This repository can be used as a template to create new collections of OGC Building Blocks.
Building Blocks can be reused by either:
-
cut and paste "ready to use" forms from the "build/" directory
-
directly reference the artefacts in the "build" directory using the URL pattern specified in the building block description
-
including as source using
git submodule add {building block repository}and referencing reused components directly. (in which case the build/ resources of the submodule will referenced in the build/ outputs, but the source definitions will be used for consistency checking and optimisation)
The following image summarizes the general usage of a building block:
The _sources directory will contain the sources for the building blocks inside this repository.
bblock.json: Contains the metadata for the building block. Please refer to this JSON schema for more information.description.md: Human-readable, Markdown document with the description of this building block.examples.yaml: A list of examples for this building block. See Examples below.schema.json: JSON schema for this building block, if any. See JSON schema below.schema.yaml, in YAML format, is also accepted (and even preferred).
assets/: Documentation assets (e.g. images) directory. See Assets below.tests/: Test resources. See Validation.
This repository includes a sample building block in the my-building-block directory.
Building Block identifiers are automatically generated in the form:
<identifier-prefix><bb-path>
where:
identifier-prefixis read frombblocks-config.yaml. This will initially be a placeholder value, but should have an official value eventually (see How-to).bb-pathis the dot-separated path to the building block inside the repository.
For example, given a r1.branch1. identifier prefix and a cat1/cat2/my-bb/bblock.json metadata file,
the generated identifier would be r1.branch1.cat1.cat2.my-bb. This applies to the documentation
subdirectories as well, after removing the first element (e.g., Markdown documentation will be written to
generateddocs/markdown/branch1/cat1/cat2/my-bb/index.md).
The build/ directory will contain the reusable assets for implementing this building block.
Sources minimise redundant information and preserve original forms of inputs, such as externally published schemas, etc. This allow these to be updated safely, and also allows for alternative forms of original source material to be used whilst preserving uniformity of the reusable assets.
The build directory should never be edited. Moreover, applications should only use (copy or reference) resources
from this directory.
Each example consists of Markdown content and/or a list of snippets. snippets, in turn,
have a language (for highlighting, language tabs in Slate, etc.) and the code itself.
The examples.yaml file in my-building-block can be used as a template.
If a schema.json (or schema.yaml) file is found, it is not necessary to add the schema property
to bblock.json; it will be done automatically on the OGC Building Blocks Register. The same thing
applies to the context.jsonld file and the ldContext property.
References to the schemas of other building blocks can be added using $ref. The special $_ROOT_/ directory
can be used to refer to the root of the central OGC Building Blocks tree.
The Building block design allows for "semantic annotation" through the use of a context document that cross references each schema element to a URI, using the JSON-LD syntax. The end result is still a valid JSON schema, but may also be parsed as flexible RDF graphs if desired.
This provides multiple significant improvements over undocument schemas:
- differentiates between the same and different meanings for common element names used in different places
- can be used to link to a semantic model further describing each element
- allows use of advanced, standardised validation of instance data
- allows automated annotation of schemas themselves for tools able ot exploit additional information
The JSON schema for a building block is optionally linked to a conceptual model by using a root-level x-jsonld-context
property pointing to a JSON-LD context document (relative paths are ok). The Building Blocks Register can
then annotate every property inside the JSON schemas with their corresponding RDF predicate automatically.
The tests directory contains test resources that can be used for performing validation tasks. There are two
types of validations:
- JSON schema
- RDF / SHACL
Inside the tests directory, 4 types of files will be processed:
*.shacl: SHACL documents that will be used for RDF validation.*.ttl: Turtle RDF files that will be validated against the SHACL rules.*.jsonld: JSON-LD files that will be first validated against the Building Block JSON Schema and then against the SHACL rules.*.json: JSON files that will be first validated against the JSON Schema, then "semantically uplifted" by embedding the Building Block'scontext.jsonld, and finally validated against the SHACL rules.
Assets (e.g., images) can be placed in the assets/ directory for later use in documentation pages,
by using references to @@assets@@/filename.ext.
For example, a sample.png image in that directory can be included in the description
Markdown code of a building block like this:
A super building block is a building block whose schema.yaml is automatically generated as the oneOf
union of all the schemas recursively found in all its subdirectories. This needs to be enabled
in bblock.json by setting the superBBlock property to true.
When super building block mode is enabled, the schema.yaml inside the source directory for the building
block will be overwritten.
- Fork (or click on "Use this template" on GitHub) this repository.
- For each new building block, replace or create a copy of the
my-building-block. Note: the name of the new directory will be part of the building block identifier. - Update the building block's files.
- Replace this README.md file with documentation about the new building block(s).
- Contact OGC and request that your new building block(s) be added to the official Register.
- Set the
identifier-prefixprovided by OGC inbblocks-config.yaml.
Note: building blocks subdirectories can be grouped inside other directories, like so:
type1/
bb1-1/
bblock.json
bb1-2/
bblock.json
type2/
subtype2-1/
bb2-1-1/
bblock.json
[...]
In that case, type1, type2 and subtype2-1 will also be part of the building block identifiers.
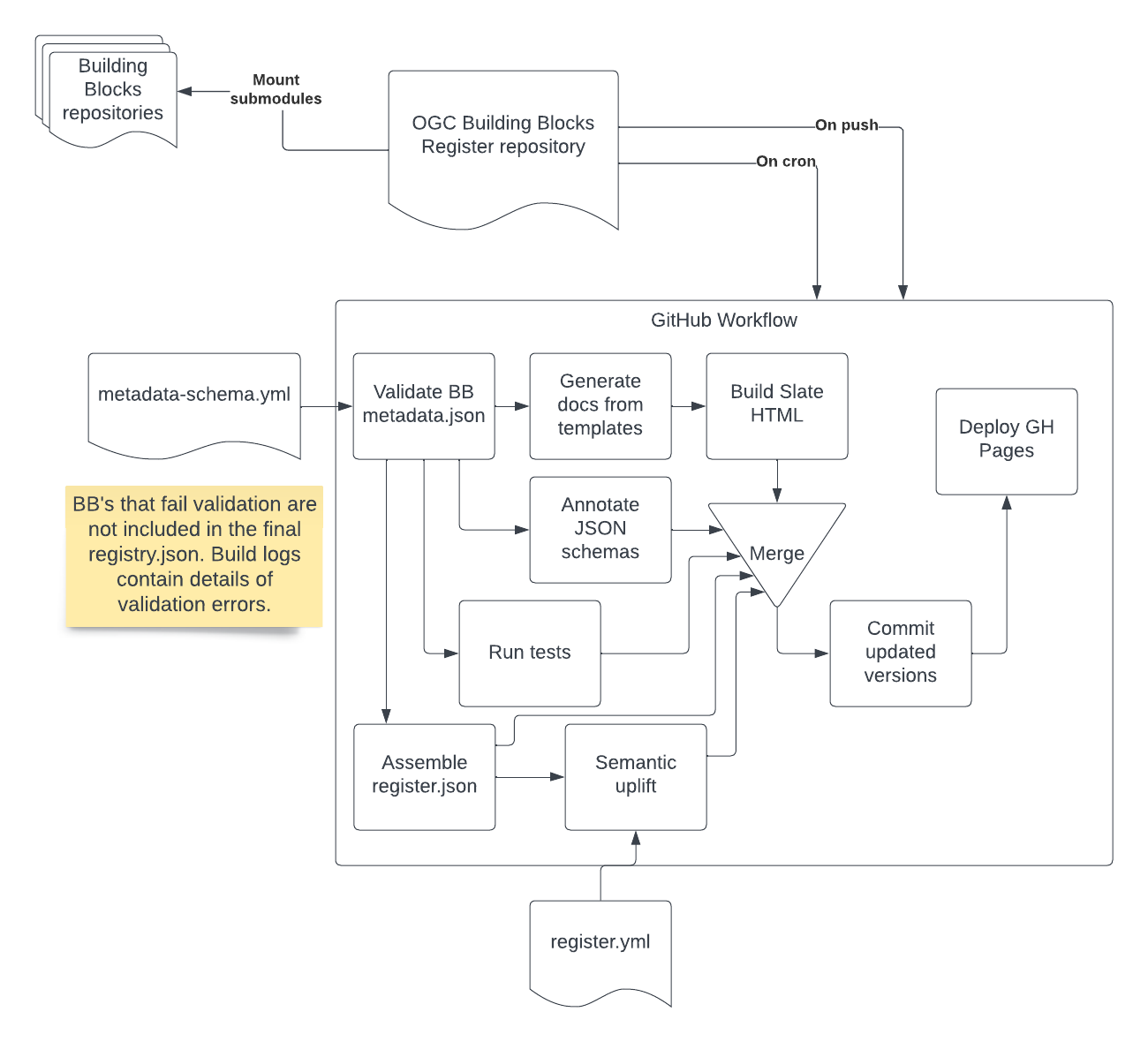
This repository comes with a GitHub workflow that detects, validates and processes its building blocks, so that their outputs can be tested before inclusion in the main OGC Register:
The outputs can be generated locally by running the following:
# Process building blocks
docker run --rm --workdir /workspace -v $(pwd):/workspace ghcr.io/opengeospatial/bblocks-postprocess \
--clean --base-url https://example.com/base-url/
# Optional - build Slate docs
docker run --rm -v "$(pwd)/generateddocs/slate:/srv/slate/source" \
-v "$(pwd)/generateddocs/slate-build:/srv/slate/build" slatedocs/slate buildNotes:
- Docker must be installed locally for the above commands to run
- The value for
--base-urlwill be used to generate the public URLs (schemas, documentation, etc.) - If you want to clean your build (go back to the original repository status), you can do so by running
git checkout build; git clean -xf build