4 **5 8** ]
+Now, the array is already sorted, but the algorithm does not know if it is completed. The algorithm needs one whole pass without any swap to know it is sorted.
+
+##### Third Pass
+[ **1 2** 4 5 8 ] -> [ **1 2** 4 5 8 ]
+
+[ 1 **2 4** 5 8 ] -> [ 1 **2 4** 5 8 ]
+
+[ 1 2 **4 5** 8 ] -> [ 1 2 **4 5** 8 ]
+
+[ 1 2 4 **5 8** ] -> [ 1 2 4 **5 8** ]
+
+This is the same for the forth and fifth passes.
+
+#### Code
+```swift
+for i in 0.. [ **1 5** 4 2 8 ], Swaps since 5 > 1
+
+[ 1 **5 4** 2 8 ] -> [ 1 **4 5** 2 8 ], Swap since 5 > 4
+
+[ 1 4 **5 2** 8 ] -> [ 1 4 **2 5** 8 ], Swap since 5 > 2
+
+[ 1 4 2 **5 8** ] -> [ 1 4 2 **5 8** ], Now, since these elements are already in order (8 > 5), algorithm does not swap them.
+
+*by the end of the first pass, the last element is guaranteed to be the largest*
+
+##### Second Pass
+[ **1 4** 2 5 8 ] -> [ **1 4** 2 5 8 ]
+
+[ 1 **4 2** 5 8 ] -> [ 1 **2 4** 5 8 ], Swap since 4 > 2
+
+[ 1 2 **4 5** 8 ] -> [ 1 2 **4 5** 8 ], As the first loop has occured once, the inner loop stops here, not comparing 5 with 8
+
+##### Third Pass
+[ **1 2** 4 5 8 ] -> [ **1 2** 4 5 8 ]
+
+[ 1 **2 4** 5 8 ] -> [ 1 **2 4** 5 8 ] again, stoping one comparison short
+
+##### Fourth Pass
+[ **1 2** 4 5 8 ] -> [ **1 2** 4 5 8 ]
+
+There is no Fifth pass
+
+#### Conclusion
+
+Even with the proposed optimizations, this is still a terribly inefficient sorting algorithm. A good alternative is [Merge Sort](https://github.com/raywenderlich/swift-algorithm-club/tree/master/Merge%20Sort), that not only is better performing, has a similar degree of dificulty to implement.
+
+*Updated for the Swift Algorithm Club by Julio Brazil*
+
+##### Supporting Links
+[Code Pumpkin](https://codepumpkin.com/bubble-sort/)
+[Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bubble_sort)
+[GeeksforGeeks](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/bubble-sort/)
diff --git a/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.playground/Sources/BucketSort.swift b/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.playground/Sources/BucketSort.swift
index bafd216fa..64408eca4 100644
--- a/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.playground/Sources/BucketSort.swift
+++ b/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.playground/Sources/BucketSort.swift
@@ -20,31 +20,6 @@
//
//
-import Foundation
-// FIXME: comparison operators with optionals were removed from the Swift Standard Libary.
-// Consider refactoring the code to use the non-optional operators.
-fileprivate func < (lhs: T?, rhs: T?) -> Bool {
- switch (lhs, rhs) {
- case let (l?, r?):
- return l < r
- case (nil, _?):
- return true
- default:
- return false
- }
-}
-
-// FIXME: comparison operators with optionals were removed from the Swift Standard Libary.
-// Consider refactoring the code to use the non-optional operators.
-fileprivate func >= (lhs: T?, rhs: T?) -> Bool {
- switch (lhs, rhs) {
- case let (l?, r?):
- return l >= r
- default:
- return !(lhs < rhs)
- }
-}
-
//////////////////////////////////////
// MARK: Main algorithm
//////////////////////////////////////
@@ -87,7 +62,11 @@ private func enoughSpaceInBuckets(_ buckets: [Bucket], elements: [T]) -> B
let maximumValue = elements.max()?.toInt()
let totalCapacity = buckets.count * (buckets.first?.capacity)!
- return totalCapacity >= maximumValue
+ guard let max = maximumValue else {
+ return false
+ }
+
+ return totalCapacity >= max
}
//////////////////////////////////////
diff --git a/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.playground/contents.xcplayground b/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.playground/contents.xcplayground
index 5da2641c9..9f5f2f40c 100644
--- a/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.playground/contents.xcplayground
+++ b/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.playground/contents.xcplayground
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.swift b/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.swift
index 108073288..4c2abd372 100644
--- a/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.swift
+++ b/Bucket Sort/BucketSort.swift
@@ -20,31 +20,6 @@
//
//
-import Foundation
-// FIXME: comparison operators with optionals were removed from the Swift Standard Libary.
-// Consider refactoring the code to use the non-optional operators.
-fileprivate func < (lhs: T?, rhs: T?) -> Bool {
- switch (lhs, rhs) {
- case let (l?, r?):
- return l < r
- case (nil, _?):
- return true
- default:
- return false
- }
-}
-
-// FIXME: comparison operators with optionals were removed from the Swift Standard Libary.
-// Consider refactoring the code to use the non-optional operators.
-fileprivate func >= (lhs: T?, rhs: T?) -> Bool {
- switch (lhs, rhs) {
- case let (l?, r?):
- return l >= r
- default:
- return !(lhs < rhs)
- }
-}
-
//////////////////////////////////////
// MARK: Main algorithm
//////////////////////////////////////
@@ -87,7 +62,11 @@ private func enoughSpaceInBuckets(_ buckets: [Bucket], elements: [T]) -> B
let maximumValue = elements.max()?.toInt()
let totalCapacity = buckets.count * (buckets.first?.capacity)!
- return totalCapacity >= maximumValue
+ guard let max = maximumValue else {
+ return false
+ }
+
+ return totalCapacity >= max
}
//////////////////////////////////////
diff --git a/Bucket Sort/README.markdown b/Bucket Sort/README.markdown
index f572fc9a1..f2708d71e 100644
--- a/Bucket Sort/README.markdown
+++ b/Bucket Sort/README.markdown
@@ -256,4 +256,4 @@ The following are some of the variation to the general [Bucket Sort](https://en.
- [Postman Sort](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bucket_sort#Postman.27s_sort)
- [Shuffle Sort](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bucket_sort#Shuffle_sort)
-*Written for Swift Algorithm Club by Barbara Rodeker. Images from Wikipedia.*
+*Written for Swift Algorithm Club by Barbara Rodeker. Images from Wikipedia. Updated by Bruno Scheele.*
diff --git a/Bucket Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Bucket Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index 84a305784..6df507720 100644
--- a/Bucket Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Bucket Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -83,7 +83,7 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0730;
- LastUpgradeCheck = 0900;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1000;
ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Swift Algorithm Club";
TargetAttributes = {
7B2BBC7F1C779D720067B71D = {
@@ -145,12 +145,14 @@
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
@@ -197,12 +199,14 @@
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
diff --git a/Bucket Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Bucket Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Bucket Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Bucket Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/Bucket Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
index 538a6f4fa..afd69e6a7 100644
--- a/Bucket Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/Bucket Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
(minimum:Double, firstPoint:Point, secondPoint:Point) {
+ var innerPoints = mergeSort(points, sortAccording : true)
+ let result = ClosestPair(&innerPoints, innerPoints.count)
+ return (result.minValue, result.firstPoint, result.secondPoint)
+}
+
+func ClosestPair(_ p : inout [Point],_ n : Int) -> (minValue: Double,firstPoint: Point,secondPoint: Point)
+{
+ // Brute force if only 3 points (To end recursion)
+ if n <= 3
+ {
+ var i=0, j = i+1
+ var minDist = Double.infinity
+ var newFirst:Point? = nil
+ var newSecond:Point? = nil
+ while i min { break }
+ if dist(strip[i], strip[x]) < temp
+ {
+ temp = dist(strip[i], strip[x])
+ tempFirst = strip[i]
+ tempSecond = strip[x]
+ }
+ x+=1
+ }
+ i+=1
+ }
+
+ if temp < min
+ {
+ min = temp;
+ first = tempFirst
+ second = tempSecond
+ }
+ return (min, first, second)
+}
+
+
+
+
+// MergeSort the array (Taken from Swift Algorithms Club with
+// minor addition)
+// sortAccodrding : true -> x, false -> y.
+func mergeSort(_ array: [Point], sortAccording : Bool) -> [Point] {
+ guard array.count > 1 else { return array }
+ let middleIndex = array.count / 2
+ let leftArray = mergeSort(Array(array[0.. [Point] {
+
+ var compare : (Point, Point) -> Bool
+
+ // Choose to compare with X or Y.
+ if sortAccording
+ {
+ compare = { p1,p2 in
+ return p1.x < p2.x
+ }
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ compare = { p1, p2 in
+ return p1.y < p2.y
+ }
+ }
+
+ var leftIndex = 0
+ var rightIndex = 0
+ var orderedPile = [Point]()
+ if orderedPile.capacity < leftPile.count + rightPile.count {
+ orderedPile.reserveCapacity(leftPile.count + rightPile.count)
+ }
+
+ while true {
+ guard leftIndex < leftPile.endIndex else {
+ orderedPile.append(contentsOf: rightPile[rightIndex.. Double
+{
+ let equation:Double = (((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x))) + (((a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)))
+ return equation.squareRoot()
+}
+
+
+var a = Point(0,2)
+var b = Point(6,67)
+var c = Point(43,71)
+var d = Point(1000,1000)
+var e = Point(39,107)
+var f = Point(2000,2000)
+var g = Point(3000,3000)
+var h = Point(4000,4000)
+
+
+var points = [a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h]
+let endResult = ClosestPairOf(points: points)
+print("Minimum Distance : \(endResult.minimum), The two points : (\(endResult.firstPoint.x ),\(endResult.firstPoint.y)), (\(endResult.secondPoint.x),\(endResult.secondPoint.y))")
+
diff --git a/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/contents.xcplayground b/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/contents.xcplayground
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a93d4844a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/contents.xcplayground
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata b/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..919434a62
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/playground.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcuserdata/admin.xcuserdatad/UserInterfaceState.xcuserstate b/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcuserdata/admin.xcuserdatad/UserInterfaceState.xcuserstate
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..82b130340
Binary files /dev/null and b/Closest Pair/ClosestPair.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcuserdata/admin.xcuserdatad/UserInterfaceState.xcuserstate differ
diff --git a/Closest Pair/Images/1200px-Closest_pair_of_points.png b/Closest Pair/Images/1200px-Closest_pair_of_points.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..cf61a3eff
Binary files /dev/null and b/Closest Pair/Images/1200px-Closest_pair_of_points.png differ
diff --git a/Closest Pair/Images/Case.png b/Closest Pair/Images/Case.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..20b171a1a
Binary files /dev/null and b/Closest Pair/Images/Case.png differ
diff --git a/Closest Pair/Images/Strip.png b/Closest Pair/Images/Strip.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b0193a127
Binary files /dev/null and b/Closest Pair/Images/Strip.png differ
diff --git a/Closest Pair/README.markdown b/Closest Pair/README.markdown
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a4de4a28b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Closest Pair/README.markdown
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+# ClosestPair
+
+Closest Pair is an algorithm that finds the closest pair of a given array of points By utilizing the Divide and Conquer methodology of solving problems so that it reaches the correct solution with O(nlogn) complexity.
+
+
+
+As we see in the above image there are an array of points and we need to find the closest two, But how do we do that without having to compare each two points which results in a whopping O(n^2) complexity?
+
+Here is the main algorithm (Steps) we'll follow.
+
+- Sort the array according to their position on the X-axis so that they are sorted in the array as they are naturally in math.
+
+```swift
+var innerPoints = mergeSort(points, sortAccording : true)
+```
+
+- Divide the points into two arrays Left, Right and keep dividing until you reach to only having 3 points in your array.
+
+- The base case is you have less than 3 points compare those against each other (Brute force) then return the minimum distance you found and the two points.
+
+- Now we get the first observation in the below image, There could be 2 points both very close to each other and indeed those two are the closest pair but since our algorithm so far divides from the middle
+
+```swift
+let line:Double = (p[mid].x + p[mid+1].x)/2
+```
+
+and just recursively calls itself until it reaches the base case we don't detect those points.
+
+
+
+- To solve this we start by sorting the array on the Y-axis to get the points in their natural order and then we start getting the difference between the X position of the point and the line we drew to divide and if it is less than the min we got so far from the recursion we add it to the strip
+
+```swift
+var strip = [Point]()
+var i=0, j = 0
+while i min { break }
+ if dist(strip[i], strip[x]) < temp
+ {
+ temp = dist(strip[i], strip[x])
+ tempFirst = strip[i]
+ tempSecond = strip[x]
+ }
+ x+=1
+ }
+ i+=1
+ }
+```
+
+- Of course not every time you end up with the same shape but this is the worst case and it's rare to happen so in reality you end up with far less points valid for comparison and this is why the algorithm gets performance in addition to the sorting tricks we did.
+
+- Compare the points in the strip and if you find a smaller distance replace the current one with it.
+
+
+So this is the rundown of how the algorithm works and you could see the fun little math tricks used to optimize this and we end up with O(nlogn) complexity mainly because of the sorting.
+
+
+## See also
+
+See the playground to play around with the implementation of the algorithm
+
+[Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Closest_pair_of_points_problem)
+
+*Written for Swift Algorithm Club by [Ahmed Nader](https://github.com/ahmednader42)*
diff --git a/Comb Sort/Comb Sort.playground/Contents.swift b/Comb Sort/Comb Sort.playground/Contents.swift
index 39e24248a..1f7723838 100644
--- a/Comb Sort/Comb Sort.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Comb Sort/Comb Sort.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -2,11 +2,7 @@
// Created by Stephen Rutstein
// 7-16-2016
-import Cocoa
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
+import Foundation
// Test Comb Sort with small array of ten values
let array = [2, 32, 9, -1, 89, 101, 55, -10, -12, 67]
diff --git a/Comb Sort/README.markdown b/Comb Sort/README.markdown
index d30d429b3..20c939307 100644
--- a/Comb Sort/README.markdown
+++ b/Comb Sort/README.markdown
@@ -64,8 +64,8 @@ This will sort the values of the array into ascending order -- increasing in val
## Performance
Comb Sort was created to improve upon the worst case time complexity of Bubble Sort. With Comb
-Sort, the worst case scenario for performance is exponential -- O(n^2). At best though, Comb Sort
-performs at O(n logn) time complexity. This creates a drastic improvement over Bubble Sort's performance.
+Sort, the worst case scenario for performance is polynomial -- O(n^2). At best though, Comb Sort
+performs at O(n logn) time complexity -- loglinear. This creates a drastic improvement over Bubble Sort's performance.
Similar to Bubble Sort, the space complexity for Comb Sort is constant -- O(1).
This is extremely space efficient as it sorts the array in place.
diff --git a/Comb Sort/Tests/CombSortTests.swift b/Comb Sort/Tests/CombSortTests.swift
index e972c0a57..1d83af002 100644
--- a/Comb Sort/Tests/CombSortTests.swift
+++ b/Comb Sort/Tests/CombSortTests.swift
@@ -9,25 +9,20 @@
import XCTest
class CombSortTests: XCTestCase {
- var sequence: [Int]!
- let expectedSequence: [Int] = [-12, -10, -1, 2, 9, 32, 55, 67, 89, 101]
+ var sequence: [Int]!
+ let expectedSequence: [Int] = [-12, -10, -1, 2, 9, 32, 55, 67, 89, 101]
+
+ override func setUp() {
+ super.setUp()
+ sequence = [2, 32, 9, -1, 89, 101, 55, -10, -12, 67]
+ }
- func testSwift4(){
- #if swift(>=4.0)
- print("Hello, Swift 4!")
- #endif
- }
- override func setUp() {
- super.setUp()
- sequence = [2, 32, 9, -1, 89, 101, 55, -10, -12, 67]
- }
+ override func tearDown() {
+ super.tearDown()
+ }
- override func tearDown() {
- super.tearDown()
- }
-
- func testCombSort() {
- let sortedSequence = combSort(sequence)
- XCTAssertEqual(sortedSequence, expectedSequence)
- }
+ func testCombSort() {
+ let sortedSequence = combSort(sequence)
+ XCTAssertEqual(sortedSequence, expectedSequence)
+ }
}
diff --git a/Comb Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Comb Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index 7530acbdc..4582b3f2d 100644
--- a/Comb Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Comb Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -82,7 +82,7 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0820;
- LastUpgradeCheck = 0820;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1000;
ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Swift Algorithm Club";
TargetAttributes = {
056E92741E2483D300B30F52 = {
@@ -142,15 +142,23 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_DOCUMENTATION_COMMENTS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -179,7 +187,7 @@
SDKROOT = macosx;
SWIFT_ACTIVE_COMPILATION_CONDITIONS = DEBUG;
SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Onone";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -192,15 +200,23 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_DOCUMENTATION_COMMENTS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -221,7 +237,7 @@
MTL_ENABLE_DEBUG_INFO = NO;
SDKROOT = macosx;
SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Owholemodule";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
@@ -235,7 +251,7 @@
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = "Swift-Algorithm-Club.Tests";
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Onone";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -248,7 +264,7 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = "Swift-Algorithm-Club.Tests";
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/Comb Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/Comb Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
index 55e697ad3..48faa2df7 100644
--- a/Comb Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/Comb Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
(_ a: [T], _ n: Int) {
- if n == 0 {
- print(a) // display the current permutation
- } else {
- var a = a
- permuteWirth(a, n - 1)
- for i in 0..
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Convex Hull/Convex Hull.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/Convex Hull/Convex Hull.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
index 1f93a0c4f..8f04a0f51 100644
--- a/Convex Hull/Convex Hull.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/Convex Hull/Convex Hull.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
=4.0)
- print("Hello, Swift 4!")
- #endif
-
- generatePoints()
+ generateRandomPoints()
quickHull(points: points)
}
@@ -32,11 +24,11 @@ class View: UIView {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
- func generatePoints() {
+ func generateRandomPoints() {
for _ in 0..=4.0)
- print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-func countOccurrencesOfKey(_ key: Int, inArray a: [Int]) -> Int {
- func leftBoundary() -> Int {
+func countOccurrences(of key: T, in array: [T]) -> Int {
+ var leftBoundary: Int {
var low = 0
- var high = a.count
+ var high = array.count
while low < high {
let midIndex = low + (high - low)/2
- if a[midIndex] < key {
+ if array[midIndex] < key {
low = midIndex + 1
} else {
high = midIndex
@@ -18,12 +14,12 @@ func countOccurrencesOfKey(_ key: Int, inArray a: [Int]) -> Int {
return low
}
- func rightBoundary() -> Int {
+ var rightBoundary: Int {
var low = 0
- var high = a.count
+ var high = array.count
while low < high {
let midIndex = low + (high - low)/2
- if a[midIndex] > key {
+ if array[midIndex] > key {
high = midIndex
} else {
low = midIndex + 1
@@ -32,13 +28,13 @@ func countOccurrencesOfKey(_ key: Int, inArray a: [Int]) -> Int {
return low
}
- return rightBoundary() - leftBoundary()
+ return rightBoundary - leftBoundary
}
// Simple test
let a = [ 0, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 6, 8, 10, 11, 11 ]
-countOccurrencesOfKey(3, inArray: a)
+countOccurrences(of: 3, in: a)
// Test with arrays of random size and contents (see debug output)
@@ -63,6 +59,6 @@ for _ in 0..<10 {
// Note: we also test -1 and 6 to check the edge cases.
for k in -1...6 {
- print("\t\(k): \(countOccurrencesOfKey(k, inArray: a))")
+ print("\t\(k): \(countOccurrences(of: k, in: a))")
}
}
diff --git a/Count Occurrences/CountOccurrences.swift b/Count Occurrences/CountOccurrences.swift
index 10dd12c4f..532e3810e 100644
--- a/Count Occurrences/CountOccurrences.swift
+++ b/Count Occurrences/CountOccurrences.swift
@@ -1,14 +1,15 @@
-/*
- Counts the number of times a value appears in an array in O(lg n) time.
- The array must be sorted from low to high.
-*/
-func countOccurrencesOfKey(_ key: Int, inArray a: [Int]) -> Int {
- func leftBoundary() -> Int {
+/// Counts the number of times a value appears in an array in O(log n) time. The array must be sorted from low to high.
+///
+/// - Parameter key: the key to be searched for in the array
+/// - Parameter array: the array to search
+/// - Returns: the count of occurences of the key in the given array
+func countOccurrences(of key: T, in array: [T]) -> Int {
+ var leftBoundary: Int {
var low = 0
- var high = a.count
+ var high = array.count
while low < high {
let midIndex = low + (high - low)/2
- if a[midIndex] < key {
+ if array[midIndex] < key {
low = midIndex + 1
} else {
high = midIndex
@@ -17,12 +18,12 @@ func countOccurrencesOfKey(_ key: Int, inArray a: [Int]) -> Int {
return low
}
- func rightBoundary() -> Int {
+ var rightBoundary: Int {
var low = 0
- var high = a.count
+ var high = array.count
while low < high {
let midIndex = low + (high - low)/2
- if a[midIndex] > key {
+ if array[midIndex] > key {
high = midIndex
} else {
low = midIndex + 1
@@ -31,5 +32,5 @@ func countOccurrencesOfKey(_ key: Int, inArray a: [Int]) -> Int {
return low
}
- return rightBoundary() - leftBoundary()
+ return rightBoundary - leftBoundary
}
diff --git a/Count Occurrences/README.markdown b/Count Occurrences/README.markdown
index 85b77d2d0..8e935ea58 100644
--- a/Count Occurrences/README.markdown
+++ b/Count Occurrences/README.markdown
@@ -22,10 +22,10 @@ The trick is to use two binary searches, one to find where the `3`s start (the l
In code this looks as follows:
```swift
-func countOccurrencesOfKey(_ key: Int, inArray a: [Int]) -> Int {
- func leftBoundary() -> Int {
+func countOccurrences(of key: T, in array: [T]) -> Int {
+ var leftBoundary: Int {
var low = 0
- var high = a.count
+ var high = array.count
while low < high {
let midIndex = low + (high - low)/2
if a[midIndex] < key {
@@ -37,9 +37,9 @@ func countOccurrencesOfKey(_ key: Int, inArray a: [Int]) -> Int {
return low
}
- func rightBoundary() -> Int {
+ var rightBoundary: Int {
var low = 0
- var high = a.count
+ var high = array.count
while low < high {
let midIndex = low + (high - low)/2
if a[midIndex] > key {
@@ -51,18 +51,18 @@ func countOccurrencesOfKey(_ key: Int, inArray a: [Int]) -> Int {
return low
}
- return rightBoundary() - leftBoundary()
+ return rightBoundary - leftBoundary
}
```
-Notice that the helper functions `leftBoundary()` and `rightBoundary()` are very similar to the [binary search](../Binary%20Search/) algorithm. The big difference is that they don't stop when they find the search key, but keep going.
+Notice that the variables `leftBoundary` and `rightBoundary` are very similar to the [binary search](../Binary%20Search/) algorithm. The big difference is that they don't stop when they find the search key, but keep going. Also, notice that we constrain the type `T` to be Comparable so that the algorithm can be applied to an array of Strings, Ints or other types that conform to the Swift Comparable protocol.
To test this algorithm, copy the code to a playground and then do:
```swift
let a = [ 0, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 6, 8, 10, 11, 11 ]
-countOccurrencesOfKey(3, inArray: a) // returns 4
+countOccurrences(of: 3, in: a) // returns 4
```
> **Remember:** If you use your own array, make sure it is sorted first!
@@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ The right boundary is at index 7. The difference between the two boundaries is 7
Each binary search took 4 steps, so in total this algorithm took 8 steps. Not a big gain on an array of only 12 items, but the bigger the array, the more efficient this algorithm becomes. For a sorted array with 1,000,000 items, it only takes 2 x 20 = 40 steps to count the number of occurrences for any particular value.
-By the way, if the value you're looking for is not in the array, then `rightBoundary()` and `leftBoundary()` return the same value and so the difference between them is 0.
+By the way, if the value you're looking for is not in the array, then `rightBoundary` and `leftBoundary` return the same value and so the difference between them is 0.
This is an example of how you can modify the basic binary search to solve other algorithmic problems as well. Of course, it does require that the array is sorted.
diff --git a/Counting Sort/CountingSort.playground/Contents.swift b/Counting Sort/CountingSort.playground/Contents.swift
index 4d918e384..dc375512a 100644
--- a/Counting Sort/CountingSort.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Counting Sort/CountingSort.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,10 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
enum CountingSortError: Error {
case arrayEmpty
}
diff --git a/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Edge.o b/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Edge.o
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ab1e89b3a
Binary files /dev/null and b/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Edge.o differ
diff --git a/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Graph.o b/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Graph.o
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..dde35fb0f
Binary files /dev/null and b/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Graph.o differ
diff --git a/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Node.o b/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Node.o
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1090b3a9c
Binary files /dev/null and b/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Node.o differ
diff --git a/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Pages/Simple Example.xcplaygroundpage/Contents.swift b/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Pages/Simple Example.xcplaygroundpage/Contents.swift
index 99f20a729..c83f52af8 100644
--- a/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Pages/Simple Example.xcplaygroundpage/Contents.swift
+++ b/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Pages/Simple Example.xcplaygroundpage/Contents.swift
@@ -1,7 +1,4 @@
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
+// last checked with Xcode 10.1
func depthFirstSearch(_ graph: Graph, source: Node) -> [String] {
var nodesExplored = [source.label]
diff --git a/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Sources/Graph.swift b/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Sources/Graph.swift
index 34ee2fa3a..48b8feed5 100644
--- a/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Sources/Graph.swift
+++ b/Depth-First Search/DepthFirstSearch.playground/Sources/Graph.swift
@@ -5,6 +5,7 @@ public class Graph: CustomStringConvertible, Equatable {
self.nodes = []
}
+ @discardableResult
public func addNode(_ label: String) -> Node {
let node = Node(label)
nodes.append(node)
diff --git a/Depth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Depth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index 8f6058600..2b433bd96 100644
--- a/Depth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Depth-First Search/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -234,7 +234,7 @@
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Onone";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -247,7 +247,7 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/Deque/Deque-Simple.swift b/Deque/Deque-Simple.swift
index f4f5f0409..fc0fcb2b2 100644
--- a/Deque/Deque-Simple.swift
+++ b/Deque/Deque-Simple.swift
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ public struct Deque {
}
public mutating func enqueueFront(_ element: T) {
- array.insert(element, atIndex: 0)
+ array.insert(element, at: 0)
}
public mutating func dequeue() -> T? {
diff --git a/Deque/Deque.playground/Contents.swift b/Deque/Deque.playground/Contents.swift
index df9b57a5e..9e7b22c02 100644
--- a/Deque/Deque.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Deque/Deque.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,10 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
public struct Deque {
private var array = [T]()
diff --git a/Deque/README.markdown b/Deque/README.markdown
index fda1de5f8..f3172e16e 100644
--- a/Deque/README.markdown
+++ b/Deque/README.markdown
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ public struct Deque {
}
public mutating func enqueueFront(_ element: T) {
- array.insert(element, atIndex: 0)
+ array.insert(element, at: 0)
}
public mutating func dequeue() -> T? {
diff --git a/Dijkstra Algorithm/Dijkstra.playground/Contents.swift b/Dijkstra Algorithm/Dijkstra.playground/Contents.swift
index 1cd1254b1..7c7f1a4b0 100644
--- a/Dijkstra Algorithm/Dijkstra.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Dijkstra Algorithm/Dijkstra.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,11 +1,6 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
import Foundation
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
var vertices: Set = Set()
func createNotConnectedVertices() {
diff --git a/Dijkstra Algorithm/Dijkstra.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Dijkstra Algorithm/Dijkstra.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Dijkstra Algorithm/Dijkstra.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Dijkstra Algorithm/VisualizedDijkstra.playground/Contents.swift b/Dijkstra Algorithm/VisualizedDijkstra.playground/Contents.swift
index 8e61ef49b..de6b49834 100644
--- a/Dijkstra Algorithm/VisualizedDijkstra.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Dijkstra Algorithm/VisualizedDijkstra.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -9,11 +9,6 @@
import UIKit
import PlaygroundSupport
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
/*:
First of all, let's set up colors for our window and graph. The visited color will be applied to visited vertices. The checking color will be applied to an edge and an edge neighbor every time the algorithm is checking some vertex neighbors. And default colors are just initial colors for elements.
*/
diff --git a/Dijkstra Algorithm/VisualizedDijkstra.playground/Sources/Window.swift b/Dijkstra Algorithm/VisualizedDijkstra.playground/Sources/Window.swift
index 73c512e6b..9a169b8c7 100644
--- a/Dijkstra Algorithm/VisualizedDijkstra.playground/Sources/Window.swift
+++ b/Dijkstra Algorithm/VisualizedDijkstra.playground/Sources/Window.swift
@@ -134,7 +134,7 @@ public class Window: UIView, GraphDelegate {
let origin = CGPoint(x: center.x - 25, y: 100)
let activityIndicatorFrame = CGRect(origin: origin, size: size)
activityIndicator = UIActivityIndicatorView(frame: activityIndicatorFrame)
- activityIndicator.activityIndicatorViewStyle = .whiteLarge
+ activityIndicator.style = .whiteLarge
}
@objc private func createGraphButtonTap() {
diff --git a/Dijkstra Algorithm/VisualizedDijkstra.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Dijkstra Algorithm/VisualizedDijkstra.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Dijkstra Algorithm/VisualizedDijkstra.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/DiningPhilosophers/DiningPhilosophers.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/DiningPhilosophers/DiningPhilosophers.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index ecb060026..7699219de 100755
--- a/DiningPhilosophers/DiningPhilosophers.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/DiningPhilosophers/DiningPhilosophers.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -11,6 +11,7 @@
/* End PBXBuildFile section */
/* Begin PBXFileReference section */
+ 232D7939216F76F700831A74 /* README.md */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; lastKnownFileType = net.daringfireball.markdown; path = README.md; sourceTree = ""; };
OBJ_12 /* DiningPhilosophers */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; explicitFileType = "compiled.mach-o.executable"; path = DiningPhilosophers; sourceTree = BUILT_PRODUCTS_DIR; };
OBJ_6 /* Package.swift */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; explicitFileType = sourcecode.swift; path = Package.swift; sourceTree = ""; };
OBJ_9 /* main.swift */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; lastKnownFileType = sourcecode.swift; path = main.swift; sourceTree = ""; };
@@ -27,13 +28,6 @@
/* End PBXFrameworksBuildPhase section */
/* Begin PBXGroup section */
- OBJ_10 /* Tests */ = {
- isa = PBXGroup;
- children = (
- );
- path = Tests;
- sourceTree = "";
- };
OBJ_11 /* Products */ = {
isa = PBXGroup;
children = (
@@ -42,15 +36,14 @@
name = Products;
sourceTree = BUILT_PRODUCTS_DIR;
};
- OBJ_5 /* */ = {
+ OBJ_5 = {
isa = PBXGroup;
children = (
+ 232D7939216F76F700831A74 /* README.md */,
OBJ_6 /* Package.swift */,
OBJ_7 /* Sources */,
- OBJ_10 /* Tests */,
OBJ_11 /* Products */,
);
- name = "";
sourceTree = "";
};
OBJ_7 /* Sources */ = {
@@ -96,6 +89,11 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastUpgradeCheck = 9999;
+ TargetAttributes = {
+ OBJ_13 = {
+ LastSwiftMigration = 1000;
+ };
+ };
};
buildConfigurationList = OBJ_2 /* Build configuration list for PBXProject "DiningPhilosophers" */;
compatibilityVersion = "Xcode 3.2";
@@ -104,7 +102,7 @@
knownRegions = (
en,
);
- mainGroup = OBJ_5 /* */;
+ mainGroup = OBJ_5;
productRefGroup = OBJ_11 /* Products */;
projectDirPath = "";
projectRoot = "";
@@ -139,7 +137,7 @@
SWIFT_ACTIVE_COMPILATION_CONDITIONS = SWIFT_PACKAGE;
SWIFT_FORCE_DYNAMIC_LINK_STDLIB = YES;
SWIFT_FORCE_STATIC_LINK_STDLIB = NO;
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
TARGET_NAME = DiningPhilosophers;
};
name = Debug;
@@ -157,7 +155,7 @@
SWIFT_ACTIVE_COMPILATION_CONDITIONS = SWIFT_PACKAGE;
SWIFT_FORCE_DYNAMIC_LINK_STDLIB = YES;
SWIFT_FORCE_STATIC_LINK_STDLIB = NO;
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
TARGET_NAME = DiningPhilosophers;
};
name = Release;
diff --git a/DiningPhilosophers/DiningPhilosophers.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/DiningPhilosophers/DiningPhilosophers.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/DiningPhilosophers/DiningPhilosophers.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/DiningPhilosophers/README.md b/DiningPhilosophers/README.md
index ae84cb63b..aed9dfe59 100755
--- a/DiningPhilosophers/README.md
+++ b/DiningPhilosophers/README.md
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ Based on the Chandy and Misra's analysis, a system of preference levels is deriv
# Swift implementation
-This Swift 3.0 implementation of the Chandy/Misra solution is based on the GCD and Semaphore tecnique that can be built on both macOS and Linux.
+This Swift 3.0 implementation of the Chandy/Misra solution is based on the GCD and Semaphore technique that can be built on both macOS and Linux.
The code is based on a ForkPair struct used for holding an array of DispatchSemaphore and a Philosopher struct for associate a couple of forks to each Philosopher.
@@ -57,3 +57,4 @@ A background DispatchQueue is then used to let any Philosopher run asyncrounosly
Dining Philosophers on Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dining_philosophers_problem
Written for Swift Algorithm Club by Jacopo Mangiavacchi
+Swift 4.2 check by Bruno Scheele
diff --git a/Egg Drop Problem/EggDrop.playground/Contents.swift b/Egg Drop Problem/EggDrop.playground/Contents.swift
index 0b707da98..decaacdca 100644
--- a/Egg Drop Problem/EggDrop.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Egg Drop Problem/EggDrop.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,7 +1,3 @@
-#if swift(>=4.0)
- print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
drop(numberOfEggs: 2, numberOfFloors: 2) //expected answer: 2
drop(numberOfEggs: 2, numberOfFloors: 4) //expected answer: 3
drop(numberOfEggs: 2, numberOfFloors: 6) //expected answer: 3
diff --git a/Egg Drop Problem/EggDrop.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Egg Drop Problem/EggDrop.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Egg Drop Problem/EggDrop.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Egg Drop Problem/EggDrop.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/WorkspaceSettings.xcsettings b/Egg Drop Problem/EggDrop.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/WorkspaceSettings.xcsettings
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0c67376eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Egg Drop Problem/EggDrop.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/WorkspaceSettings.xcsettings
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/Egg Drop Problem/README.markdown b/Egg Drop Problem/README.markdown
index b2f45d09e..416984193 100644
--- a/Egg Drop Problem/README.markdown
+++ b/Egg Drop Problem/README.markdown
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ If the object is incredibly resilient, and you may need to do the testing on the
## Description
-You're in a building with **m** floors and you are given **n** eggs. What is the maximum number of attempts it will take to find out the floor that breaks the egg?
+You're in a building with **m** floors and you are given **n** eggs. What is the minimum number of attempts it will take to find out the floor that breaks the egg?
For convenience, here are a few rules to keep in mind:
diff --git a/Encode and Decode Tree/EncodeAndDecodeTree.playground/Contents.swift b/Encode and Decode Tree/EncodeAndDecodeTree.playground/Contents.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..44c2440d5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Encode and Decode Tree/EncodeAndDecodeTree.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
+
+func printTree(_ root: BinaryNode?) {
+ guard let root = root else {
+ return
+ }
+
+ let leftVal = root.left == nil ? "nil" : root.left!.val
+ let rightVal = root.right == nil ? "nil" : root.right!.val
+
+ print("val: \(root.val) left: \(leftVal) right: \(rightVal)")
+
+ printTree(root.left)
+ printTree(root.right)
+}
+
+let coder = BinaryNodeCoder()
+
+let node1 = BinaryNode("a")
+let node2 = BinaryNode("b")
+let node3 = BinaryNode("c")
+let node4 = BinaryNode("d")
+let node5 = BinaryNode("e")
+
+node1.left = node2
+node1.right = node3
+node3.left = node4
+node3.right = node5
+
+let encodeStr = try coder.encode(node1)
+print(encodeStr)
+// "a b # # c d # # e # #"
+
+
+let root: BinaryNode = coder.decode(from: encodeStr)!
+print("Tree:")
+printTree(root)
+/*
+ Tree:
+ val: a left: b right: c
+ val: b left: nil right: nil
+ val: c left: d right: e
+ val: d left: nil right: nil
+ val: e left: nil right: nil
+ */
+
diff --git a/Encode and Decode Tree/EncodeAndDecodeTree.playground/Sources/EncodeAndDecodeTree.swift b/Encode and Decode Tree/EncodeAndDecodeTree.playground/Sources/EncodeAndDecodeTree.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..10bb277f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Encode and Decode Tree/EncodeAndDecodeTree.playground/Sources/EncodeAndDecodeTree.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+//
+// EncodeAndDecodeTree.swift
+//
+//
+// Created by Kai Chen on 19/07/2017.
+//
+//
+
+import Foundation
+
+protocol BinaryNodeEncoder {
+ func encode(_ node: BinaryNode?) throws -> String
+}
+
+protocol BinaryNodeDecoder {
+ func decode(from string: String) -> BinaryNode?
+}
+
+public class BinaryNodeCoder: BinaryNodeEncoder, BinaryNodeDecoder {
+
+ // MARK: Private
+
+ private let separator: Character = ","
+ private let nilNode = "X"
+
+ private func decode(from array: inout [String]) -> BinaryNode? {
+ guard !array.isEmpty else {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ let value = array.removeLast()
+
+ guard value != nilNode, let val = value as? T else {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ let node = BinaryNode(val)
+ node.left = decode(from: &array)
+ node.right = decode(from: &array)
+
+ return node
+ }
+
+ // MARK: Public
+
+ public init() {}
+
+ public func encode(_ node: BinaryNode?) throws -> String {
+ var str = ""
+ node?.preOrderTraversal { data in
+ if let data = data {
+ let string = String(describing: data)
+ str.append(string)
+ } else {
+ str.append(nilNode)
+ }
+ str.append(separator)
+ }
+
+ return str
+ }
+
+ public func decode(from string: String) -> BinaryNode? {
+ var components = string.split(separator: separator).reversed().map(String.init)
+ return decode(from: &components)
+ }
+}
+
+public class BinaryNode {
+ public var val: Element
+ public var left: BinaryNode?
+ public var right: BinaryNode?
+
+ public init(_ val: Element, left: BinaryNode? = nil, right: BinaryNode? = nil) {
+ self.val = val
+ self.left = left
+ self.right = right
+ }
+
+ public func preOrderTraversal(visit: (Element?) throws -> ()) rethrows {
+ try visit(val)
+
+ if let left = left {
+ try left.preOrderTraversal(visit: visit)
+ } else {
+ try visit(nil)
+ }
+
+ if let right = right {
+ try right.preOrderTraversal(visit: visit)
+ } else {
+ try visit(nil)
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.playground/contents.xcplayground b/Encode and Decode Tree/EncodeAndDecodeTree.playground/contents.xcplayground
similarity index 100%
rename from Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.playground/contents.xcplayground
rename to Encode and Decode Tree/EncodeAndDecodeTree.playground/contents.xcplayground
diff --git a/Encode and Decode Tree/EncodeAndDecodeTree.swift b/Encode and Decode Tree/EncodeAndDecodeTree.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6ec8a3046
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Encode and Decode Tree/EncodeAndDecodeTree.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+//
+// EncodeAndDecodeTree.swift
+//
+//
+// Created by Kai Chen on 19/07/2017.
+//
+//
+
+import Foundation
+
+protocol BinaryNodeEncoder {
+ func encode(_ node: BinaryNode?) throws -> String
+}
+
+protocol BinaryNodeDecoder {
+ func decode(from string: String) -> BinaryNode?
+}
+
+public class BinaryNodeCoder: BinaryNodeEncoder, BinaryNodeDecoder {
+
+ // MARK: Private
+
+ private let separator: Character = ","
+ private let nilNode = "X"
+
+ private func decode(from array: inout [String]) -> BinaryNode? {
+ guard !array.isEmpty else {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ let value = array.removeLast()
+
+ guard value != nilNode, let val = value as? T else {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ let node = BinaryNode(val)
+ node.left = decode(from: &array)
+ node.right = decode(from: &array)
+
+ return node
+ }
+
+ // MARK: Public
+
+ public init() {}
+
+ public func encode(_ node: BinaryNode?) throws -> String {
+ var str = ""
+ node?.preOrderTraversal { data in
+ if let data = data {
+ let string = String(describing: data)
+ str.append(string)
+ } else {
+ str.append(nilNode)
+ }
+ str.append(separator)
+ }
+
+ return str
+ }
+
+ public func decode(from string: String) -> BinaryNode? {
+ var components = string.split(separator: separator).reversed().map(String.init)
+ return decode(from: &components)
+ }
+}
+
+public class BinaryNode {
+ public var val: Element
+ public var left: BinaryNode?
+ public var right: BinaryNode?
+
+ public init(_ val: Element, left: BinaryNode? = nil, right: BinaryNode? = nil) {
+ self.val = val
+ self.left = left
+ self.right = right
+ }
+
+ public func preOrderTraversal(visit: (Element?) throws -> ()) rethrows {
+ try visit(val)
+
+ if let left = left {
+ try left.preOrderTraversal(visit: visit)
+ } else {
+ try visit(nil)
+ }
+
+ if let right = right {
+ try right.preOrderTraversal(visit: visit)
+ } else {
+ try visit(nil)
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/Encode and Decode Tree/readme.md b/Encode and Decode Tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b60e0a504
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Encode and Decode Tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,199 @@
+# Encode and Decode Binary Tree
+
+> **Note**: The prerequisite for this article is an understanding of how [binary trees](https://github.com/raywenderlich/swift-algorithm-club/tree/master/Binary%20Tree) work.
+
+Trees are complex structures. Unlike linear collections such as arrays or linked lists, trees are *non-linear* and each element in a tree has positional information such as the *parent-child* relationship between nodes. When you want to send a tree structure to your backend, you need to send the data of each node, and a way to represent the parent-child relationship for each node.
+
+Your strategy in how you choose to represent this information is called your **encoding** strategy. The opposite of that - changing your encoded data back to its original form - is your **decoding** strategy.
+
+There are many ways to encode a tree and decode a tree. The important thing to keep in mind is that encoding and decoding strategies are closely related. The way you choose to encode a tree directly affects how you might decode a tree.
+
+Encoding and decoding are synonyms to *serializing* and *deserializing* trees.
+
+As a reference, the following code represents the typical `Node` type of a binary tree:
+
+```swift
+class BinaryNode {
+ var data: Element
+ var leftChild: BinaryNode?
+ var rightChild: BinaryNode?
+
+ // ... (rest of the implementation)
+}
+```
+
+Your encoding and decoding methods will reside in the `BinaryNodeEncoder` and `BinaryNodeDecoder` classes:
+
+```swift
+class BinaryNodeCoder {
+
+ // transforms nodes into string representation
+ func encode(_ node: BinaryNode) throws -> String where T: Encodable {
+
+ }
+
+ // transforms string into `BinaryNode` representation
+ func decode(from string: String)
+ throws -> BinaryNode where T: Decodable {
+
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## Encoding
+
+As mentioned before, there are different ways to do encoding. For no particular reason, you'll opt for the following rules:
+
+1. The result of the encoding will be a `String` object.
+2. You'll encode using *pre-order* traversal.
+
+Here's an example of this operation in code:
+
+```swift
+fileprivate extension BinaryNode {
+
+ // 1
+ func preOrderTraversal(visit: (Element?) throws -> ()) rethrows {
+ try visit(data)
+
+ if let leftChild = leftChild {
+ try leftChild.preOrderTraversal(visit: visit)
+ } else {
+ try visit(nil)
+ }
+
+ if let rightChild = rightChild {
+ try rightChild.preOrderTraversal(visit: visit)
+ } else {
+ try visit(nil)
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+class BinaryNodeCoder {
+
+ // 2
+ private var separator: String { return "," }
+
+ // 3
+ private var nilNode: String { return "X" }
+
+ // 4
+ func encode(_ node: BinaryNode) -> String {
+ var str = ""
+ node.preOrderTraversal { data in
+ if let data = data {
+ let string = String(describing: data)
+ str.append(string)
+ } else {
+ str.append(nilNode)
+ }
+ str.append(separator)
+ }
+ return str
+ }
+
+ // ...
+}
+```
+
+Here's a high level overview of the above code:
+
+2. `separator` is a way to distinguish the nodes in a string. To illustrate its importance, consider the following encoded string "banana". How did the tree structure look like before encoding? Without the `separator`, you can't tell.
+
+3. `nilNode` is used to identify empty children. This a necesssary piece of information to retain in order to rebuild the tree later.
+
+4. `encode` returns a `String` representation of the `BinaryNode`. For example: "ba,nana,nil" represents a tree with two nodes - "ba" and "nana" - in pre-order format.
+
+## Decoding
+
+Your decoding strategy is the exact opposite of your encoding strategy. You'll take an encoded string, and turn it back into your binary tree.
+
+Your encoding strategy followed the following rules:
+
+1. The result of the encoding will be a `String` object.
+2. You'll encode using *pre-order* traversal.
+
+The implementation also added a few important details:
+
+* node values are separated by `,`
+* `nil` children are denoted by the `nil` string
+
+These details will shape your `decode` operation. Here's a possible implementation:
+
+```swift
+
+class BinaryNodeCoder {
+
+ // ...
+
+ // 1
+ func decode(_ string: String) -> BinaryNode? {
+ let components = encoded.lazy.split(separator: separator).reversed().map(String.init)
+ return decode(from: components)
+ }
+
+ // 2
+ private func decode(from array: inout [String]) -> BinaryNode? {
+ guard !array.isEmpty else { return nil }
+ let value = array.removeLast()
+ guard value != "\(nilNode)" else { return nil }
+
+ let node = AVLNode(value: value)
+ node.leftChild = decode(from: &array)
+ node.rightChild = decode(from: &array)
+ return node
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Here's a high level overview of the above code:
+
+1. Takes a `String`, and uses `split` to partition the contents of `string` into an array based on the `separator` defined in the encoding step. The result is first `reversed`, and then mapped to a `String`. The `reverse` step is an optimization for the next function, allowing us to use `array.removeLast()` instead of `array.removeFirst()`.
+
+2. Using an array as a stack, you recursively decode each node. The array keeps track of sequence of nodes and progress.
+
+Here's an example output of a tree undergoing the encoding and decoding process:
+
+```
+Original Tree
+
+ ┌──8423
+ ┌──8391
+ │ └──nil
+┌──7838
+│ │ ┌──4936
+│ └──3924
+│ └──2506
+830
+│ ┌──701
+└──202
+ └──169
+
+Encoded tree: 830,202,169,X,X,701,X,X,7838,3924,2506,X,X,4936,X,X,8391,X,8423,X,X,
+
+Decoded tree
+
+ ┌──8423
+ ┌──8391
+ │ └──nil
+┌──7838
+│ │ ┌──4936
+│ └──3924
+│ └──2506
+830
+│ ┌──701
+└──202
+ └──169
+ ```
+
+Notice the original tree and decoded tree are identical.
+
+## Further Reading & References
+
+- [LeetCode](https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree/description/)
+
+*Written for the Swift Algorithm Club by Kai Chen & Kelvin Lau*
+
+
+
diff --git a/Fixed Size Array/FixedSizeArray.playground/Contents.swift b/Fixed Size Array/FixedSizeArray.playground/Contents.swift
index 8b5bc1147..616f8443d 100644
--- a/Fixed Size Array/FixedSizeArray.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Fixed Size Array/FixedSizeArray.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,10 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
- print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
/*
An unordered array with a maximum size.
diff --git a/Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.playground/Contents.swift b/Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.playground/Contents.swift
index 37acdab61..2ab13b362 100644
--- a/Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,26 +1,23 @@
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
+// Last checked with Xcode Version 11.4.1 (11E503a)
func fizzBuzz(_ numberOfTurns: Int) {
- for i in 1...numberOfTurns {
- var result = ""
-
- if i % 3 == 0 {
- result += "Fizz"
+ guard numberOfTurns >= 1 else {
+ print("Number of turns must be >= 1")
+ return
}
-
- if i % 5 == 0 {
- result += (result.isEmpty ? "" : " ") + "Buzz"
+
+ for i in 1...numberOfTurns {
+ switch (i.isMultiple(of: 3), i.isMultiple(of: 5)) {
+ case (false, false):
+ print("\(i)")
+ case (true, false):
+ print("Fizz")
+ case (false, true):
+ print("Buzz")
+ case (true, true):
+ print("Fizz Buzz")
+ }
}
-
- if result.isEmpty {
- result += "\(i)"
- }
-
- print(result)
- }
}
-fizzBuzz(100)
+fizzBuzz(15)
diff --git a/Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.swift b/Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.swift
index b6bb410e7..bf753e648 100644
--- a/Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.swift
+++ b/Fizz Buzz/FizzBuzz.swift
@@ -1,19 +1,21 @@
-func fizzBuzz(_ numberOfTurns: Int) {
- for i in 1...numberOfTurns {
- var result = ""
-
- if i % 3 == 0 {
- result += "Fizz"
- }
+// Last checked with Xcode Version 11.4.1 (11E503a)
- if i % 5 == 0 {
- result += (result.isEmpty ? "" : " ") + "Buzz"
+func fizzBuzz(_ numberOfTurns: Int) {
+ guard numberOfTurns >= 1 else {
+ print("Number of turns must be >= 1")
+ return
}
-
- if result.isEmpty {
- result += "\(i)"
+
+ for i in 1...numberOfTurns {
+ switch (i.isMultiple(of: 3), i.isMultiple(of: 5)) {
+ case (false, false):
+ print("\(i)")
+ case (true, false):
+ print("Fizz")
+ case (false, true):
+ print("Buzz")
+ case (true, true):
+ print("Fizz Buzz")
+ }
}
-
- print(result)
- }
-}
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/Fizz Buzz/README.markdown b/Fizz Buzz/README.markdown
index 8c250da27..be516bd46 100644
--- a/Fizz Buzz/README.markdown
+++ b/Fizz Buzz/README.markdown
@@ -16,46 +16,48 @@ The modulus operator `%` is the key to solving fizz buzz.
The modulus operator returns the remainder after an integer division. Here is an example of the modulus operator:
-| Division | Division Result | Modulus | Modulus Result |
-| ------------- | -------------------------- | --------------- | ---------------:|
-| 1 / 3 | 0 with a remainder of 3 | 1 % 3 | 1 |
-| 5 / 3 | 1 with a remainder of 2 | 5 % 3 | 2 |
-| 16 / 3 | 5 with a remainder of 1 | 16 % 3 | 1 |
+| Division | Division Result | Modulus | Modulus Result|
+| ----------- | --------------------- | ------------- | :-----------: |
+| 1 / 3 | 0 with a remainder of 3 | 1 % 3 | 1 |
+| 5 / 3 | 1 with a remainder of 2 | 5 % 3 | 2 |
+| 16 / 3 | 5 with a remainder of 1 | 16 % 3 | 1 |
A common approach to determine if a number is even or odd is to use the modulus operator:
-| Modulus | Result | Swift Code | Swift Code Result | Comment |
-| ------------- | ---------------:| ------------------------------- | -----------------:| --------------------------------------------- |
-| 6 % 2 | 0 | `let isEven = (number % 2 == 0)` | `true` | If a number is divisible by 2 it is *even* |
-| 5 % 2 | 1 | `let isOdd = (number % 2 != 0)` | `true` | If a number is not divisible by 2 it is *odd* |
+| Modulus | Result | Swift Code | Swift Code
Result | Comment |
+| -------- | :-----:| -------------------------------- | :----------------:| --------------------------------------------- |
+| 6 % 2 | 0 | `let isEven = (number % 2 == 0)` | `true` | If a number is divisible by 2 it is *even* |
+| 5 % 2 | 1 | `let isOdd = (number % 2 != 0)` | `true` | If a number is not divisible by 2 it is *odd* |
+
+Alternatively, Swift's built in function .isMultiple(of:) can be used, i.e. 6.isMultiple(of: 2) will return true, 5.isMultiple(of: 2) will return false
## Solving fizz buzz
-Now we can use the modulus operator `%` to solve fizz buzz.
+Now we can use the modulus operator `%` or .isMultiple(of:) method to solve fizz buzz.
Finding numbers divisible by three:
-| Modulus | Modulus Result | Swift Code | Swift Code Result |
-| ------- | --------------:| ------------- |------------------:|
-| 1 % 3 | 1 | `1 % 3 == 0` | `false` |
-| 2 % 3 | 2 | `2 % 3 == 0` | `false` |
-| 3 % 3 | 0 | `3 % 3 == 0` | `true` |
-| 4 % 3 | 1 | `4 % 3 == 0` | `false` |
+| Modulus | Modulus
Result | Swift Code
using Modulo | Swift Code
using .isMultiple(of:) | Swift Code
Result |
+| ------- | :---------------: | -------------------------- | ------------------------------------ | ------------------- |
+|1 % 3 | 1 | `1 % 3 == 0` | `1.isMultiple(of: 3)` | `false` |
+|2 % 3 | 2 | `2 % 3 == 0` | `2.isMultiple(of: 3)` | `false` |
+|3 % 3 | 0 | `3 % 3 == 0` | `3.isMultiple(of: 3)` | `true` |
+|4 % 3 | 1 | `4 % 3 == 0` | `4.isMultiple(of: 3)` | `false` |
Finding numbers divisible by five:
-| Modulus | Modulus Result | Swift Code | Swift Code Result |
-| ------- | --------------:| ------------- |------------------:|
-| 1 % 5 | 1 | `1 % 5 == 0` | `false` |
-| 2 % 5 | 2 | `2 % 5 == 0` | `false` |
-| 3 % 5 | 3 | `3 % 5 == 0` | `false` |
-| 4 % 5 | 4 | `4 % 5 == 0` | `false` |
-| 5 % 5 | 0 | `5 % 5 == 0` | `true` |
-| 6 % 5 | 1 | `6 % 5 == 0` | `false` |
+| Modulus | Modulus
Result | Swift Code
using Modulo | Swift Code
using .isMultiple(of:) | Swift Code
Result |
+| ------- | :---------------: | -------------------------- | ------------------------------------ | -------------------- |
+| 1 % 5 | 1 | `1 % 5 == 0` | `1.isMultiple(of: 5)` | `false` |
+| 2 % 5 | 2 | `2 % 5 == 0` | `2.isMultiple(of: 5)` | `false` |
+| 3 % 5 | 3 | `3 % 5 == 0` | `3.isMultiple(of: 5)` | `false` |
+| 4 % 5 | 4 | `4 % 5 == 0` | `4.isMultiple(of: 5)` | `false` |
+| 5 % 5 | 0 | `5 % 5 == 0` | `5.isMultiple(of: 5)` | `true` |
+| 6 % 5 | 1 | `6 % 5 == 0` | `6.isMultiple(of: 5)` | `false` |
## The code
-Here is a simple implementation in Swift:
+Here is a simple implementation in Swift using Modulus approach
```swift
func fizzBuzz(_ numberOfTurns: Int) {
@@ -79,7 +81,31 @@ func fizzBuzz(_ numberOfTurns: Int) {
}
```
-Put this code in a playground and test it like so:
+Here is simple implementation in Swift using .isMultiple(of:) and switch statement
+
+```swift
+func fizzBuzz(_ numberOfTurns: Int) {
+ guard numberOfTurns >= 1 else {
+ print("Number of turns must be >= 1")
+ return
+ }
+
+ for i in 1...numberOfTurns {
+ switch (i.isMultiple(of: 3), i.isMultiple(of: 5)) {
+ case (false, false):
+ print("\(i)")
+ case (true, false):
+ print("Fizz")
+ case (false, true):
+ print("Buzz")
+ case (true, true):
+ print("Fizz Buzz")
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Put either code in a playground and test it like so:
```swift
fizzBuzz(15)
@@ -87,10 +113,25 @@ fizzBuzz(15)
This will output:
- 1, 2, Fizz, 4, Buzz, Fizz, 7, 8, Fizz, Buzz, 11, Fizz, 13, 14, Fizz Buzz
+1
+2
+Fizz
+4
+Buzz
+Fizz
+7
+8
+Fizz
+Buzz
+11
+Fizz
+13
+14
+Fizz Buzz
## See also
[Fizz buzz on Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fizz_buzz)
-*Written by [Chris Pilcher](https://github.com/chris-pilcher)*
+*Originally written by [Chris Pilcher](https://github.com/chris-pilcher)*
+*Updated by [Lance Rettberg](https://github.com/l-rettberg)*
diff --git a/GCD/GCD.playground/Contents.swift b/GCD/GCD.playground/Contents.swift
index f0fceb0da..bb8d49055 100644
--- a/GCD/GCD.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/GCD/GCD.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,44 +1,21 @@
-//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
-// Recursive version
-func gcd(_ a: Int, _ b: Int) -> Int {
- let r = a % b
- if r != 0 {
- return gcd(b, r)
- } else {
- return b
- }
-}
-
-/*
-// Iterative version
-func gcd(m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
- var a = 0
- var b = max(m, n)
- var r = min(m, n)
-
- while r != 0 {
- a = b
- b = r
- r = a % b
- }
- return b
-}
-*/
-
-func lcm(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
- return m / gcd(m, n) * n // we divide before multiplying to avoid integer overflow
-}
-
gcd(52, 39) // 13
gcd(228, 36) // 12
gcd(51357, 3819) // 57
gcd(841, 299) // 1
-lcm(2, 3) // 6
-lcm(10, 8) // 40
+gcd(52, 39, using: gcdRecursiveEuklid) // 13
+gcd(228, 36, using: gcdRecursiveEuklid) // 12
+gcd(51357, 3819, using: gcdRecursiveEuklid) // 57
+gcd(841, 299, using: gcdRecursiveEuklid) // 1
+
+gcd(52, 39, using: gcdBinaryRecursiveStein) // 13
+gcd(228, 36, using: gcdBinaryRecursiveStein) // 12
+gcd(51357, 3819, using: gcdBinaryRecursiveStein) // 57
+gcd(841, 299, using: gcdBinaryRecursiveStein) // 1
+
+do {
+ try lcm(2, 3) // 6
+ try lcm(10, 8, using: gcdRecursiveEuklid) // 40
+} catch {
+ dump(error)
+}
diff --git a/GCD/GCD.playground/Sources/GCD.swift b/GCD/GCD.playground/Sources/GCD.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4eb0c7621
--- /dev/null
+++ b/GCD/GCD.playground/Sources/GCD.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+/*
+ Finds the largest positive integer that divides both
+ m and n without a remainder.
+
+ - Parameter m: First natural number
+ - Parameter n: Second natural number
+ - Parameter using: The used algorithm to calculate the gcd.
+ If nothing provided, the Iterative Euclidean
+ algorithm is used.
+ - Returns: The natural gcd of m and n.
+ */
+public func gcd(_ m: Int, _ n: Int, using gcdAlgorithm: (Int, Int) -> (Int) = gcdIterativeEuklid) -> Int {
+ return gcdAlgorithm(m, n)
+}
+
+/*
+ Iterative approach based on the Euclidean algorithm.
+ The Euclidean algorithm is based on the principle that the greatest
+ common divisor of two numbers does not change if the larger number
+ is replaced by its difference with the smaller number.
+ - Parameter m: First natural number
+ - Parameter n: Second natural number
+ - Returns: The natural gcd of m and n.
+ */
+public func gcdIterativeEuklid(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
+ var a: Int = 0
+ var b: Int = max(m, n)
+ var r: Int = min(m, n)
+
+ while r != 0 {
+ a = b
+ b = r
+ r = a % b
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+/*
+ Recursive approach based on the Euclidean algorithm.
+
+ - Parameter m: First natural number
+ - Parameter n: Second natural number
+ - Returns: The natural gcd of m and n.
+ - Note: The recursive version makes only tail recursive calls.
+ Most compilers for imperative languages do not optimize these.
+ The swift compiler as well as the obj-c compiler is able to do
+ optimizations for tail recursive calls, even though it still ends
+ up to be the same in terms of complexity. That said, tail call
+ elimination is not mutually exclusive to recursion.
+ */
+public func gcdRecursiveEuklid(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
+ let r: Int = m % n
+ if r != 0 {
+ return gcdRecursiveEuklid(n, r)
+ } else {
+ return n
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ The binary GCD algorithm, also known as Stein's algorithm,
+ is an algorithm that computes the greatest common divisor of two
+ nonnegative integers. Stein's algorithm uses simpler arithmetic
+ operations than the conventional Euclidean algorithm; it replaces
+ division with arithmetic shifts, comparisons, and subtraction.
+
+ - Parameter m: First natural number
+ - Parameter n: Second natural number
+ - Returns: The natural gcd of m and n
+ - Complexity: worst case O(n^2), where n is the number of bits
+ in the larger of the two numbers. Although each step reduces
+ at least one of the operands by at least a factor of 2,
+ the subtract and shift operations take linear time for very
+ large integers
+ */
+public func gcdBinaryRecursiveStein(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
+ if let easySolution = findEasySolution(m, n) { return easySolution }
+
+ if (m & 1) == 0 {
+ // m is even
+ if (n & 1) == 1 {
+ // and n is odd
+ return gcdBinaryRecursiveStein(m >> 1, n)
+ } else {
+ // both m and n are even
+ return gcdBinaryRecursiveStein(m >> 1, n >> 1) << 1
+ }
+ } else if (n & 1) == 0 {
+ // m is odd, n is even
+ return gcdBinaryRecursiveStein(m, n >> 1)
+ } else if (m > n) {
+ // reduce larger argument
+ return gcdBinaryRecursiveStein((m - n) >> 1, n)
+ } else {
+ // reduce larger argument
+ return gcdBinaryRecursiveStein((n - m) >> 1, m)
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ Finds an easy solution for the gcd.
+ - Parameter m: First natural number
+ - Parameter n: Second natural number
+ - Returns: A natural gcd of m and n if possible.
+ - Note: It might be relevant for different usecases to
+ try finding an easy solution for the GCD calculation
+ before even starting more difficult operations.
+ */
+func findEasySolution(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int? {
+ if m == n {
+ return m
+ }
+ if m == 0 {
+ return n
+ }
+ if n == 0 {
+ return m
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+
+public enum LCMError: Error {
+ case divisionByZero
+}
+
+/*
+ Calculates the lcm for two given numbers using a specified gcd algorithm.
+
+ - Parameter m: First natural number.
+ - Parameter n: Second natural number.
+ - Parameter using: The used gcd algorithm to calculate the lcm.
+ If nothing provided, the Iterative Euclidean
+ algorithm is used.
+ - Throws: Can throw a `divisionByZero` error if one of the given
+ attributes turns out to be zero or less.
+ - Returns: The least common multiplier of the two attributes as
+ an unsigned integer
+ */
+public func lcm(_ m: Int, _ n: Int, using gcdAlgorithm: (Int, Int) -> (Int) = gcdIterativeEuklid) throws -> Int {
+ guard m & n != 0 else { throw LCMError.divisionByZero }
+ return m / gcdAlgorithm(m, n) * n
+}
diff --git a/GCD/GCD.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/GCD/GCD.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/GCD/GCD.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/GCD/GCD.playground/timeline.xctimeline b/GCD/GCD.playground/timeline.xctimeline
deleted file mode 100644
index bf468afec..000000000
--- a/GCD/GCD.playground/timeline.xctimeline
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,6 +0,0 @@
-
-
-
-
-
diff --git a/GCD/GCD.swift b/GCD/GCD.swift
deleted file mode 100644
index bd903e58a..000000000
--- a/GCD/GCD.swift
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
-/*
- Euclid's algorithm for finding the greatest common divisor
-*/
-func gcd(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
- var a = 0
- var b = max(m, n)
- var r = min(m, n)
-
- while r != 0 {
- a = b
- b = r
- r = a % b
- }
- return b
-}
-
-/*
-// Recursive version
-func gcd(_ a: Int, _ b: Int) -> Int {
- let r = a % b
- if r != 0 {
- return gcd(b, r)
- } else {
- return b
- }
-}
-*/
-
-/*
- Returns the least common multiple of two numbers.
-*/
-func lcm(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
- return m / gcd(m, n) * n
-}
diff --git a/GCD/README.markdown b/GCD/README.markdown
index d7e9304bd..4c459eff0 100644
--- a/GCD/README.markdown
+++ b/GCD/README.markdown
@@ -1,14 +1,19 @@
# Greatest Common Divisor
-The *greatest common divisor* (or Greatest Common Factor) of two numbers `a` and `b` is the largest positive integer that divides both `a` and `b` without a remainder.
+The *greatest common divisor* (or Greatest Common Factor) of two numbers `a` and `b` is the largest positive integer that divides both `a` and `b` without a remainder. The GCD.swift file contains three different algorithms of how to calculate the greatest common divisor.
+For example, `gcd(39, 52) = 13` because 13 divides 39 (`39 / 13 = 3`) as well as 52 (`52 / 13 = 4`). But there is no larger number than 13 that divides them both.
+You've probably had to learn about this in school at some point. :-)
-For example, `gcd(39, 52) = 13` because 13 divides 39 (`39/13 = 3`) as well as 52 (`52/13 = 4`). But there is no larger number than 13 that divides them both.
+You probably won't need to use the GCD or LCM in any real-world problems, but it's cool to play around with this ancient algorithm. It was first described by Euklid in his [Elements](http://publicdomainreview.org/collections/the-first-six-books-of-the-elements-of-euclid-1847/) around 300 BC. Rumor has it that he discovered this algorithm while he was hacking on his Commodore 64.
-You've probably had to learn about this in school at some point. :-)
+## Different Algorithms
-The laborious way to find the GCD of two numbers is to first figure out the factors of both numbers, then take the greatest number they have in common. The problem is that factoring numbers is quite difficult, especially when they get larger. (On the plus side, that difficulty is also what keeps your online payments secure.)
+This example includes three different algorithms to find the same result.
+
+### Iterative Euklidean
-There is a smarter way to calculate the GCD: Euclid's algorithm. The big idea here is that,
+The laborious way to find the GCD of two numbers is to first figure out the factors of both numbers, then take the greatest number they have in common. The problem is that factoring numbers is quite difficult, especially when they get larger. (On the plus side, that difficulty is also what keeps your online payments secure.)
+There is a smarter way to calculate the GCD: Euklid's algorithm. The big idea here is that,
gcd(a, b) = gcd(b, a % b)
@@ -17,29 +22,58 @@ where `a % b` calculates the remainder of `a` divided by `b`.
Here is an implementation of this idea in Swift:
```swift
-func gcd(_ a: Int, _ b: Int) -> Int {
- let r = a % b
- if r != 0 {
- return gcd(b, r)
- } else {
+func gcdIterativeEuklid(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
+ var a: Int = 0
+ var b: Int = max(m, n)
+ var r: Int = min(m, n)
+
+ while r != 0 {
+ a = b
+ b = r
+ r = a % b
+ }
return b
- }
}
```
Put it in a playground and try it out with these examples:
```swift
-gcd(52, 39) // 13
-gcd(228, 36) // 12
-gcd(51357, 3819) // 57
+gcd(52, 39, using: gcdIterativeEuklid) // 13
+gcd(228, 36, using: gcdIterativeEuklid) // 12
+gcd(51357, 3819, using: gcdIterativeEuklid) // 57
+```
+
+### Recursive Euklidean
+
+Here is a slightly different implementation of Euklid's algorithm. Unlike the first version this doesn't use a `while` loop, but leverages recursion.
+
+```swift
+func gcdRecursiveEuklid(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
+ let r: Int = m % n
+ if r != 0 {
+ return gcdRecursiveEuklid(n, r)
+ } else {
+ return n
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Put it in a playground and compare it with the results of the iterative Eulidean gcd. They should return the same results:
+
+```swift
+gcd(52, 39, using: gcdRecursiveEuklid) // 13
+gcd(228, 36, using: gcdRecursiveEuklid) // 12
+gcd(51357, 3819, using: gcdRecursiveEuklid) // 57
```
-Let's step through the third example:
+The `max()` and `min()` at the top of the function make sure we always divide the larger number by the smaller one.
+
+Let's step through the third example using the *recursive Euklidean algorithm* here:
gcd(51357, 3819)
-According to Euclid's rule, this is equivalent to,
+According to Euklid's rule, this is equivalent to,
gcd(3819, 51357 % 3819) = gcd(3819, 1710)
@@ -47,17 +81,17 @@ because the remainder of `51357 % 3819` is `1710`. If you work out this division
So `gcd(51357, 3819)` is the same as `gcd(3819, 1710)`. That's useful because we can keep simplifying:
- gcd(3819, 1710) = gcd(1710, 3819 % 1710) =
- gcd(1710, 399) = gcd(399, 1710 % 399) =
- gcd(399, 114) = gcd(114, 399 % 114) =
- gcd(114, 57) = gcd(57, 114 % 57) =
+ gcd(3819, 1710) = gcd(1710, 3819 % 1710) =
+ gcd(1710, 399) = gcd(399, 1710 % 399) =
+ gcd(399, 114) = gcd(114, 399 % 114) =
+ gcd(114, 57) = gcd(57, 114 % 57) =
gcd(57, 0)
And now can't divide any further. The remainder of `114 / 57` is zero because `114 = 57 * 2` exactly. That means we've found the answer:
gcd(3819, 51357) = gcd(57, 0) = 57
-So in each step of Euclid's algorithm the numbers become smaller and at some point it ends when one of them becomes zero.
+So in each step of Euklid's algorithm the numbers become smaller and at some point it ends when one of them becomes zero.
By the way, it's also possible that two numbers have a GCD of 1. They are said to be *relatively prime*. This happens when there is no number that divides them both, for example:
@@ -65,44 +99,82 @@ By the way, it's also possible that two numbers have a GCD of 1. They are said t
gcd(841, 299) // 1
```
-Here is a slightly different implementation of Euclid's algorithm. Unlike the first version this doesn't use recursion but only a basic `while` loop.
+### Binary Recursive Stein
+
+The binary GCD algorithm, also known as Stein's algorithm, is an algorithm that computes the greatest common divisor of two nonnegative integers. Stein's algorithm is very similar to the recursive Eulidean algorithm, but uses arithmetical operations, which are simpler for computers to perform, than the conventional Euclidean algorithm does. It replaces division with arithmetic shifts, comparisons, and subtraction.
```swift
-func gcd(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
- var a = 0
- var b = max(m, n)
- var r = min(m, n)
-
- while r != 0 {
- a = b
- b = r
- r = a % b
- }
- return b
+func gcdBinaryRecursiveStein(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
+ if let easySolution = findEasySolution(m, n) { return easySolution }
+
+ if (m & 1) == 0 {
+ // m is even
+ if (n & 1) == 1 {
+ // and n is odd
+ return gcdBinaryRecursiveStein(m >> 1, n)
+ } else {
+ // both m and n are even
+ return gcdBinaryRecursiveStein(m >> 1, n >> 1) << 1
+ }
+ } else if (n & 1) == 0 {
+ // m is odd, n is even
+ return gcdBinaryRecursiveStein(m, n >> 1)
+ } else if (m > n) {
+ // reduce larger argument
+ return gcdBinaryRecursiveStein((m - n) >> 1, n)
+ } else {
+ // reduce larger argument
+ return gcdBinaryRecursiveStein((n - m) >> 1, m)
+ }
}
```
-The `max()` and `min()` at the top of the function make sure we always divide the larger number by the smaller one.
+Depending on your application and your input expectations, it might be reasonable to also search for an "easy solution" using the other gcd implementations:
-## Least Common Multiple
+```swift
+func findEasySolution(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int? {
+ if m == n {
+ return m
+ }
+ if m == 0 {
+ return n
+ }
+ if n == 0 {
+ return m
+ }
+ return nil
+}
-An idea related to the GCD is the *least common multiple* or LCM.
+```
-The least common multiple of two numbers `a` and `b` is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of both. In other words, the LCM is evenly divisible by `a` and `b`.
+Put it in a playground and compare it with the results of the other gcd implementations:
-For example: `lcm(2, 3) = 6` because 6 can be divided by 2 and also by 3.
+```swift
+gcd(52, 39, using: gcdBinaryRecursiveStein) // 13
+gcd(228, 36, using: gcdBinaryRecursiveStein) // 12
+gcd(51357, 3819, using: gcdBinaryRecursiveStein) // 57
+```
+
+### Least Common Multiple
+
+Another algorithm related to the GCD is the *least common multiple* or LCM.
+
+The least common multiple of two numbers `a` and `b` is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of both. In other words, the LCM is evenly divisible by `a` and `b`. The example implementation of the LCM takes two numbers and an optional specification which GCD algorithm is used.
-We can calculate the LCM using Euclid's algorithm too:
+For example: `lcm(2, 3, using: gcdRecursiveEuklid) = 6` , which tells us that 6 is the smallest number that can be devided by 2 as well as 3.
- a * b
- lcm(a, b) = ---------
- gcd(a, b)
+We can calculate the LCM using Euklid's algorithm too:
+
+a * b
+lcm(a, b) = ---------
+gcd(a, b)
In code:
```swift
-func lcm(_ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> Int {
- return m / gcd(m, n) * n
+func lcm(_ m: Int, _ n: Int, using gcdAlgorithm: (Int, Int) -> (Int) = gcdIterativeEuklid) throws -> Int {
+guard (m & n) != 0 else { throw LCMError.divisionByZero }
+return m / gcdAlgorithm(m, n) * n
}
```
@@ -112,6 +184,11 @@ And to try it out in a playground:
lcm(10, 8) // 40
```
-You probably won't need to use the GCD or LCM in any real-world problems, but it's cool to play around with this ancient algorithm. It was first described by Euclid in his [Elements](http://publicdomainreview.org/collections/the-first-six-books-of-the-elements-of-euclid-1847/) around 300 BC. Rumor has it that he discovered this algorithm while he was hacking on his Commodore 64.
+## Discussion
+
+While these algorithms all calculate the same result, comparing their plane complexity might not be enough to decide for one of them, though. The original iterative Euklidean algorithm is easier to understand. The recursive Euklidean and Stein's algorithm, while being generally faster, their runtime is heavily dependend on the environment they are running on.
+_If a fast calculation of the gcd is necessary, a runtime comparison for the specific platform and compiler optimization level should be done for the rekursive Euklidean and Stein's algorithm._
*Written for Swift Algorithm Club by Matthijs Hollemans*
+
+*Extended by Simon C. Krüger*
diff --git a/Genetic/README.markdown b/Genetic/README.markdown
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5dc4747f2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Genetic/README.markdown
@@ -0,0 +1,312 @@
+# Genetic Algorthim
+
+## What is it?
+
+A genetic algorithm (GA) is process inspired by natural selection to find high quality solutions. Most commonly used for optimization. GAs rely on the bio-inspired processes of natural selection, more specifically the process of selection (fitness), crossover and mutation. To understand more, let's walk through these processes in terms of biology:
+
+### Selection
+>**Selection**, in biology, the preferential survival and reproduction or preferential elimination of individuals with certain genotypes (genetic compositions), by means of natural or artificial controlling factors.
+
+In other words, survival of the fittest. Organisms that survive in their environment tend to reproduce more. With GAs we generate a fitness model that will rank individuals and give them a better chance for reproduction.
+
+### Crossover
+>**Chromosomal crossover** (or crossing over) is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes that results in recombinant chromosomes during sexual reproduction [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosomal_crossover)
+
+Simply reproduction. A generation will be a mixed representation of the previous generation, with offspring taking DNA from both parents. GAs do this by randomly, but weightily, mating offspring to create new generations.
+
+### Mutation
+>**Mutation**, an alteration in the genetic material (the genome) of a cell of a living organism or of a virus that is more or less permanent and that can be transmitted to the cell’s or the virus’s descendants. [Britannica](https://www.britannica.com/science/mutation-genetics)
+
+The randomization that allows for organisms to change over time. In GAs we build a randomization process that will mutate offspring in a population in order to introduce fitness variance.
+
+### Resources:
+* [Genetic Algorithms in Search Optimization, and Machine Learning](https://www.amazon.com/Genetic-Algorithms-Optimization-Machine-Learning/dp/0201157675/ref=sr_1_sc_1?ie=UTF8&qid=1520628364&sr=8-1-spell&keywords=Genetic+Algortithms+in+search)
+* [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_algorithm)
+* [My Original Gist](https://gist.github.com/blainerothrock/efda6e12fe10792c99c990f8ff3daeba)
+
+## The Code
+
+### Problem
+For this quick and dirty example, we are going to produce an optimized string using a simple genetic algorithm. More specifically we are trying to take a randomly generated origin string of a fixed length and evolve it into the most optimized string of our choosing.
+
+We will be creating a bio-inspired world where the absolute existence is the string `Hello, World!`. Nothing in this universe is better and it's our goal to get as close to it as possible to ensure survival.
+
+### Define the Universe
+
+Before we dive into the core processes we need to set up our "universe". First let's define a lexicon, a set of everything that exists in our universe.
+
+```swift
+let lex: [UInt8] = " !\"#$%&\'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~".asciiArray
+```
+
+To make things easier, we are actually going to work in [Unicode values](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Unicode_characters), so let's define a String extension to help with that.
+
+```swift
+extension String {
+ var unicodeArray: [UInt8] {
+ return [UInt8](self.utf8)
+ }
+}
+```
+
+ Now, let's define a few global variables for the universe:
+ * `OPTIMAL`: This is the end goal and what we will be using to rate fitness. In the real world this will not exist
+ * `DNA_SIZE`: The length of the string in our population. Organisms need to be similar
+ * `POP_SIZE`: Size of each generation
+ * `MAX_GENERATIONS`: Max number of generations, script will stop when it reach 5000 if the optimal value is not found
+ * `MUTATION_CHANCE`: The chance in which a random nucleotide can mutate (`1/MUTATION_CHANCE`)
+
+ ```swift
+let OPTIMAL:[UInt8] = "Hello, World".unicodeArray
+let DNA_SIZE = OPTIMAL.count
+let POP_SIZE = 50
+let GENERATIONS = 5000
+let MUTATION_CHANCE = 100
+ ```
+
+ ### Population Zero
+
+Before selecting, crossover and mutation, we need a population to start with. Now that we have the universe defined we can write that function:
+
+ ```swift
+ func randomPopulation(from lexicon: [UInt8], populationSize: Int, dnaSize: Int) -> [[UInt8]] {
+ guard lexicon.count > 1 else { return [] }
+ var pop = [[UInt8]]()
+
+ (0.. Int {
+ guard dna.count == optimal.count else { return -1 }
+ var fitness = 0
+ for index in dna.indices {
+ fitness += abs(Int(dna[index]) - Int(optimal[index]))
+ }
+ return fitness
+}
+```
+
+The above will produce a fitness value to an individual. The perfect solution, "Hello, World" will have a fitness of 0. "Gello, World" will have a fitness of 1 since it is one unicode value off from the optimal (`H->G`).
+
+This example is very simple, but it'll work for our example. In a real world problem, the optimal solution is unknown or impossible. [Here](https://iccl.inf.tu-dresden.de/w/images/b/b7/GA_for_TSP.pdf) is a paper about optimizing a solution for the famous [traveling salesman problem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Travelling_salesman_problem) using a GA. In this example the problem is unsolvable by modern computers, but you can rate a individual solution by distance traveled. The optimal fitness here is an impossible 0. The closer the solution is to 0, the better chance for survival. In our example we will reach our goal, a fitness of 0.
+
+The second part to selection is weighted choice, also called roulette wheel selection. This defines how individuals are selected for the reproduction process out of the current population. Just because you are the best choice for natural selection doesn't mean the environment will select you. The individual could fall off a cliff, get dysentery or be unable to reproduce.
+
+Let's take a second and ask why on this one. Why would you not always want to select the most fit from a population? It's hard to see from this simple example, but let's think about dog breeding, because breeders remove this process and hand select dogs for the next generation. As a result you get improved desired characteristics, but the individuals will also continue to carry genetic disorders that come along with those traits. A certain "branch" of evolution may beat out the current fittest solution at a later time. This may be ok depending on the problem, but to keep this educational we will go with the bio-inspired way.
+
+With all that, here is our weight choice function:
+
+func weightedChoice(items: [(dna: [UInt8], weight: Double)]) -> (dna: [UInt8], weight: Double) {
+
+ let total = items.reduce(0) { $0 + $1.weight }
+ var n = Double.random(in: 0..<(total * 1000000)) / 1000000.0
+
+ for item in items {
+ if n < item.weight {
+ return item
+ }
+ n = n - item.weight
+ }
+ return items[1]
+}
+
+
+The above function takes a list of individuals with their calculated fitness. Then selects one at random offset by their fitness value. The horrible 1,000,000 multiplication and division is to insure precision by calculating decimals. `Double.random` only uses integers so this is required to convert to a precise Double, it's not perfect, but enough for our example.
+
+## Mutation
+
+The all powerful mutation, the thing that introduces otherwise non existent fitness variance. It can either hurt of improve a individuals fitness but over time it will cause evolution towards more fit populations. Imagine if our initial random population was missing the charachter `H`, in that case we need to rely on mutation to introduce that character into the population in order to achieve the optimal solution.
+
+```swift
+func mutate(lexicon: [UInt8], dna: [UInt8], mutationChance: Int) -> [UInt8] {
+ var outputDna = dna
+ (0.. [UInt8] {
+ let pos = Int.random(in: 0..?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~".unicodeArray
+
+// This is the end goal and what we will be using to rate fitness. In the real world this will not exist
+let OPTIMAL:[UInt8] = "Hello, World".unicodeArray
+
+// The length of the string in our population. Organisms need to be similar
+let DNA_SIZE = OPTIMAL.count
+
+// Size of each generation
+let POP_SIZE = 50
+
+// Max number of generations, script will stop when it reaches 5000 if the optimal value is not found
+let GENERATIONS = 5000
+
+// The chance in which a random nucleotide can mutate (1/n)
+let MUTATION_CHANCE = 100
+
+func randomPopulation(from lexicon: [UInt8], populationSize: Int, dnaSize: Int) -> [[UInt8]] {
+ var pop = [[UInt8]]()
+
+ (0.. Int {
+ var fitness = 0
+ for index in dna.indices {
+ fitness += abs(Int(dna[index]) - Int(optimal[index]))
+ }
+ return fitness
+}
+
+func weightedChoice(items: [(dna: [UInt8], weight: Double)]) -> (dna: [UInt8], weight: Double) {
+
+ let total = items.reduce(0) { $0 + $1.weight }
+ var n = Double.random(in: 0..<(total * 1000000)) / 1000000.0
+
+ for item in items {
+ if n < item.weight {
+ return item
+ }
+ n = n - item.weight
+ }
+ return items[1]
+}
+
+func mutate(lexicon: [UInt8], dna: [UInt8], mutationChance: Int) -> [UInt8] {
+ var outputDna = dna
+ (0.. [UInt8] {
+ let pos = Int.random(in: 0..
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/Genetic/gen.swift b/Genetic/gen.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a61e61785
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Genetic/gen.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
+//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
+
+import Foundation
+
+extension String {
+ var unicodeArray: [UInt8] {
+ return [UInt8](self.utf8)
+ }
+}
+
+
+let lex: [UInt8] = " !\"#$%&\'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[\\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~".unicodeArray
+
+// This is the end goal and what we will be using to rate fitness. In the real world this will not exist
+let OPTIMAL:[UInt8] = "Hello, World".unicodeArray
+
+// The length of the string in our population. Organisms need to be similar
+let DNA_SIZE = OPTIMAL.count
+
+// size of each generation
+let POP_SIZE = 50
+
+// max number of generations, script will stop when it reach 5000 if the optimal value is not found
+let MAX_GENERATIONS = 5000
+
+// The chance in which a random nucleotide can mutate (1/n)
+let MUTATION_CHANCE = 100
+
+func randomChar(from lexicon: [UInt8]) -> UInt8 {
+ let len = UInt32(lexicon.count-1)
+ let rand = Int(arc4random_uniform(len))
+ return lexicon[rand]
+}
+
+func randomPopulation(from lexicon: [UInt8], populationSize: Int, dnaSize: Int) -> [[UInt8]] {
+
+ var pop = [[UInt8]]()
+
+ (0.. Int {
+ var fitness = 0
+ (0...dna.count-1).forEach { c in
+ fitness += abs(Int(dna[c]) - Int(optimal[c]))
+ }
+ return fitness
+}
+
+func weightedChoice(items:[(dna:[UInt8], weight:Double)]) -> (dna:[UInt8], weight:Double) {
+
+ let total = items.reduce(0.0) { return $0 + $1.weight}
+
+ var n = Double(arc4random_uniform(UInt32(total * 1000000.0))) / 1000000.0
+
+ for item in items {
+ if n < item.weight {
+ return item
+ }
+ n = n - item.weight
+ }
+ return items[1]
+}
+
+func mutate(lexicon: [UInt8], dna:[UInt8], mutationChance:Int) -> [UInt8] {
+ var outputDna = dna
+
+ (0.. [UInt8] {
+ let pos = Int(arc4random_uniform(UInt32(dnaSize-1)))
+
+ let dna1Index1 = dna1.index(dna1.startIndex, offsetBy: pos)
+ let dna2Index1 = dna2.index(dna2.startIndex, offsetBy: pos)
+
+ return [UInt8](dna1.prefix(upTo: dna1Index1) + dna2.suffix(from: dna2Index1))
+}
+
+func main() {
+
+ // generate the starting random population
+ var population:[[UInt8]] = randomPopulation(from: lex, populationSize: POP_SIZE, dnaSize: DNA_SIZE)
+ // print("population: \(population), dnaSize: \(DNA_SIZE) ")
+ var fittest = [UInt8]()
+
+ for generation in 0...MAX_GENERATIONS {
+
+ var weightedPopulation = [(dna:[UInt8], weight:Double)]()
+
+ // calulcated the fitness of each individual in the population
+ // and add it to the weight population (weighted = 1.0/fitness)
+ for individual in population {
+ let fitnessValue = calculateFitness(dna: individual, optimal: OPTIMAL)
+
+ let pair = ( individual, fitnessValue == 0 ? 1.0 : Double(100/POP_SIZE)/Double( fitnessValue ) )
+
+ weightedPopulation.append(pair)
+ }
+
+ population = []
+
+ // create a new generation using the individuals in the origional population
+ (0...POP_SIZE).forEach { _ in
+ let ind1 = weightedChoice(items: weightedPopulation)
+ let ind2 = weightedChoice(items: weightedPopulation)
+
+ let offspring = crossover(dna1: ind1.dna, dna2: ind2.dna, dnaSize: DNA_SIZE)
+
+ // append to the population and mutate
+ population.append(mutate(lexicon: lex, dna: offspring, mutationChance: MUTATION_CHANCE))
+ }
+
+ fittest = population[0]
+ var minFitness = calculateFitness(dna: fittest, optimal: OPTIMAL)
+
+ // parse the population for the fittest string
+ population.forEach { indv in
+ let indvFitness = calculateFitness(dna: indv, optimal: OPTIMAL)
+ if indvFitness < minFitness {
+ fittest = indv
+ minFitness = indvFitness
+ }
+ }
+ if minFitness == 0 { break; }
+ print("\(generation): \(String(bytes: fittest, encoding: .utf8)!)")
+
+ }
+ print("fittest string: \(String(bytes: fittest, encoding: .utf8)!)")
+}
+
+main()
diff --git a/Graph/Graph.playground/Contents.swift b/Graph/Graph.playground/Contents.swift
index 0410942f8..fde396e64 100644
--- a/Graph/Graph.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Graph/Graph.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,11 +1,5 @@
import Graph
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
-
for graph in [AdjacencyMatrixGraph(), AdjacencyListGraph()] {
let v1 = graph.createVertex(1)
diff --git a/Graph/Graph.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Graph/Graph.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Graph/Graph.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Graph/Graph.playground/timeline.xctimeline b/Graph/Graph.playground/timeline.xctimeline
index 6afe06b6f..59717856a 100644
--- a/Graph/Graph.playground/timeline.xctimeline
+++ b/Graph/Graph.playground/timeline.xctimeline
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
version = "3.0">
diff --git a/Graph/Graph.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Graph/Graph.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index 17a5a7d6b..790f6ac18 100644
--- a/Graph/Graph.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Graph/Graph.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -158,7 +158,7 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0730;
- LastUpgradeCheck = 0900;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1000;
ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Swift Algorithm Club";
TargetAttributes = {
49BFA2FC1CDF886B00522D66 = {
@@ -251,12 +251,14 @@
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
@@ -289,7 +291,7 @@
ONLY_ACTIVE_ARCH = YES;
SDKROOT = macosx;
SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Onone";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
VERSIONING_SYSTEM = "apple-generic";
VERSION_INFO_PREFIX = "";
};
@@ -308,12 +310,14 @@
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
@@ -339,7 +343,7 @@
MTL_ENABLE_DEBUG_INFO = NO;
SDKROOT = macosx;
SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Owholemodule";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
VERSIONING_SYSTEM = "apple-generic";
VERSION_INFO_PREFIX = "";
};
@@ -364,7 +368,7 @@
SKIP_INSTALL = YES;
SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Onone";
SWIFT_SWIFT3_OBJC_INFERENCE = Off;
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -386,7 +390,7 @@
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
SKIP_INSTALL = YES;
SWIFT_SWIFT3_OBJC_INFERENCE = Off;
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/Graph/Graph.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Graph.xcscheme b/Graph/Graph.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Graph.xcscheme
index a12d85dad..84c688e66 100644
--- a/Graph/Graph.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Graph.xcscheme
+++ b/Graph/Graph.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Graph.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Graph/Graph/Edge.swift b/Graph/Graph/Edge.swift
index ac5ed6a25..9ddd4e23d 100644
--- a/Graph/Graph/Edge.swift
+++ b/Graph/Graph/Edge.swift
@@ -29,13 +29,14 @@ extension Edge: CustomStringConvertible {
extension Edge: Hashable {
- public var hashValue: Int {
- var string = "\(from.description)\(to.description)"
+ public func hash(into hasher: inout Hasher) {
+ hasher.combine(from)
+ hasher.combine(to)
if weight != nil {
- string.append("\(weight!)")
+ hasher.combine(weight)
}
- return string.hashValue
}
+
}
public func == (lhs: Edge, rhs: Edge) -> Bool {
diff --git a/Graph/Graph/Vertex.swift b/Graph/Graph/Vertex.swift
index 758a367bb..f74b38396 100644
--- a/Graph/Graph/Vertex.swift
+++ b/Graph/Graph/Vertex.swift
@@ -24,9 +24,16 @@ extension Vertex: CustomStringConvertible {
extension Vertex: Hashable {
- public var hashValue: Int {
- return "\(data)\(index)".hashValue
- }
+
+
+
+ public func hasher(into hasher: inout Hasher){
+
+ hasher.combine(data)
+ hasher.combine(index)
+ }
+
+
}
diff --git a/Graph/GraphTests/GraphTests.swift b/Graph/GraphTests/GraphTests.swift
index 92a4ce828..289d9aa64 100644
--- a/Graph/GraphTests/GraphTests.swift
+++ b/Graph/GraphTests/GraphTests.swift
@@ -10,13 +10,6 @@ import XCTest
class GraphTests: XCTestCase {
- func testSwift4() {
- // last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
- #if swift(>=4.0)
- print("Hello, Swift 4!")
- #endif
- }
-
func testAdjacencyMatrixGraphDescription() {
let graph = AdjacencyMatrixGraph()
diff --git a/Hash Set/HashSet.playground/Contents.swift b/Hash Set/HashSet.playground/Contents.swift
index 5edb76bb4..551c6dc86 100644
--- a/Hash Set/HashSet.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Hash Set/HashSet.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,8 +1,4 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
var set = HashSet()
diff --git a/Hash Set/HashSet.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Hash Set/HashSet.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Hash Set/HashSet.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Hash Table/HashTable.playground/Contents.swift b/Hash Table/HashTable.playground/Contents.swift
index 273113440..121fb6032 100644
--- a/Hash Table/HashTable.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Hash Table/HashTable.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,8 +1,5 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
// Playing with hash values
"firstName".hashValue
diff --git a/Hash Table/HashTable.playground/Sources/HashTable.swift b/Hash Table/HashTable.playground/Sources/HashTable.swift
index 2383b8192..f2a1be040 100644
--- a/Hash Table/HashTable.playground/Sources/HashTable.swift
+++ b/Hash Table/HashTable.playground/Sources/HashTable.swift
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@
Insert: O(1) O(n)
Delete: O(1) O(n)
*/
-public struct HashTable: CustomStringConvertible {
+public struct HashTable {
private typealias Element = (key: Key, value: Value)
private typealias Bucket = [Element]
private var buckets: [Bucket]
@@ -41,23 +41,6 @@ public struct HashTable: CustomStringConvertible {
/// A Boolean value that indicates whether the hash table is empty.
public var isEmpty: Bool { return count == 0 }
- /// A string that represents the contents of the hash table.
- public var description: String {
- let pairs = buckets.flatMap { b in b.map { e in "\(e.key) = \(e.value)" } }
- return pairs.joined(separator: ", ")
- }
-
- /// A string that represents the contents of
- /// the hash table, suitable for debugging.
- public var debugDescription: String {
- var str = ""
- for (i, bucket) in buckets.enumerated() {
- let pairs = bucket.map { e in "\(e.key) = \(e.value)" }
- str += "bucket \(i): " + pairs.joined(separator: ", ") + "\n"
- }
- return str
- }
-
/**
Create a hash table with the given capacity.
*/
@@ -148,6 +131,25 @@ public struct HashTable: CustomStringConvertible {
Returns the given key's array index.
*/
private func index(forKey key: Key) -> Int {
- return abs(key.hashValue) % buckets.count
+ return abs(key.hashValue % buckets.count)
+ }
+}
+
+extension HashTable: CustomStringConvertible {
+ /// A string that represents the contents of the hash table.
+ public var description: String {
+ let pairs = buckets.flatMap { b in b.map { e in "\(e.key) = \(e.value)" } }
+ return pairs.joined(separator: ", ")
+ }
+
+ /// A string that represents the contents of
+ /// the hash table, suitable for debugging.
+ public var debugDescription: String {
+ var str = ""
+ for (i, bucket) in buckets.enumerated() {
+ let pairs = bucket.map { e in "\(e.key) = \(e.value)" }
+ str += "bucket \(i): " + pairs.joined(separator: ", ") + "\n"
+ }
+ return str
}
}
diff --git a/Hash Table/HashTable.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Hash Table/HashTable.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Hash Table/HashTable.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Hash Table/README.markdown b/Hash Table/README.markdown
index 9c4065a51..fb0bda788 100644
--- a/Hash Table/README.markdown
+++ b/Hash Table/README.markdown
@@ -141,7 +141,7 @@ The hash table does not do anything yet, so let's add the remaining functionalit
```swift
private func index(forKey key: Key) -> Int {
- return abs(key.hashValue) % buckets.count
+ return abs(key.hashValue % buckets.count)
}
```
diff --git a/Hashed Heap/HashedHeap.swift b/Hashed Heap/HashedHeap.swift
index be7d9ab78..106cdacb0 100644
--- a/Hashed Heap/HashedHeap.swift
+++ b/Hashed Heap/HashedHeap.swift
@@ -57,7 +57,12 @@ public struct HashedHeap {
public var count: Int {
return elements.count
}
-
+
+ /// Accesses an element by its index.
+ public subscript(index: Int) -> T {
+ return elements[index]
+ }
+
/// Returns the index of the given element.
///
/// This is the operation that a hashed heap optimizes in compassion with a normal heap. In a normal heap this
@@ -141,6 +146,12 @@ public struct HashedHeap {
}
return removeLast()
}
+
+ /// Removes all elements from the heap.
+ public mutating func removeAll() {
+ elements.removeAll()
+ indices.removeAll()
+ }
/// Removes the last element from the heap.
///
diff --git a/HaversineDistance/HaversineDistance.playground/Contents.swift b/HaversineDistance/HaversineDistance.playground/Contents.swift
index 5b3f591d6..ed89b4462 100644
--- a/HaversineDistance/HaversineDistance.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/HaversineDistance/HaversineDistance.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,10 +1,6 @@
import UIKit
-// last checked with Xcode 9.04
-#if swift(>=4)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-func haversineDinstance(la1: Double, lo1: Double, la2: Double, lo2: Double, radius: Double = 6367444.7) -> Double {
+func haversineDistance(la1: Double, lo1: Double, la2: Double, lo2: Double, radius: Double = 6367444.7) -> Double {
let haversin = { (angle: Double) -> Double in
return (1 - cos(angle))/2
@@ -16,7 +12,7 @@ func haversineDinstance(la1: Double, lo1: Double, la2: Double, lo2: Double, radi
// Converts from degrees to radians
let dToR = { (angle: Double) -> Double in
- return (angle / 360) * 2 * M_PI
+ return (angle / 360) * 2 * .pi
}
let lat1 = dToR(la1)
@@ -31,4 +27,4 @@ let amsterdam = (52.3702, 4.8952)
let newYork = (40.7128, -74.0059)
// Google says it's 5857 km so our result is only off by 2km which could be due to all kinds of things, not sure how google calculates the distance or which latitude and longitude google uses to calculate the distance.
-haversineDinstance(la1: amsterdam.0, lo1: amsterdam.1, la2: newYork.0, lo2: newYork.1)
+haversineDistance(la1: amsterdam.0, lo1: amsterdam.1, la2: newYork.0, lo2: newYork.1)
diff --git a/Heap Sort/HeapSort.swift b/Heap Sort/HeapSort.swift
index 6b5e91dc5..0354817a6 100644
--- a/Heap Sort/HeapSort.swift
+++ b/Heap Sort/HeapSort.swift
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
extension Heap {
public mutating func sort() -> [T] {
- for i in stride(from: (elements.count - 1), through: 1, by: -1) {
- elements.swapAt(0, i)
- shiftDown(0, heapSize: i)
+ for i in stride(from: (nodes.count - 1), through: 1, by: -1) {
+ nodes.swapAt(0, i)
+ shiftDown(from: 0, until: i)
}
- return elements
+ return nodes
}
}
diff --git a/Heap Sort/README.markdown b/Heap Sort/README.markdown
index a45dad6f9..5bec58626 100644
--- a/Heap Sort/README.markdown
+++ b/Heap Sort/README.markdown
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ As you can see, the largest items are making their way to the back. We repeat th
> **Note:** This process is very similar to [selection sort](../Selection%20Sort/), which repeatedly looks for the minimum item in the remainder of the array. Extracting the minimum or maximum value is what heaps are good at.
-Performance of heap sort is **O(n lg n)** in best, worst, and average case. Because we modify the array directly, heap sort can be performed in-place. But it is not a stable sort: the relative order of identical elements is not preserved.
+Performance of heap sort is **O(n log n)** in best, worst, and average case. Because we modify the array directly, heap sort can be performed in-place. But it is not a stable sort: the relative order of identical elements is not preserved.
Here's how you can implement heap sort in Swift:
diff --git a/Heap Sort/Tests/HeapSortTests.swift b/Heap Sort/Tests/HeapSortTests.swift
index b36f605e3..dae1f8a68 100644
--- a/Heap Sort/Tests/HeapSortTests.swift
+++ b/Heap Sort/Tests/HeapSortTests.swift
@@ -1,12 +1,6 @@
import XCTest
class HeapSortTests: XCTestCase {
- func testSwift4() {
- // last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
- #if swift(>=4.0)
- print("Hello, Swift 4!")
- #endif
- }
func testSort() {
var h1 = Heap(array: [5, 13, 2, 25, 7, 17, 20, 8, 4], sort: >)
diff --git a/Heap Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Heap Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index ff1f4937f..62e6d4e3f 100644
--- a/Heap Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Heap Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
archiveVersion = 1;
classes = {
};
- objectVersion = 46;
+ objectVersion = 51;
objects = {
/* Begin PBXBuildFile section */
@@ -86,17 +86,17 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0720;
- LastUpgradeCheck = 0900;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1010;
ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Swift Algorithm Club";
TargetAttributes = {
7B2BBC7F1C779D720067B71D = {
CreatedOnToolsVersion = 7.2;
- LastSwiftMigration = 0820;
+ LastSwiftMigration = 1010;
};
};
};
buildConfigurationList = 7B2BBC6C1C779D710067B71D /* Build configuration list for PBXProject "Tests" */;
- compatibilityVersion = "Xcode 3.2";
+ compatibilityVersion = "Xcode 10.0";
developmentRegion = English;
hasScannedForEncodings = 0;
knownRegions = (
@@ -149,12 +149,14 @@
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
@@ -201,12 +203,14 @@
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
@@ -230,7 +234,8 @@
MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET = 10.11;
MTL_ENABLE_DEBUG_INFO = NO;
SDKROOT = macosx;
- SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Owholemodule";
+ SWIFT_COMPILATION_MODE = wholemodule;
+ SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-O";
};
name = Release;
};
@@ -239,10 +244,14 @@
buildSettings = {
COMBINE_HIDPI_IMAGES = YES;
INFOPLIST_FILE = Info.plist;
- LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
+ LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = (
+ "$(inherited)",
+ "@executable_path/../Frameworks",
+ "@loader_path/../Frameworks",
+ );
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -251,10 +260,14 @@
buildSettings = {
COMBINE_HIDPI_IMAGES = YES;
INFOPLIST_FILE = Info.plist;
- LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
+ LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = (
+ "$(inherited)",
+ "@executable_path/../Frameworks",
+ "@loader_path/../Frameworks",
+ );
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/Heap Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Heap Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Heap Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Heap Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/Heap Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
index 538a6f4fa..1608804f9 100644
--- a/Heap Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/Heap Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
{
+
/** The array that stores the heap's nodes. */
- var elements = [T]()
+ var nodes = [T]()
- /** Determines whether this is a max-heap (>) or min-heap (<). */
- fileprivate var isOrderedBefore: (T, T) -> Bool
+ /**
+ * Determines how to compare two nodes in the heap.
+ * Use '>' for a max-heap or '<' for a min-heap,
+ * or provide a comparing method if the heap is made
+ * of custom elements, for example tuples.
+ */
+ private var orderCriteria: (T, T) -> Bool
/**
* Creates an empty heap.
* The sort function determines whether this is a min-heap or max-heap.
- * For integers, > makes a max-heap, < makes a min-heap.
+ * For comparable data types, > makes a max-heap, < makes a min-heap.
*/
public init(sort: @escaping (T, T) -> Bool) {
- self.isOrderedBefore = sort
+ self.orderCriteria = sort
}
/**
* Creates a heap from an array. The order of the array does not matter;
* the elements are inserted into the heap in the order determined by the
- * sort function.
+ * sort function. For comparable data types, '>' makes a max-heap,
+ * '<' makes a min-heap.
*/
public init(array: [T], sort: @escaping (T, T) -> Bool) {
- self.isOrderedBefore = sort
- buildHeap(fromArray: array)
- }
-
- /*
- // This version has O(n log n) performance.
- private mutating func buildHeap(array: [T]) {
- elements.reserveCapacity(array.count)
- for value in array {
- insert(value)
- }
- }
- */
+ self.orderCriteria = sort
+ configureHeap(from: array)
+ }
/**
- * Converts an array to a max-heap or min-heap in a bottom-up manner.
+ * Configures the max-heap or min-heap from an array, in a bottom-up manner.
* Performance: This runs pretty much in O(n).
*/
- fileprivate mutating func buildHeap(fromArray array: [T]) {
- elements = array
- for i in stride(from: (elements.count/2 - 1), through: 0, by: -1) {
- shiftDown(i, heapSize: elements.count)
+ private mutating func configureHeap(from array: [T]) {
+ nodes = array
+ for i in stride(from: (nodes.count/2-1), through: 0, by: -1) {
+ shiftDown(i)
}
}
public var isEmpty: Bool {
- return elements.isEmpty
+ return nodes.isEmpty
}
public var count: Int {
- return elements.count
+ return nodes.count
}
/**
* Returns the index of the parent of the element at index i.
* The element at index 0 is the root of the tree and has no parent.
*/
- @inline(__always) func parentIndex(ofIndex i: Int) -> Int {
+ @inline(__always) internal func parentIndex(ofIndex i: Int) -> Int {
return (i - 1) / 2
}
@@ -71,7 +68,7 @@ public struct Heap {
* Note that this index can be greater than the heap size, in which case
* there is no left child.
*/
- @inline(__always) func leftChildIndex(ofIndex i: Int) -> Int {
+ @inline(__always) internal func leftChildIndex(ofIndex i: Int) -> Int {
return 2*i + 1
}
@@ -80,7 +77,7 @@ public struct Heap {
* Note that this index can be greater than the heap size, in which case
* there is no right child.
*/
- @inline(__always) func rightChildIndex(ofIndex i: Int) -> Int {
+ @inline(__always) internal func rightChildIndex(ofIndex i: Int) -> Int {
return 2*i + 2
}
@@ -89,7 +86,7 @@ public struct Heap {
* value (for a min-heap).
*/
public func peek() -> T? {
- return elements.first
+ return nodes.first
}
/**
@@ -97,10 +94,14 @@ public struct Heap {
* or min-heap property still holds. Performance: O(log n).
*/
public mutating func insert(_ value: T) {
- elements.append(value)
- shiftUp(elements.count - 1)
+ nodes.append(value)
+ shiftUp(nodes.count - 1)
}
+ /**
+ * Adds a sequence of values to the heap. This reorders the heap so that
+ * the max-heap or min-heap property still holds. Performance: O(log n).
+ */
public mutating func insert(_ sequence: S) where S.Iterator.Element == T {
for value in sequence {
insert(value)
@@ -108,15 +109,14 @@ public struct Heap {
}
/**
- * Allows you to change an element. In a max-heap, the new element should be
- * larger than the old one; in a min-heap it should be smaller.
+ * Allows you to change an element. This reorders the heap so that
+ * the max-heap or min-heap property still holds.
*/
public mutating func replace(index i: Int, value: T) {
- guard i < elements.count else { return }
+ guard i < nodes.count else { return }
- assert(isOrderedBefore(value, elements[i]))
- elements[i] = value
- shiftUp(i)
+ remove(at: i)
+ insert(value)
}
/**
@@ -124,104 +124,100 @@ public struct Heap {
* value; for a min-heap it is the minimum value. Performance: O(log n).
*/
@discardableResult public mutating func remove() -> T? {
- if elements.isEmpty {
- return nil
- } else if elements.count == 1 {
- return elements.removeLast()
+ guard !nodes.isEmpty else { return nil }
+
+ if nodes.count == 1 {
+ return nodes.removeLast()
} else {
// Use the last node to replace the first one, then fix the heap by
// shifting this new first node into its proper position.
- let value = elements[0]
- elements[0] = elements.removeLast()
- shiftDown()
+ let value = nodes[0]
+ nodes[0] = nodes.removeLast()
+ shiftDown(0)
return value
}
}
/**
- * Removes an arbitrary node from the heap. Performance: O(log n). You need
- * to know the node's index, which may actually take O(n) steps to find.
+ * Removes an arbitrary node from the heap. Performance: O(log n).
+ * Note that you need to know the node's index.
*/
- public mutating func removeAt(_ index: Int) -> T? {
- guard index < elements.count else { return nil }
+ @discardableResult public mutating func remove(at index: Int) -> T? {
+ guard index < nodes.count else { return nil }
- let size = elements.count - 1
+ let size = nodes.count - 1
if index != size {
- elements.swapAt(index, size)
- shiftDown(index, heapSize: size)
+ nodes.swapAt(index, size)
+ shiftDown(from: index, until: size)
shiftUp(index)
}
- return elements.removeLast()
+ return nodes.removeLast()
}
/**
* Takes a child node and looks at its parents; if a parent is not larger
* (max-heap) or not smaller (min-heap) than the child, we exchange them.
*/
- mutating func shiftUp(_ index: Int) {
+ internal mutating func shiftUp(_ index: Int) {
var childIndex = index
- let child = elements[childIndex]
+ let child = nodes[childIndex]
var parentIndex = self.parentIndex(ofIndex: childIndex)
- while childIndex > 0 && isOrderedBefore(child, elements[parentIndex]) {
- elements[childIndex] = elements[parentIndex]
+ while childIndex > 0 && orderCriteria(child, nodes[parentIndex]) {
+ nodes[childIndex] = nodes[parentIndex]
childIndex = parentIndex
parentIndex = self.parentIndex(ofIndex: childIndex)
}
- elements[childIndex] = child
- }
-
- mutating func shiftDown() {
- shiftDown(0, heapSize: elements.count)
+ nodes[childIndex] = child
}
/**
* Looks at a parent node and makes sure it is still larger (max-heap) or
* smaller (min-heap) than its childeren.
*/
- mutating func shiftDown(_ index: Int, heapSize: Int) {
- var parentIndex = index
+ internal mutating func shiftDown(from index: Int, until endIndex: Int) {
+ let leftChildIndex = self.leftChildIndex(ofIndex: index)
+ let rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1
- while true {
- let leftChildIndex = self.leftChildIndex(ofIndex: parentIndex)
- let rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1
-
- // Figure out which comes first if we order them by the sort function:
- // the parent, the left child, or the right child. If the parent comes
- // first, we're done. If not, that element is out-of-place and we make
- // it "float down" the tree until the heap property is restored.
- var first = parentIndex
- if leftChildIndex < heapSize && isOrderedBefore(elements[leftChildIndex], elements[first]) {
- first = leftChildIndex
- }
- if rightChildIndex < heapSize && isOrderedBefore(elements[rightChildIndex], elements[first]) {
- first = rightChildIndex
- }
- if first == parentIndex { return }
-
- elements.swapAt(parentIndex, first)
- parentIndex = first
+ // Figure out which comes first if we order them by the sort function:
+ // the parent, the left child, or the right child. If the parent comes
+ // first, we're done. If not, that element is out-of-place and we make
+ // it "float down" the tree until the heap property is restored.
+ var first = index
+ if leftChildIndex < endIndex && orderCriteria(nodes[leftChildIndex], nodes[first]) {
+ first = leftChildIndex
}
+ if rightChildIndex < endIndex && orderCriteria(nodes[rightChildIndex], nodes[first]) {
+ first = rightChildIndex
+ }
+ if first == index { return }
+
+ nodes.swapAt(index, first)
+ shiftDown(from: first, until: endIndex)
}
+
+ internal mutating func shiftDown(_ index: Int) {
+ shiftDown(from: index, until: nodes.count)
+ }
+
}
// MARK: - Searching
extension Heap where T: Equatable {
- /**
- * Searches the heap for the given element. Performance: O(n).
- */
- public func index(of element: T) -> Int? {
- return index(of: element, 0)
+
+ /** Get the index of a node in the heap. Performance: O(n). */
+ public func index(of node: T) -> Int? {
+ return nodes.index(where: { $0 == node })
}
- fileprivate func index(of element: T, _ i: Int) -> Int? {
- if i >= count { return nil }
- if isOrderedBefore(element, elements[i]) { return nil }
- if element == elements[i] { return i }
- if let j = index(of: element, self.leftChildIndex(ofIndex: i)) { return j }
- if let j = index(of: element, self.rightChildIndex(ofIndex: i)) { return j }
+ /** Removes the first occurrence of a node from the heap. Performance: O(n). */
+ @discardableResult public mutating func remove(node: T) -> T? {
+ if let index = index(of: node) {
+ return remove(at: index)
+ }
return nil
}
+
}
diff --git a/Heap/README.markdown b/Heap/README.markdown
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 4344d9e7c..fee881129
--- a/Heap/README.markdown
+++ b/Heap/README.markdown
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ As a result of this heap property, a max-heap always stores its largest item at
## How does a heap compare to regular trees?
-A heap is not a replacement for a binary search tree, and there are similarities and differnces between them. Here are some main differences:
+A heap is not a replacement for a binary search tree, and there are similarities and differences between them. Here are some main differences:
**Order of the nodes.** In a [binary search tree (BST)](../Binary%20Search%20Tree/), the left child must be smaller than its parent, and the right child must be greater. This is not true for a heap. In a max-heap both children must be smaller than the parent, while in a min-heap they both must be greater.
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ A heap is not a replacement for a binary search tree, and there are similarities
**Balancing.** A binary search tree must be "balanced" so that most operations have **O(log n)** performance. You can either insert and delete your data in a random order or use something like an [AVL tree](../AVL%20Tree/) or [red-black tree](../Red-Black%20Tree/), but with heaps we don't actually need the entire tree to be sorted. We just want the heap property to be fulfilled, so balancing isn't an issue. Because of the way the heap is structured, heaps can guarantee **O(log n)** performance.
-**Searching.** Whereas searching is fast in a binary tree, it is slow in a heap. Searching isn't a top priority in a heap since the purpose of a heap is to put the largest (or smallest) node at the front and to allow relatively fast inserts and deletes.
+**Searching.** Whereas searching is fast in a binary tree, it is slow in a heap. Searching isn't a top priority in a heap since the purpose of a heap is to put the largest (or smallest) node at the front and to allow relatively fast inserts and deletes.
## The tree inside an array
@@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ array[parent(i)] >= array[i]
Verify that this heap property holds for the array from the example heap.
-As you can see, these equations allow us to find the parent or child index for any node without the need for pointers. It is complicated than just dereferencing a pointer, but that is the tradeoff: we save memory space but pay with extra computations. Fortunately, the computations are fast and only take **O(1)** time.
+As you can see, these equations allow us to find the parent or child index for any node without the need for pointers. It is more complicated than just dereferencing a pointer, but that is the tradeoff: we save memory space but pay with extra computations. Fortunately, the computations are fast and only take **O(1)** time.
It is important to understand this relationship between array index and position in the tree. Here is a larger heap which has 15 nodes divided over four levels:
@@ -148,7 +148,7 @@ There are two primitive operations necessary to make sure the heap is a valid ma
Shifting up or down is a recursive procedure that takes **O(log n)** time.
-Here are other operations that are built on primitive operations:
+Here are other operations that are built on primitive operations:
- `insert(value)`: Adds the new element to the end of the heap and then uses `shiftUp()` to fix the heap.
@@ -164,7 +164,7 @@ All of the above take time **O(log n)** because shifting up or down is expensive
- `buildHeap(array)`: Converts an (unsorted) array into a heap by repeatedly calling `insert()`. If you are smart about this, it can be done in **O(n)** time.
-- [Heap sort](../Heap%20Sort/). Since the heap is an array, we can use its unique properties to sort the array from low to high. Time: **O(n lg n).**
+- [Heap sort](../Heap%20Sort/). Since the heap is an array, we can use its unique properties to sort the array from low to high. Time: **O(n log n).**
The heap also has a `peek()` function that returns the maximum (max-heap) or minimum (min-heap) element, without removing it from the heap. Time: **O(1)**.
@@ -190,7 +190,7 @@ The `(16)` was added to the first available space on the last row.
Unfortunately, the heap property is no longer satisfied because `(2)` is above `(16)`, and we want higher numbers above lower numbers. (This is a max-heap.)
-To restore the heap property, we swap `(16)` and `(2)`.
+To restore the heap property, we swap `(16)` and `(2)`.

@@ -214,7 +214,7 @@ What happens to the empty spot at the top?

-When inserting, we put the new value at the end of the array. Here, we do the opposite: we take the last object we have, stick it up on top of the tree, and restore the heap property.
+When inserting, we put the new value at the end of the array. Here, we do the opposite: we take the last object we have, stick it up on top of the tree, and restore the heap property.

@@ -226,7 +226,7 @@ Keep shifting down until the node does not have any children or it is larger tha

-The time required for shifting all the way down is proportional to the height of the tree which takes **O(log n)** time.
+The time required for shifting all the way down is proportional to the height of the tree which takes **O(log n)** time.
> **Note:** `shiftUp()` and `shiftDown()` can only fix one out-of-place element at a time. If there are multiple elements in the wrong place, you need to call these functions once for each of those elements.
@@ -279,7 +279,7 @@ In code:
```swift
private mutating func buildHeap(fromArray array: [T]) {
elements = array
- for i in (elements.count/2 - 1).stride(through: 0, by: -1) {
+ for i in stride(from: (nodes.count/2-1), through: 0, by: -1) {
shiftDown(index: i, heapSize: elements.count)
}
}
diff --git a/Heap/Tests/HeapTests.swift b/Heap/Tests/HeapTests.swift
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 66be0931c..ecf143778
--- a/Heap/Tests/HeapTests.swift
+++ b/Heap/Tests/HeapTests.swift
@@ -7,21 +7,14 @@ import XCTest
class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
- func testSwift4() {
- // last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
- #if swift(>=4.0)
- print("Hello, Swift 4!")
- #endif
- }
-
fileprivate func verifyMaxHeap(_ h: Heap) -> Bool {
for i in 0.. 0 && h.elements[parent] < h.elements[i] { return false }
+ if left < h.count && h.nodes[i] < h.nodes[left] { return false }
+ if right < h.count && h.nodes[i] < h.nodes[right] { return false }
+ if i > 0 && h.nodes[parent] < h.nodes[i] { return false }
}
return true
}
@@ -31,9 +24,9 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
let left = h.leftChildIndex(ofIndex: i)
let right = h.rightChildIndex(ofIndex: i)
let parent = h.parentIndex(ofIndex: i)
- if left < h.count && h.elements[i] > h.elements[left] { return false }
- if right < h.count && h.elements[i] > h.elements[right] { return false }
- if i > 0 && h.elements[parent] > h.elements[i] { return false }
+ if left < h.count && h.nodes[i] > h.nodes[left] { return false }
+ if right < h.count && h.nodes[i] > h.nodes[right] { return false }
+ if i > 0 && h.nodes[parent] > h.nodes[i] { return false }
}
return true
}
@@ -90,7 +83,7 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
let h1 = Heap(array: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], sort: >)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h1))
XCTAssertFalse(verifyMinHeap(h1))
- XCTAssertEqual(h1.elements, [7, 5, 6, 4, 2, 1, 3])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h1.nodes, [7, 5, 6, 4, 2, 1, 3])
XCTAssertFalse(h1.isEmpty)
XCTAssertEqual(h1.count, 7)
XCTAssertEqual(h1.peek()!, 7)
@@ -98,7 +91,7 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
let h2 = Heap(array: [7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], sort: >)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h2))
XCTAssertFalse(verifyMinHeap(h2))
- XCTAssertEqual(h2.elements, [7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h2.nodes, [7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1])
XCTAssertFalse(h2.isEmpty)
XCTAssertEqual(h2.count, 7)
XCTAssertEqual(h2.peek()!, 7)
@@ -106,7 +99,7 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
let h3 = Heap(array: [4, 1, 3, 2, 16, 9, 10, 14, 8, 7], sort: >)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h3))
XCTAssertFalse(verifyMinHeap(h3))
- XCTAssertEqual(h3.elements, [16, 14, 10, 8, 7, 9, 3, 2, 4, 1])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h3.nodes, [16, 14, 10, 8, 7, 9, 3, 2, 4, 1])
XCTAssertFalse(h3.isEmpty)
XCTAssertEqual(h3.count, 10)
XCTAssertEqual(h3.peek()!, 16)
@@ -114,7 +107,7 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
let h4 = Heap(array: [27, 17, 3, 16, 13, 10, 1, 5, 7, 12, 4, 8, 9, 0], sort: >)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h4))
XCTAssertFalse(verifyMinHeap(h4))
- XCTAssertEqual(h4.elements, [27, 17, 10, 16, 13, 9, 1, 5, 7, 12, 4, 8, 3, 0])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h4.nodes, [27, 17, 10, 16, 13, 9, 1, 5, 7, 12, 4, 8, 3, 0])
XCTAssertFalse(h4.isEmpty)
XCTAssertEqual(h4.count, 14)
XCTAssertEqual(h4.peek()!, 27)
@@ -124,7 +117,7 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
let h1 = Heap(array: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], sort: <)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMinHeap(h1))
XCTAssertFalse(verifyMaxHeap(h1))
- XCTAssertEqual(h1.elements, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h1.nodes, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
XCTAssertFalse(h1.isEmpty)
XCTAssertEqual(h1.count, 7)
XCTAssertEqual(h1.peek()!, 1)
@@ -132,7 +125,7 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
let h2 = Heap(array: [7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], sort: <)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMinHeap(h2))
XCTAssertFalse(verifyMaxHeap(h2))
- XCTAssertEqual(h2.elements, [1, 3, 2, 4, 6, 7, 5])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h2.nodes, [1, 3, 2, 4, 6, 7, 5])
XCTAssertFalse(h2.isEmpty)
XCTAssertEqual(h2.count, 7)
XCTAssertEqual(h2.peek()!, 1)
@@ -140,7 +133,7 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
let h3 = Heap(array: [4, 1, 3, 2, 16, 9, 10, 14, 8, 7], sort: <)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMinHeap(h3))
XCTAssertFalse(verifyMaxHeap(h3))
- XCTAssertEqual(h3.elements, [1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, 10, 14, 8, 16])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h3.nodes, [1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, 10, 14, 8, 16])
XCTAssertFalse(h3.isEmpty)
XCTAssertEqual(h3.count, 10)
XCTAssertEqual(h3.peek()!, 1)
@@ -148,24 +141,24 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
let h4 = Heap(array: [27, 17, 3, 16, 13, 10, 1, 5, 7, 12, 4, 8, 9, 0], sort: <)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMinHeap(h4))
XCTAssertFalse(verifyMaxHeap(h4))
- XCTAssertEqual(h4.elements, [0, 4, 1, 5, 12, 8, 3, 16, 7, 17, 13, 10, 9, 27])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h4.nodes, [0, 4, 1, 5, 12, 8, 3, 16, 7, 17, 13, 10, 9, 27])
XCTAssertFalse(h4.isEmpty)
XCTAssertEqual(h4.count, 14)
XCTAssertEqual(h4.peek()!, 0)
}
- func testCreateMaxHeapEqualElements() {
+ func testCreateMaxHeapEqualnodes() {
let heap = Heap(array: [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], sort: >)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(heap))
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMinHeap(heap))
- XCTAssertEqual(heap.elements, [1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
+ XCTAssertEqual(heap.nodes, [1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
}
- func testCreateMinHeapEqualElements() {
+ func testCreateMinHeapEqualnodes() {
let heap = Heap(array: [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], sort: <)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMinHeap(heap))
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(heap))
- XCTAssertEqual(heap.elements, [1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
+ XCTAssertEqual(heap.nodes, [1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
}
fileprivate func randomArray(_ n: Int) -> [Int] {
@@ -183,7 +176,7 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
XCTAssertFalse(h.isEmpty)
XCTAssertEqual(h.count, n)
- XCTAssertTrue(isPermutation(a, h.elements))
+ XCTAssertTrue(isPermutation(a, h.nodes))
}
}
@@ -194,58 +187,58 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMinHeap(h))
XCTAssertFalse(h.isEmpty)
XCTAssertEqual(h.count, n)
- XCTAssertTrue(isPermutation(a, h.elements))
+ XCTAssertTrue(isPermutation(a, h.nodes))
}
}
func testRemoving() {
var h = Heap(array: [100, 50, 70, 10, 20, 60, 65], sort: >)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [100, 50, 70, 10, 20, 60, 65])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [100, 50, 70, 10, 20, 60, 65])
//test index out of bounds
- let v = h.removeAt(10)
+ let v = h.remove(at: 10)
XCTAssertEqual(v, nil)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [100, 50, 70, 10, 20, 60, 65])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [100, 50, 70, 10, 20, 60, 65])
- let v1 = h.removeAt(5)
+ let v1 = h.remove(at: 5)
XCTAssertEqual(v1, 60)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [100, 50, 70, 10, 20, 65])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [100, 50, 70, 10, 20, 65])
- let v2 = h.removeAt(4)
+ let v2 = h.remove(at: 4)
XCTAssertEqual(v2, 20)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [100, 65, 70, 10, 50])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [100, 65, 70, 10, 50])
- let v3 = h.removeAt(4)
+ let v3 = h.remove(at: 4)
XCTAssertEqual(v3, 50)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [100, 65, 70, 10])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [100, 65, 70, 10])
- let v4 = h.removeAt(0)
+ let v4 = h.remove(at: 0)
XCTAssertEqual(v4, 100)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [70, 65, 10])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [70, 65, 10])
XCTAssertEqual(h.peek()!, 70)
let v5 = h.remove()
XCTAssertEqual(v5, 70)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [65, 10])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [65, 10])
XCTAssertEqual(h.peek()!, 65)
let v6 = h.remove()
XCTAssertEqual(v6, 65)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [10])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [10])
XCTAssertEqual(h.peek()!, 10)
let v7 = h.remove()
XCTAssertEqual(v7, 10)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [])
XCTAssertNil(h.peek())
}
@@ -259,12 +252,12 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
func testRemoveRoot() {
var h = Heap(array: [15, 13, 9, 5, 12, 8, 7, 4, 0, 6, 2, 1], sort: >)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [15, 13, 9, 5, 12, 8, 7, 4, 0, 6, 2, 1])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [15, 13, 9, 5, 12, 8, 7, 4, 0, 6, 2, 1])
XCTAssertEqual(h.peek()!, 15)
let v = h.remove()
XCTAssertEqual(v, 15)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [13, 12, 9, 5, 6, 8, 7, 4, 0, 1, 2])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [13, 12, 9, 5, 6, 8, 7, 4, 0, 1, 2])
}
func testRemoveRandomItems() {
@@ -272,19 +265,19 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
var a = randomArray(n)
var h = Heap(array: a, sort: >)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertTrue(isPermutation(a, h.elements))
+ XCTAssertTrue(isPermutation(a, h.nodes))
let m = (n + 1)/2
for k in 1...m {
let i = Int(arc4random_uniform(UInt32(n - k + 1)))
- let v = h.removeAt(i)!
+ let v = h.remove(at: i)!
let j = a.index(of: v)!
a.remove(at: j)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
XCTAssertEqual(h.count, a.count)
XCTAssertEqual(h.count, n - k)
- XCTAssertTrue(isPermutation(a, h.elements))
+ XCTAssertTrue(isPermutation(a, h.nodes))
}
}
}
@@ -292,17 +285,17 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
func testInsert() {
var h = Heap(array: [15, 13, 9, 5, 12, 8, 7, 4, 0, 6, 2, 1], sort: >)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [15, 13, 9, 5, 12, 8, 7, 4, 0, 6, 2, 1])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [15, 13, 9, 5, 12, 8, 7, 4, 0, 6, 2, 1])
h.insert(10)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [15, 13, 10, 5, 12, 9, 7, 4, 0, 6, 2, 1, 8])
+ XCTAssertEqual(h.nodes, [15, 13, 10, 5, 12, 9, 7, 4, 0, 6, 2, 1, 8])
}
func testInsertArrayAndRemove() {
var heap = Heap(sort: >)
heap.insert([1, 3, 2, 7, 5, 9])
- XCTAssertEqual(heap.elements, [9, 5, 7, 1, 3, 2])
+ XCTAssertEqual(heap.nodes, [9, 5, 7, 1, 3, 2])
XCTAssertEqual(9, heap.remove())
XCTAssertEqual(7, heap.remove())
@@ -316,15 +309,13 @@ class HeapTests: XCTestCase {
func testReplace() {
var h = Heap(array: [16, 14, 10, 8, 7, 9, 3, 2, 4, 1], sort: >)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [16, 14, 10, 8, 7, 9, 3, 2, 4, 1])
h.replace(index: 5, value: 13)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [16, 14, 13, 8, 7, 10, 3, 2, 4, 1])
//test index out of bounds
h.replace(index: 20, value: 2)
XCTAssertTrue(verifyMaxHeap(h))
- XCTAssertEqual(h.elements, [16, 14, 13, 8, 7, 10, 3, 2, 4, 1])
}
+
}
diff --git a/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 617e29f27..0ab48ba3b
--- a/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
archiveVersion = 1;
classes = {
};
- objectVersion = 46;
+ objectVersion = 51;
objects = {
/* Begin PBXBuildFile section */
@@ -83,17 +83,17 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0720;
- LastUpgradeCheck = 0800;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1010;
ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Swift Algorithm Club";
TargetAttributes = {
7B2BBC7F1C779D720067B71D = {
CreatedOnToolsVersion = 7.2;
- LastSwiftMigration = 0820;
+ LastSwiftMigration = 1010;
};
};
};
buildConfigurationList = 7B2BBC6C1C779D710067B71D /* Build configuration list for PBXProject "Tests" */;
- compatibilityVersion = "Xcode 3.2";
+ compatibilityVersion = "Xcode 10.0";
developmentRegion = English;
hasScannedForEncodings = 0;
knownRegions = (
@@ -141,14 +141,22 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -187,14 +195,22 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -214,7 +230,8 @@
MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET = 10.11;
MTL_ENABLE_DEBUG_INFO = NO;
SDKROOT = macosx;
- SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Owholemodule";
+ SWIFT_COMPILATION_MODE = wholemodule;
+ SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-O";
};
name = Release;
};
@@ -223,10 +240,14 @@
buildSettings = {
COMBINE_HIDPI_IMAGES = YES;
INFOPLIST_FILE = Info.plist;
- LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
+ LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = (
+ "$(inherited)",
+ "@executable_path/../Frameworks",
+ "@loader_path/../Frameworks",
+ );
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -235,10 +256,14 @@
buildSettings = {
COMBINE_HIDPI_IMAGES = YES;
INFOPLIST_FILE = Info.plist;
- LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
+ LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = (
+ "$(inherited)",
+ "@executable_path/../Frameworks",
+ "@loader_path/../Frameworks",
+ );
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 4.0;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata b/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
diff --git a/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 80ed35600..1608804f9
--- a/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/Heap/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
import Foundation
let s1 = "so much words wow many compression"
diff --git a/Images/DataStructuresAndAlgorithmsInSwiftBook.png b/Images/DataStructuresAndAlgorithmsInSwiftBook.png
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f8de0ba72
Binary files /dev/null and b/Images/DataStructuresAndAlgorithmsInSwiftBook.png differ
diff --git a/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.playground/Contents.swift b/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.playground/Contents.swift
index 91e18640f..184fc36e4 100644
--- a/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,24 +1,46 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4!")
-#endif
-
+/// Performs the Insertion sort algorithm to a given array
+///
+/// - Parameters:
+/// - array: the array of elements to be sorted
+/// - isOrderedBefore: returns true if the elements provided are in the corect order
+/// - Returns: a sorted array containing the same elements
func insertionSort(_ array: [T], _ isOrderedBefore: (T, T) -> Bool) -> [T] {
- var a = array
- for x in 1.. 0 && isOrderedBefore(temp, a[y - 1]) {
- a[y] = a[y - 1]
- y -= 1
+ guard array.count > 1 else { return array }
+
+ var a = array
+ for x in 1.. 0 && isOrderedBefore(temp, a[y - 1]) {
+ a[y] = a[y - 1]
+ y -= 1
+ }
+ a[y] = temp
+ }
+ return a
+}
+
+/// Performs the Insertion sort algorithm to a given array
+///
+/// - Parameter array: the array to be sorted, conatining elements that conform to the Comparable protocol
+/// - Returns: a sorted array containing the same elements
+func insertionSort(_ array: [T]) -> [T] {
+ var a = array
+ for x in 1.. 0 && temp < a[y - 1] {
+ a[y] = a[y - 1]
+ y -= 1
+ }
+ a[y] = temp
}
- a[y] = temp
- }
- return a
+ return a
}
let list = [ 10, -1, 3, 9, 2, 27, 8, 5, 1, 3, 0, 26 ]
-insertionSort(list, <)
-insertionSort(list, >)
+print(insertionSort(list))
+print(insertionSort(list, <))
+print(insertionSort(list, >))
diff --git a/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.playground/contents.xcplayground b/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.playground/contents.xcplayground
index 06828af92..9f9eecc96 100644
--- a/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.playground/contents.xcplayground
+++ b/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.playground/contents.xcplayground
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.swift b/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.swift
index 5d8a9565b..2ad607ac8 100644
--- a/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.swift
+++ b/Insertion Sort/InsertionSort.swift
@@ -1,3 +1,9 @@
+/// Performs the Insertion sort algorithm to a given array
+///
+/// - Parameters:
+/// - array: the array of elements to be sorted
+/// - isOrderedBefore: returns true if the elements provided are in the corect order
+/// - Returns: a sorted array containing the same elements
func insertionSort(_ array: [T], _ isOrderedBefore: (T, T) -> Bool) -> [T] {
guard array.count > 1 else { return array }
@@ -13,3 +19,23 @@ func insertionSort(_ array: [T], _ isOrderedBefore: (T, T) -> Bool) -> [T] {
}
return a
}
+
+/// Performs the Insertion sort algorithm to a given array
+///
+/// - Parameter array: the array to be sorted, containing elements that conform to the Comparable protocol
+/// - Returns: a sorted array containing the same elements
+func insertionSort(_ array: [T]) -> [T] {
+ guard array.count > 1 else { return array }
+
+ var a = array
+ for x in 1.. 0 && temp < a[y - 1] {
+ a[y] = a[y - 1]
+ y -= 1
+ }
+ a[y] = temp
+ }
+ return a
+}
diff --git a/Insertion Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Insertion Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
index ee3ca1cae..e9ea3bc53 100644
--- a/Insertion Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
+++ b/Insertion Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -86,12 +86,12 @@
isa = PBXProject;
attributes = {
LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 0720;
- LastUpgradeCheck = 0800;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1000;
ORGANIZATIONNAME = "Swift Algorithm Club";
TargetAttributes = {
7B2BBC7F1C779D720067B71D = {
CreatedOnToolsVersion = 7.2;
- LastSwiftMigration = 0800;
+ LastSwiftMigration = 1000;
};
};
};
@@ -145,14 +145,22 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -191,14 +199,22 @@
CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
@@ -230,7 +246,8 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_SWIFT3_OBJC_INFERENCE = On;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Debug;
};
@@ -242,7 +259,8 @@
LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = "$(inherited) @executable_path/../Frameworks @loader_path/../Frameworks";
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
- SWIFT_VERSION = 3.0;
+ SWIFT_SWIFT3_OBJC_INFERENCE = On;
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
};
name = Release;
};
diff --git a/Insertion Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Insertion Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Insertion Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Insertion Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/Insertion Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
index 14f27f777..afd69e6a7 100644
--- a/Insertion Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/Insertion Sort/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
(_ elements: inout [T], _ index: Int, _ range: Range, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ let countToIndex = elements.distance(from: range.lowerBound, to: index)
+ let countFromIndex = elements.distance(from: index, to: range.upperBound)
+
+ guard countToIndex + 1 < countFromIndex else { return }
+
+ let left = elements.index(index, offsetBy: countToIndex + 1)
+ var largest = index
+ if areInIncreasingOrder(elements[largest], elements[left]) {
+ largest = left
+ }
+
+ if countToIndex + 2 < countFromIndex {
+ let right = elements.index(after: left)
+ if areInIncreasingOrder(elements[largest], elements[right]) {
+ largest = right
+ }
+ }
+
+ if largest != index {
+ elements.swapAt(index, largest)
+ shiftDown(&elements, largest, range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ }
+
+}
+
+private func heapify(_ list: inout [T], _ range: Range, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ let root = range.lowerBound
+ var node = list.index(root, offsetBy: list.distance(from: range.lowerBound, to: range.upperBound)/2)
+
+ while node != root {
+ list.formIndex(before: &node)
+ shiftDown(&list, node, range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ }
+}
+
+public func heapsort(for array: inout [T], range: Range, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ var hi = range.upperBound
+ let lo = range.lowerBound
+ heapify(&array, range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ array.formIndex(before: &hi)
+
+ while hi != lo {
+ array.swapAt(lo, hi)
+ shiftDown(&array, lo, lo..(for array: inout [T], range: Range, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ guard !range.isEmpty else { return }
+
+ let start = range.lowerBound
+ var sortedEnd = start
+
+ array.formIndex(after: &sortedEnd)
+ while sortedEnd != range.upperBound {
+ let x = array[sortedEnd]
+
+ var i = sortedEnd
+ repeat {
+ let predecessor = array[array.index(before: i)]
+
+ guard areInIncreasingOrder(x, predecessor) else { break }
+ array[i] = predecessor
+ array.formIndex(before: &i)
+ } while i != start
+
+ if i != sortedEnd {
+ array[i] = x
+ }
+ array.formIndex(after: &sortedEnd)
+ }
+
+}
diff --git a/Introsort/IntroSort.swift b/Introsort/IntroSort.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..866b2603f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Introsort/IntroSort.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+import Foundation
+
+public func introsort(_ array: inout [T], by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ //The depth limit is as best practice 2 * log( n )
+ let depthLimit = 2 * floor(log2(Double(array.count)))
+
+ introSortImplementation(for: &array, range: 0..(for array: inout [T], range: Range, depthLimit: Int, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ if array.distance(from: range.lowerBound, to: range.upperBound) < 20 {
+ //if the partition count is less than 20 we can sort it using insertion sort. This algorithm in fact performs well on collections
+ //of this size, plus, at this point is quite probable that the quisksort part of the algorithm produced a partition which is
+ //nearly sorted. As we knoe insertion sort tends to O( n ) if this is the case.
+ insertionSort(for: &array, range: range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ } else if depthLimit == 0 {
+ //If we reached the depth limit for this recursion branch, it's possible that we are hitting quick sort's worst case.
+ //Since quicksort degrades to O( n^2 ) in its worst case we stop using quicksort for this recursion branch and we switch to heapsort.
+ //Our preference remains quicksort, and we hope to be rare to see this condition to be true
+ heapsort(for: &array, range: range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ } else {
+ //By default we use quicksort to sort our collection. The partition index method chose a pivot, and puts all the
+ //elements less than pivot on the left, and the ones bigger than pivot on the right. At the end of the operation the
+ //position of the pivot in the array is returned so that we can form the two partitions.
+ let partIdx = partitionIndex(for: &array, subRange: range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+
+ //We can recursively call introsort implementation, decreasing the depthLimit for the left partition and the right partition.
+ introSortImplementation(for: &array, range: range.lowerBound..(_ array: inout [T], by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ //The depth limit is as best practice 2 * log( n )
+ let depthLimit = 2 * floor(log2(Double(array.count)))
+
+ introSortImplementation(for: &array, range: 0..(for array: inout [T], range: Range, depthLimit: Int, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ if array.distance(from: range.lowerBound, to: range.upperBound) < 20 {
+ //if the partition count is less than 20 we can sort it using insertion sort. This algorithm in fact performs well on collections
+ //of this size, plus, at this point is quite probable that the quisksort part of the algorithm produced a partition which is
+ //nearly sorted. As we knoe insertion sort tends to O( n ) if this is the case.
+ insertionSort(for: &array, range: range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ } else if depthLimit == 0 {
+ //If we reached the depth limit for this recursion branch, it's possible that we are hitting quick sort's worst case.
+ //Since quicksort degrades to O( n^2 ) in its worst case we stop using quicksort for this recursion branch and we switch to heapsort.
+ //Our preference remains quicksort, and we hope to be rare to see this condition to be true
+ heapsort(for: &array, range: range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ } else {
+ //By default we use quicksort to sort our collection. The partition index method chose a pivot, and puts all the
+ //elements less than pivot on the left, and the ones bigger than pivot on the right. At the end of the operation the
+ //position of the pivot in the array is returned so that we can form the two partitions.
+ let partIdx = partitionIndex(for: &array, subRange: range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+
+ //We can recursively call introsort implementation, decreasing the depthLimit for the left partition and the right partition.
+ introSortImplementation(for: &array, range: range.lowerBound..(_ elements: inout [T], _ index: Int, _ range: Range, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ let countToIndex = elements.distance(from: range.lowerBound, to: index)
+ let countFromIndex = elements.distance(from: index, to: range.upperBound)
+
+ guard countToIndex + 1 < countFromIndex else { return }
+
+ let left = elements.index(index, offsetBy: countToIndex + 1)
+ var largest = index
+ if areInIncreasingOrder(elements[largest], elements[left]) {
+ largest = left
+ }
+
+ if countToIndex + 2 < countFromIndex {
+ let right = elements.index(after: left)
+ if areInIncreasingOrder(elements[largest], elements[right]) {
+ largest = right
+ }
+ }
+
+ if largest != index {
+ elements.swapAt(index, largest)
+ shiftDown(&elements, largest, range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ }
+
+}
+
+private func heapify(_ list: inout [T], _ range: Range, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ let root = range.lowerBound
+ var node = list.index(root, offsetBy: list.distance(from: range.lowerBound, to: range.upperBound)/2)
+
+ while node != root {
+ list.formIndex(before: &node)
+ shiftDown(&list, node, range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ }
+}
+
+public func heapsort(for array: inout [T], range: Range, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ var hi = range.upperBound
+ let lo = range.lowerBound
+ heapify(&array, range, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ array.formIndex(before: &hi)
+
+ while hi != lo {
+ array.swapAt(lo, hi)
+ shiftDown(&array, lo, lo..(for array: inout [T], range: Range, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ guard !range.isEmpty else { return }
+
+ let start = range.lowerBound
+ var sortedEnd = start
+
+ array.formIndex(after: &sortedEnd)
+ while sortedEnd != range.upperBound {
+ let x = array[sortedEnd]
+
+ var i = sortedEnd
+ repeat {
+ let predecessor = array[array.index(before: i)]
+
+ guard areInIncreasingOrder(x, predecessor) else { break }
+ array[i] = predecessor
+ array.formIndex(before: &i)
+ } while i != start
+
+ if i != sortedEnd {
+ array[i] = x
+ }
+ array.formIndex(after: &sortedEnd)
+ }
+
+}
diff --git a/Introsort/Introsort.playground/Sources/Partition.swift b/Introsort/Introsort.playground/Sources/Partition.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e24636da7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Introsort/Introsort.playground/Sources/Partition.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+import Foundation
+
+public func partitionIndex(for elements: inout [T], subRange range: Range, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) -> Int {
+ var lo = range.lowerBound
+ var hi = elements.index(before: range.upperBound)
+
+ // Sort the first, middle, and last elements, then use the middle value
+ // as the pivot for the partition.
+ let half = elements.distance(from: lo, to: hi) / 2
+ let mid = elements.index(lo, offsetBy: half)
+
+ sort3(in: &elements, a: lo, b: mid, c: hi, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ let pivot = elements[mid]
+
+ while true {
+ elements.formIndex(after: &lo)
+ guard findLo(in: elements, pivot: pivot, from: &lo, to: hi, by: areInIncreasingOrder) else { break }
+ elements.formIndex(before: &hi)
+ guard findHi(in: elements, pivot: pivot, from: lo, to: &hi, by: areInIncreasingOrder) else { break }
+ elements.swapAt(lo, hi)
+ }
+
+
+ return lo
+}
+
+private func findLo(in array: [T], pivot: T, from lo: inout Int, to hi: Int, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T)->Bool) -> Bool {
+ while lo != hi {
+ if !areInIncreasingOrder(array[lo], pivot) {
+ return true
+ }
+ array.formIndex(after: &lo)
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+private func findHi(in array: [T], pivot: T, from lo: Int, to hi: inout Int, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T)->Bool) -> Bool {
+ while hi != lo {
+ if areInIncreasingOrder(array[hi], pivot) { return true }
+ array.formIndex(before: &hi)
+ }
+ return false
+}
diff --git a/Introsort/Introsort.playground/Sources/Randomize.swift b/Introsort/Introsort.playground/Sources/Randomize.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6d1d57132
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Introsort/Introsort.playground/Sources/Randomize.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+import Foundation
+
+public func randomize(n: Int) -> [Int] {
+ var unsorted = [Int]()
+ for _ in 0..(in array: inout [T], a: Int, b: Int, c: Int, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ switch (areInIncreasingOrder(array[b], array[a]),
+ areInIncreasingOrder(array[c], array[b])) {
+ case (false, false): break
+ case (true, true): array.swapAt(a, c)
+ case (true, false):
+ array.swapAt(a, b)
+
+ if areInIncreasingOrder(array[c], array[b]) {
+ array.swapAt(b, c)
+ }
+ case (false, true):
+ array.swapAt(b, c)
+
+ if areInIncreasingOrder(array[b], array[a]) {
+ array.swapAt(a, b)
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/Introsort/Introsort.playground/contents.xcplayground b/Introsort/Introsort.playground/contents.xcplayground
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5da2641c9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Introsort/Introsort.playground/contents.xcplayground
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/Introsort/Partition.swift b/Introsort/Partition.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e24636da7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Introsort/Partition.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+import Foundation
+
+public func partitionIndex(for elements: inout [T], subRange range: Range, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) -> Int {
+ var lo = range.lowerBound
+ var hi = elements.index(before: range.upperBound)
+
+ // Sort the first, middle, and last elements, then use the middle value
+ // as the pivot for the partition.
+ let half = elements.distance(from: lo, to: hi) / 2
+ let mid = elements.index(lo, offsetBy: half)
+
+ sort3(in: &elements, a: lo, b: mid, c: hi, by: areInIncreasingOrder)
+ let pivot = elements[mid]
+
+ while true {
+ elements.formIndex(after: &lo)
+ guard findLo(in: elements, pivot: pivot, from: &lo, to: hi, by: areInIncreasingOrder) else { break }
+ elements.formIndex(before: &hi)
+ guard findHi(in: elements, pivot: pivot, from: lo, to: &hi, by: areInIncreasingOrder) else { break }
+ elements.swapAt(lo, hi)
+ }
+
+
+ return lo
+}
+
+private func findLo(in array: [T], pivot: T, from lo: inout Int, to hi: Int, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T)->Bool) -> Bool {
+ while lo != hi {
+ if !areInIncreasingOrder(array[lo], pivot) {
+ return true
+ }
+ array.formIndex(after: &lo)
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+private func findHi(in array: [T], pivot: T, from lo: Int, to hi: inout Int, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T)->Bool) -> Bool {
+ while hi != lo {
+ if areInIncreasingOrder(array[hi], pivot) { return true }
+ array.formIndex(before: &hi)
+ }
+ return false
+}
diff --git a/Introsort/README.markdown b/Introsort/README.markdown
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..280950928
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Introsort/README.markdown
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+# IntroSort
+
+Goal: Sort an array from low to high (or high to low).
+
+IntroSort is the algorithm used by Swift to sort a collection. Introsort is an hybrid algorithm invented by David Musser in 1993 with the purpose of giving a generic sorting algorithm for the C++ standard library.
+
+The classic implementation of introsort uses a recursive Quicksort with a fallback to Heapsort in the case where the recursion depth level reached a certain maximum value. The maximum depends on the number of elements in the collection and it is usually 2 * log(n). The reason behind this “fallback” is that if Quicksort was not able to get the solution after 2 * log(n) recursions for a branch, probably it hit its worst case and it is degrading to complexity O( n^2 ). To optimise even further this algorithm, the Swift implementation introduce an extra step in each recursion where the partition is sorted using InsertionSort if the count of the partition is less than 20.
+
+The number 20 is an empiric number obtained observing the behaviour of InsertionSort with lists of this size.
+
+Here's an implementation in pseudocode:
+
+```
+procedure sort(A : array):
+ let maxdepth = ⌊log(length(A))⌋ × 2
+ introSort(A, maxdepth)
+
+procedure introsort(A, maxdepth):
+ n ← length(A)
+ if n < 20:
+ insertionsort(A)
+ else if maxdepth = 0:
+ heapsort(A)
+ else:
+ p ← partition(A) // the pivot is selected using median of 3
+ introsort(A[0:p], maxdepth - 1)
+ introsort(A[p+1:n], maxdepth - 1)
+```
+
+## An example
+
+Let's walk through the example. The array is initially:
+
+ [ 10, 0, 3, 9, 2, 14, 8, 27, 1, 5, 8, -1, 26 ]
+
+
+For this example let's assume that `maxDepth` is **2** and that the size of the partition for the insertionSort to kick in is **5**
+
+The first iteration of introsort begins by attempting to use insertionSort. The collection has 13 elements, so it tries to do heapsort instead. The condition for heapsort to occur is if `maxdepth == 0` evaluates true. Since `maxdepth` is currently **2** for the first iteration, introsort will default to quicksort.
+
+The `partition` method picks the first element, the median and the last, it sorts them and uses the new median as pivot.
+
+ [ 10, 8, 26 ] -> [ 8, 10, 26 ]
+
+Our array is now
+
+ [ 8, 0, 3, 9, 2, 14, 10, 27, 1, 5, 8, -1, 26 ]
+
+**10** is the pivot. After the choice of the pivot, the `partition` method swaps elements to get all the elements less than pivot on the left, and all the elements more or equal than pivot on the right.
+
+ [ 8, 0, 3, 9, 2, 1, 5, 8, -1, 10, 27, 14, 26 ]
+
+Because of the swaps, the index of of pivot is now changed and returned. The next step of introsort is to call recursively itself for the two sub arrays:
+
+ less: [ 8, 0, 3, 9, 2, 1, 5, 8, -1, 10 ]
+ greater: [ 27, 14, 26 ]
+
+## maxDepth: 1, branch: less
+
+ [ 8, 0, 3, 9, 2, 1, 5, 8, -1, 10 ]
+
+The count of the array is still more than 5 so we don't meet yet the conditions for insertion sort to kick in. At this iteration maxDepth is decreased by one but it is still more than zero, so heapsort will not act.
+
+Just like in the previous iteration quicksort wins and the `partition` method choses a pivot and sorts the elemets less than pivot on the left and the elements more or equeal than pivot on the right.
+
+ array: [ 8, 0, 3, 9, 2, 1, 5, 8, -1, 10 ]
+ pivot candidates: [ 8, 1, 10] -> [ 1, 8, 10]
+ pivot: 8
+ before partition: [ 1, 0, 3, 9, 2, 8, 5, 8, -1, 10 ]
+ after partition: [ 1, 0, 3, -1, 2, 5, 8, 8, 9, 10 ]
+
+ less: [ 1, 0, 3, -1, 2, 5, 8 ]
+ greater: [ 8, 9, 10 ]
+
+## maxDepth: 0, branch: less
+
+ [ 1, 0, 3, -1, 2, 5, 8 ]
+
+Just like before, introsort is recursively executed for `less` and greater. This time `less`has a count more than **5** so it will not be sorted with insertion sort, but the maxDepth decreased again by 1 is now 0 and heapsort takes over sorting the array.
+
+ heapsort -> [ -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8 ]
+
+## maxDepth: 0, branch: greater
+
+ [ 8, 9, 10 ]
+
+following greater in this recursion, the count of elements is 3, which is less than 5, so this partition is sorted using insertionSort.
+
+ insertionSort -> [ 8, 9 , 10]
+
+
+## back to maxDepth = 1, branch: greater
+
+ [ 27, 14, 26 ]
+
+At this point the original array has mutated to be
+
+ [ -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 8, 9, 10, 27, 14, 26 ]
+
+now the `less` partition is sorted and since the count of the `greater` partition is 3 it will be sorted with insertion sort `[ 14, 26, 27 ]`
+
+The array is now successfully sorted
+
+ [ -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 8, 9, 10, 14, 26, 27 ]
+
+
+## See also
+
+[Introsort on Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Introsort)
+[Introsort comparison with other sorting algorithms](http://agostini.tech/2017/12/18/swift-sorting-algorithm/)
+[Introsort implementation from the Swift standard library](https://github.com/apple/swift/blob/09f77ff58d250f5d62855ea359fc304f40b531df/stdlib/public/core/Sort.swift.gyb)
+
+*Written for Swift Algorithm Club by Giuseppe Lanza*
diff --git a/Introsort/Randomize.swift b/Introsort/Randomize.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6d1d57132
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Introsort/Randomize.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+import Foundation
+
+public func randomize(n: Int) -> [Int] {
+ var unsorted = [Int]()
+ for _ in 0..(in array: inout [T], a: Int, b: Int, c: Int, by areInIncreasingOrder: (T, T) -> Bool) {
+ switch (areInIncreasingOrder(array[b], array[a]),
+ areInIncreasingOrder(array[c], array[b])) {
+ case (false, false): break
+ case (true, true): array.swapAt(a, c)
+ case (true, false):
+ array.swapAt(a, b)
+
+ if areInIncreasingOrder(array[c], array[b]) {
+ array.swapAt(b, c)
+ }
+ case (false, true):
+ array.swapAt(b, c)
+
+ if areInIncreasingOrder(array[b], array[a]) {
+ array.swapAt(a, b)
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/K-Means/KMeans.swift b/K-Means/KMeans.swift
index 4a89a3fae..bccc6efd3 100644
--- a/K-Means/KMeans.swift
+++ b/K-Means/KMeans.swift
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ class KMeans {
}
private func indexOfNearestCenter(_ x: Vector, centers: [Vector]) -> Int {
- var nearestDist = DBL_MAX
+ var nearestDist = Double.greatestFiniteMagnitude
var minIndex = 0
for (idx, center) in centers.enumerated() {
diff --git a/K-Means/Tests/KMeansTests.swift b/K-Means/Tests/KMeansTests.swift
index e6f4b08a1..7e0c93004 100644
--- a/K-Means/Tests/KMeansTests.swift
+++ b/K-Means/Tests/KMeansTests.swift
@@ -10,13 +10,6 @@ import Foundation
import XCTest
class KMeansTests: XCTestCase {
- func testSwift4() {
- // last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
- #if swift(>=4.0)
- print("Hello, Swift 4!")
- #endif
- }
-
func genPoints(_ numPoints: Int, numDimensions: Int) -> [Vector] {
var points = [Vector]()
for _ in 0..
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/K-Means/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/K-Means/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
index 2b401e86e..73ba8f37d 100644
--- a/K-Means/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
+++ b/K-Means/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift 4")
-#endif
+
precedencegroup ExponentiativePrecedence {
higherThan: MultiplicationPrecedence
lowerThan: BitwiseShiftPrecedence
@@ -18,8 +15,8 @@ func ^^ (radix: Int, power: Int) -> Int {
// Long Multiplication - O(n^2)
func multiply(_ num1: Int, by num2: Int, base: Int = 10) -> Int {
- let num1Array = String(num1).characters.reversed().map { Int(String($0))! }
- let num2Array = String(num2).characters.reversed().map { Int(String($0))! }
+ let num1Array = String(num1).reversed().map { Int(String($0))! }
+ let num2Array = String(num2).reversed().map { Int(String($0))! }
var product = Array(repeating: 0, count: num1Array.count + num2Array.count)
@@ -38,14 +35,14 @@ func multiply(_ num1: Int, by num2: Int, base: Int = 10) -> Int {
// Karatsuba Multiplication - O(n^log2(3))
func karatsuba(_ num1: Int, by num2: Int) -> Int {
- let num1Array = String(num1).characters
- let num2Array = String(num2).characters
+ let num1String = String(num1)
+ let num2String = String(num2)
- guard num1Array.count > 1 && num2Array.count > 1 else {
+ guard num1String.count > 1 && num2String.count > 1 else {
return multiply(num1, by: num2)
}
- let n = max(num1Array.count, num2Array.count)
+ let n = max(num1String.count, num2String.count)
let nBy2 = n / 2
let a = num1 / 10^^nBy2
diff --git a/Karatsuba Multiplication/KaratsubaMultiplication.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist b/Karatsuba Multiplication/KaratsubaMultiplication.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..18d981003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Karatsuba Multiplication/KaratsubaMultiplication.playground/playground.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+
+
+
+
+ IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
+
+
+
diff --git a/Karatsuba Multiplication/KaratsubaMultiplication.swift b/Karatsuba Multiplication/KaratsubaMultiplication.swift
index fb20a667d..3d14a243a 100644
--- a/Karatsuba Multiplication/KaratsubaMultiplication.swift
+++ b/Karatsuba Multiplication/KaratsubaMultiplication.swift
@@ -19,27 +19,48 @@ func ^^ (radix: Int, power: Int) -> Int {
return Int(pow(Double(radix), Double(power)))
}
+// Long Multiplication - O(n^2)
+func multiply(_ num1: Int, by num2: Int, base: Int = 10) -> Int {
+ let num1Array = String(num1).reversed().map { Int(String($0))! }
+ let num2Array = String(num2).reversed().map { Int(String($0))! }
+
+ var product = Array(repeating: 0, count: num1Array.count + num2Array.count)
+
+ for i in num1Array.indices {
+ var carry = 0
+ for j in num2Array.indices {
+ product[i + j] += carry + num1Array[i] * num2Array[j]
+ carry = product[i + j] / base
+ product[i + j] %= base
+ }
+ product[i + num2Array.count] += carry
+ }
+
+ return Int(product.reversed().map { String($0) }.reduce("", +))!
+}
+
+// Karatsuba Multiplication - O(n^log2(3))
func karatsuba(_ num1: Int, by num2: Int) -> Int {
- let num1Array = String(num1).characters
- let num2Array = String(num2).characters
-
- guard num1Array.count > 1 && num2Array.count > 1 else {
- return num1 * num2
+ let num1String = String(num1)
+ let num2String = String(num2)
+
+ guard num1String.count > 1 && num2String.count > 1 else {
+ return multiply(num1, by: num2)
}
-
- let n = max(num1Array.count, num2Array.count)
+
+ let n = max(num1String.count, num2String.count)
let nBy2 = n / 2
-
+
let a = num1 / 10^^nBy2
let b = num1 % 10^^nBy2
let c = num2 / 10^^nBy2
let d = num2 % 10^^nBy2
-
+
let ac = karatsuba(a, by: c)
let bd = karatsuba(b, by: d)
let adPlusbc = karatsuba(a+b, by: c+d) - ac - bd
-
+
let product = ac * 10^^(2 * nBy2) + adPlusbc * 10^^nBy2 + bd
-
+
return product
}
diff --git a/Karatsuba Multiplication/README.markdown b/Karatsuba Multiplication/README.markdown
index c86f69831..02e54a1bf 100644
--- a/Karatsuba Multiplication/README.markdown
+++ b/Karatsuba Multiplication/README.markdown
@@ -72,14 +72,14 @@ Here's the full implementation. Note that the recursive algorithm is most effici
```swift
// Karatsuba Multiplication
func karatsuba(_ num1: Int, by num2: Int) -> Int {
- let num1Array = String(num1).characters
- let num2Array = String(num2).characters
+ let num1String = String(num1)
+ let num2String = String(num2)
- guard num1Array.count > 1 && num2Array.count > 1 else {
- return num1*num2
+ guard num1String.count > 1 && num2String.count > 1 else {
+ return multiply(num1, by: num2)
}
- let n = max(num1Array.count, num2Array.count)
+ let n = max(num1String.count, num2String.count)
let nBy2 = n / 2
let a = num1 / 10^^nBy2
@@ -115,10 +115,10 @@ What about the running time of this algorithm? Is all this extra work worth it?
## Resources
-[Wikipedia] (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karatsuba_algorithm)
+[Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karatsuba_algorithm)
-[WolframMathWorld] (http://mathworld.wolfram.com/KaratsubaMultiplication.html)
+[WolframMathWorld](http://mathworld.wolfram.com/KaratsubaMultiplication.html)
-[Master Theorem] (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Master_theorem)
+[Master Theorem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Master_theorem)
*Written for Swift Algorithm Club by Richard Ash*
diff --git a/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/KaratsubaMultiplicationTests.swift b/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/KaratsubaMultiplicationTests.swift
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..379c9e812
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/KaratsubaMultiplicationTests.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+//
+// KaratsubaMultiplicationTests.swift
+// Tests
+//
+// Created by Afonso Graça on 8/10/18.
+//
+
+import XCTest
+
+final class KaratsubaMultiplicationTests: XCTestCase {
+
+ func testReadmeExample() {
+ let subject = karatsuba(1234, by: 5678)
+
+ XCTAssertEqual(subject, 7006652)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj b/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ef23067ee
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj
@@ -0,0 +1,305 @@
+// !$*UTF8*$!
+{
+ archiveVersion = 1;
+ classes = {
+ };
+ objectVersion = 50;
+ objects = {
+
+/* Begin PBXBuildFile section */
+ 6AF099AC216B54E200F69B16 /* KaratsubaMultiplication.swift in Sources */ = {isa = PBXBuildFile; fileRef = 6AF099AB216B54E200F69B16 /* KaratsubaMultiplication.swift */; };
+ 6AF099AE216B55A100F69B16 /* KaratsubaMultiplicationTests.swift in Sources */ = {isa = PBXBuildFile; fileRef = 6AF099AD216B55A100F69B16 /* KaratsubaMultiplicationTests.swift */; };
+/* End PBXBuildFile section */
+
+/* Begin PBXFileReference section */
+ 6AF099A2216B54D500F69B16 /* Tests.xctest */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; explicitFileType = wrapper.cfbundle; includeInIndex = 0; path = Tests.xctest; sourceTree = BUILT_PRODUCTS_DIR; };
+ 6AF099A7216B54D500F69B16 /* Info.plist */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; lastKnownFileType = text.plist.xml; name = Info.plist; path = Tests/Info.plist; sourceTree = SOURCE_ROOT; };
+ 6AF099AB216B54E200F69B16 /* KaratsubaMultiplication.swift */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; fileEncoding = 4; lastKnownFileType = sourcecode.swift; name = KaratsubaMultiplication.swift; path = ../KaratsubaMultiplication.swift; sourceTree = ""; };
+ 6AF099AD216B55A100F69B16 /* KaratsubaMultiplicationTests.swift */ = {isa = PBXFileReference; lastKnownFileType = sourcecode.swift; path = KaratsubaMultiplicationTests.swift; sourceTree = ""; };
+/* End PBXFileReference section */
+
+/* Begin PBXFrameworksBuildPhase section */
+ 6AF0999F216B54D500F69B16 /* Frameworks */ = {
+ isa = PBXFrameworksBuildPhase;
+ buildActionMask = 2147483647;
+ files = (
+ );
+ runOnlyForDeploymentPostprocessing = 0;
+ };
+/* End PBXFrameworksBuildPhase section */
+
+/* Begin PBXGroup section */
+ 6AF09997216B545D00F69B16 = {
+ isa = PBXGroup;
+ children = (
+ 6AF099AB216B54E200F69B16 /* KaratsubaMultiplication.swift */,
+ 6AF099A4216B54D500F69B16 /* Tests */,
+ 6AF099A3216B54D500F69B16 /* Products */,
+ );
+ sourceTree = "";
+ };
+ 6AF099A3216B54D500F69B16 /* Products */ = {
+ isa = PBXGroup;
+ children = (
+ 6AF099A2216B54D500F69B16 /* Tests.xctest */,
+ );
+ name = Products;
+ sourceTree = "";
+ };
+ 6AF099A4216B54D500F69B16 /* Tests */ = {
+ isa = PBXGroup;
+ children = (
+ 6AF099AD216B55A100F69B16 /* KaratsubaMultiplicationTests.swift */,
+ 6AF099A7216B54D500F69B16 /* Info.plist */,
+ );
+ name = Tests;
+ sourceTree = SOURCE_ROOT;
+ };
+/* End PBXGroup section */
+
+/* Begin PBXNativeTarget section */
+ 6AF099A1216B54D500F69B16 /* Tests */ = {
+ isa = PBXNativeTarget;
+ buildConfigurationList = 6AF099A8216B54D500F69B16 /* Build configuration list for PBXNativeTarget "Tests" */;
+ buildPhases = (
+ 6AF0999E216B54D500F69B16 /* Sources */,
+ 6AF0999F216B54D500F69B16 /* Frameworks */,
+ 6AF099A0216B54D500F69B16 /* Resources */,
+ );
+ buildRules = (
+ );
+ dependencies = (
+ );
+ name = Tests;
+ productName = Tests;
+ productReference = 6AF099A2216B54D500F69B16 /* Tests.xctest */;
+ productType = "com.apple.product-type.bundle.unit-test";
+ };
+/* End PBXNativeTarget section */
+
+/* Begin PBXProject section */
+ 6AF09998216B545D00F69B16 /* Project object */ = {
+ isa = PBXProject;
+ attributes = {
+ LastSwiftUpdateCheck = 1000;
+ LastUpgradeCheck = 1000;
+ TargetAttributes = {
+ 6AF099A1216B54D500F69B16 = {
+ CreatedOnToolsVersion = 10.0;
+ };
+ };
+ };
+ buildConfigurationList = 6AF0999B216B545D00F69B16 /* Build configuration list for PBXProject "Tests" */;
+ compatibilityVersion = "Xcode 9.3";
+ developmentRegion = en;
+ hasScannedForEncodings = 0;
+ knownRegions = (
+ en,
+ );
+ mainGroup = 6AF09997216B545D00F69B16;
+ productRefGroup = 6AF099A3216B54D500F69B16 /* Products */;
+ projectDirPath = "";
+ projectRoot = "";
+ targets = (
+ 6AF099A1216B54D500F69B16 /* Tests */,
+ );
+ };
+/* End PBXProject section */
+
+/* Begin PBXResourcesBuildPhase section */
+ 6AF099A0216B54D500F69B16 /* Resources */ = {
+ isa = PBXResourcesBuildPhase;
+ buildActionMask = 2147483647;
+ files = (
+ );
+ runOnlyForDeploymentPostprocessing = 0;
+ };
+/* End PBXResourcesBuildPhase section */
+
+/* Begin PBXSourcesBuildPhase section */
+ 6AF0999E216B54D500F69B16 /* Sources */ = {
+ isa = PBXSourcesBuildPhase;
+ buildActionMask = 2147483647;
+ files = (
+ 6AF099AE216B55A100F69B16 /* KaratsubaMultiplicationTests.swift in Sources */,
+ 6AF099AC216B54E200F69B16 /* KaratsubaMultiplication.swift in Sources */,
+ );
+ runOnlyForDeploymentPostprocessing = 0;
+ };
+/* End PBXSourcesBuildPhase section */
+
+/* Begin XCBuildConfiguration section */
+ 6AF0999C216B545D00F69B16 /* Debug */ = {
+ isa = XCBuildConfiguration;
+ buildSettings = {
+ };
+ name = Debug;
+ };
+ 6AF0999D216B545D00F69B16 /* Release */ = {
+ isa = XCBuildConfiguration;
+ buildSettings = {
+ };
+ name = Release;
+ };
+ 6AF099A9216B54D500F69B16 /* Debug */ = {
+ isa = XCBuildConfiguration;
+ buildSettings = {
+ ALWAYS_SEARCH_USER_PATHS = NO;
+ CLANG_ANALYZER_NONNULL = YES;
+ CLANG_ANALYZER_NUMBER_OBJECT_CONVERSION = YES_AGGRESSIVE;
+ CLANG_CXX_LANGUAGE_STANDARD = "gnu++14";
+ CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
+ CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
+ CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_WEAK = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_DOCUMENTATION_COMMENTS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_UNGUARDED_AVAILABILITY = YES_AGGRESSIVE;
+ CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
+ CODE_SIGN_IDENTITY = "-";
+ CODE_SIGN_STYLE = Automatic;
+ COMBINE_HIDPI_IMAGES = YES;
+ COPY_PHASE_STRIP = NO;
+ DEBUG_INFORMATION_FORMAT = dwarf;
+ ENABLE_STRICT_OBJC_MSGSEND = YES;
+ ENABLE_TESTABILITY = YES;
+ GCC_C_LANGUAGE_STANDARD = gnu11;
+ GCC_DYNAMIC_NO_PIC = NO;
+ GCC_NO_COMMON_BLOCKS = YES;
+ GCC_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = 0;
+ GCC_PREPROCESSOR_DEFINITIONS = (
+ "DEBUG=1",
+ "$(inherited)",
+ );
+ GCC_WARN_64_TO_32_BIT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_ABOUT_RETURN_TYPE = YES_ERROR;
+ GCC_WARN_UNDECLARED_SELECTOR = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_UNINITIALIZED_AUTOS = YES_AGGRESSIVE;
+ GCC_WARN_UNUSED_FUNCTION = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_UNUSED_VARIABLE = YES;
+ INFOPLIST_FILE = Tests/Info.plist;
+ LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = (
+ "$(inherited)",
+ "@executable_path/../Frameworks",
+ "@loader_path/../Frameworks",
+ );
+ MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET = 10.14;
+ MTL_ENABLE_DEBUG_INFO = INCLUDE_SOURCE;
+ MTL_FAST_MATH = YES;
+ ONLY_ACTIVE_ARCH = YES;
+ PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
+ PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
+ SDKROOT = macosx;
+ SWIFT_ACTIVE_COMPILATION_CONDITIONS = DEBUG;
+ SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-Onone";
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
+ };
+ name = Debug;
+ };
+ 6AF099AA216B54D500F69B16 /* Release */ = {
+ isa = XCBuildConfiguration;
+ buildSettings = {
+ ALWAYS_SEARCH_USER_PATHS = NO;
+ CLANG_ANALYZER_NONNULL = YES;
+ CLANG_ANALYZER_NUMBER_OBJECT_CONVERSION = YES_AGGRESSIVE;
+ CLANG_CXX_LANGUAGE_STANDARD = "gnu++14";
+ CLANG_CXX_LIBRARY = "libc++";
+ CLANG_ENABLE_MODULES = YES;
+ CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_ARC = YES;
+ CLANG_ENABLE_OBJC_WEAK = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BLOCK_CAPTURE_AUTORELEASING = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_BOOL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_COMMA = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_CONSTANT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DEPRECATED_OBJC_IMPLEMENTATIONS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_DIRECT_OBJC_ISA_USAGE = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_DOCUMENTATION_COMMENTS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_EMPTY_BODY = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_ENUM_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INFINITE_RECURSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_INT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_NON_LITERAL_NULL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_IMPLICIT_RETAIN_SELF = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_LITERAL_CONVERSION = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_OBJC_ROOT_CLASS = YES_ERROR;
+ CLANG_WARN_RANGE_LOOP_ANALYSIS = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_STRICT_PROTOTYPES = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_SUSPICIOUS_MOVE = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN_UNGUARDED_AVAILABILITY = YES_AGGRESSIVE;
+ CLANG_WARN_UNREACHABLE_CODE = YES;
+ CLANG_WARN__DUPLICATE_METHOD_MATCH = YES;
+ CODE_SIGN_IDENTITY = "-";
+ CODE_SIGN_STYLE = Automatic;
+ COMBINE_HIDPI_IMAGES = YES;
+ COPY_PHASE_STRIP = NO;
+ DEBUG_INFORMATION_FORMAT = "dwarf-with-dsym";
+ ENABLE_NS_ASSERTIONS = NO;
+ ENABLE_STRICT_OBJC_MSGSEND = YES;
+ GCC_C_LANGUAGE_STANDARD = gnu11;
+ GCC_NO_COMMON_BLOCKS = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_64_TO_32_BIT_CONVERSION = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_ABOUT_RETURN_TYPE = YES_ERROR;
+ GCC_WARN_UNDECLARED_SELECTOR = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_UNINITIALIZED_AUTOS = YES_AGGRESSIVE;
+ GCC_WARN_UNUSED_FUNCTION = YES;
+ GCC_WARN_UNUSED_VARIABLE = YES;
+ INFOPLIST_FILE = Tests/Info.plist;
+ LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = (
+ "$(inherited)",
+ "@executable_path/../Frameworks",
+ "@loader_path/../Frameworks",
+ );
+ MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET = 10.14;
+ MTL_ENABLE_DEBUG_INFO = NO;
+ MTL_FAST_MATH = YES;
+ PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = swift.algorithm.club.Tests;
+ PRODUCT_NAME = "$(TARGET_NAME)";
+ SDKROOT = macosx;
+ SWIFT_COMPILATION_MODE = wholemodule;
+ SWIFT_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL = "-O";
+ SWIFT_VERSION = 4.2;
+ };
+ name = Release;
+ };
+/* End XCBuildConfiguration section */
+
+/* Begin XCConfigurationList section */
+ 6AF0999B216B545D00F69B16 /* Build configuration list for PBXProject "Tests" */ = {
+ isa = XCConfigurationList;
+ buildConfigurations = (
+ 6AF0999C216B545D00F69B16 /* Debug */,
+ 6AF0999D216B545D00F69B16 /* Release */,
+ );
+ defaultConfigurationIsVisible = 0;
+ defaultConfigurationName = Release;
+ };
+ 6AF099A8216B54D500F69B16 /* Build configuration list for PBXNativeTarget "Tests" */ = {
+ isa = XCConfigurationList;
+ buildConfigurations = (
+ 6AF099A9216B54D500F69B16 /* Debug */,
+ 6AF099AA216B54D500F69B16 /* Release */,
+ );
+ defaultConfigurationIsVisible = 0;
+ defaultConfigurationName = Release;
+ };
+/* End XCConfigurationList section */
+ };
+ rootObject = 6AF09998216B545D00F69B16 /* Project object */;
+}
diff --git a/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme b/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1288fd9a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/Tests.xcodeproj/xcshareddata/xcschemes/Tests.xcscheme
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/Tests/Info.plist b/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/Tests/Info.plist
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6c40a6cd0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Karatsuba Multiplication/Tests/Tests/Info.plist
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+
+
+
+
+ CFBundleDevelopmentRegion
+ $(DEVELOPMENT_LANGUAGE)
+ CFBundleExecutable
+ $(EXECUTABLE_NAME)
+ CFBundleIdentifier
+ $(PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER)
+ CFBundleInfoDictionaryVersion
+ 6.0
+ CFBundleName
+ $(PRODUCT_NAME)
+ CFBundlePackageType
+ BNDL
+ CFBundleShortVersionString
+ 1.0
+ CFBundleVersion
+ 1
+
+
diff --git a/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/KnuthMorrisPratt.playground/Contents.swift b/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/KnuthMorrisPratt.playground/Contents.swift
index 6609c9abe..9b4a50fa0 100644
--- a/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/KnuthMorrisPratt.playground/Contents.swift
+++ b/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/KnuthMorrisPratt.playground/Contents.swift
@@ -1,13 +1,8 @@
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play
-// last checked with Xcode 9.0b4
-#if swift(>=4.0)
-print("Hello, Swift4!")
-#endif
-
func ZetaAlgorithm(ptnr: String) -> [Int]? {
- let pattern = Array(ptnr.characters)
+ let pattern = Array(ptnr)
let patternLength: Int = pattern.count
guard patternLength > 0 else {
@@ -65,7 +60,7 @@ extension String {
func indexesOf(ptnr: String) -> [Int]? {
- let text = Array(self.characters)
+ let text = Array(self)
let pattern = Array(ptnr.characters)
let textLength: Int = text.count
diff --git a/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/KnuthMorrisPratt.swift b/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/KnuthMorrisPratt.swift
index 81bc65278..be0cd961d 100644
--- a/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/KnuthMorrisPratt.swift
+++ b/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/KnuthMorrisPratt.swift
@@ -12,8 +12,8 @@ extension String {
func indexesOf(ptnr: String) -> [Int]? {
- let text = Array(self.characters)
- let pattern = Array(ptnr.characters)
+ let text = Array(self)
+ let pattern = Array(ptnr)
let textLength: Int = text.count
let patternLength: Int = pattern.count
diff --git a/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/README.markdown b/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/README.markdown
index 95fdea9e9..2e4d5360b 100644
--- a/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/README.markdown
+++ b/Knuth-Morris-Pratt/README.markdown
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ let concert = "🎼🎹🎹🎸🎸🎻🎻🎷🎺🎤👏👏👏"
concert.indexesOf(ptnr: "🎻🎷") // Output: [6]
```
-The [Knuth-Morris-Pratt algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knuth–Morris–Pratt_algorithm) is considered one of the best algorithms for solving the pattern matching problem. Although in practice [Boyer-Moore](../Boyer-Moore/) is usually preferred, the algorithm that we will introduce is simpler, and has the same (linear) running time.
+The [Knuth-Morris-Pratt algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knuth–Morris–Pratt_algorithm) is considered one of the best algorithms for solving the pattern matching problem. Although in practice [Boyer-Moore](../Boyer-Moore-Horspool/) is usually preferred, the algorithm that we will introduce is simpler, and has the same (linear) running time.
The idea behind the algorithm is not too different from the [naive string search](../Brute-Force%20String%20Search/) procedure. As it, Knuth-Morris-Pratt aligns the text with the pattern and goes with character comparisons from left to right. But, instead of making a shift of one character when a mismatch occurs, it uses a more intelligent way to move the pattern along the text. In fact, the algorithm features a pattern pre-processing stage where it acquires all the informations that will make the algorithm skip redundant comparisons, resulting in larger shifts.
diff --git a/Kth Largest Element/README.markdown b/Kth Largest Element/README.markdown
index aba2d9c29..b23d22b74 100644
--- a/Kth Largest Element/README.markdown
+++ b/Kth Largest Element/README.markdown
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ Now, all we must do is take the value at index `a.count - k`:
a[a.count - k] = a[8 - 4] = a[4] = 9
```
-Of course, if you were looking for the k-th *smallest* element, you'd use `a[k]`.
+Of course, if you were looking for the k-th *smallest* element, you'd use `a[k-1]`.
## A faster solution
@@ -84,29 +84,29 @@ The index of pivot `9` is 4, and that's exactly the *k* we're looking for. We're
The following function implements these ideas:
```swift
-public func randomizedSelect(array: [T], order k: Int) -> T {
+public func randomizedSelect(_ array: [T], order k: Int) -> T {
var a = array
- func randomPivot(inout a: [T], _ low: Int, _ high: Int) -> T {
+ func randomPivot(_ a: inout [T], _ low: Int, _ high: Int) -> T {
let pivotIndex = random(min: low, max: high)
- swap(&a, pivotIndex, high)
+ a.swapAt(pivotIndex, high)
return a[high]
}
- func randomizedPartition(inout a: [T], _ low: Int, _ high: Int) -> Int {
+ func randomizedPartition