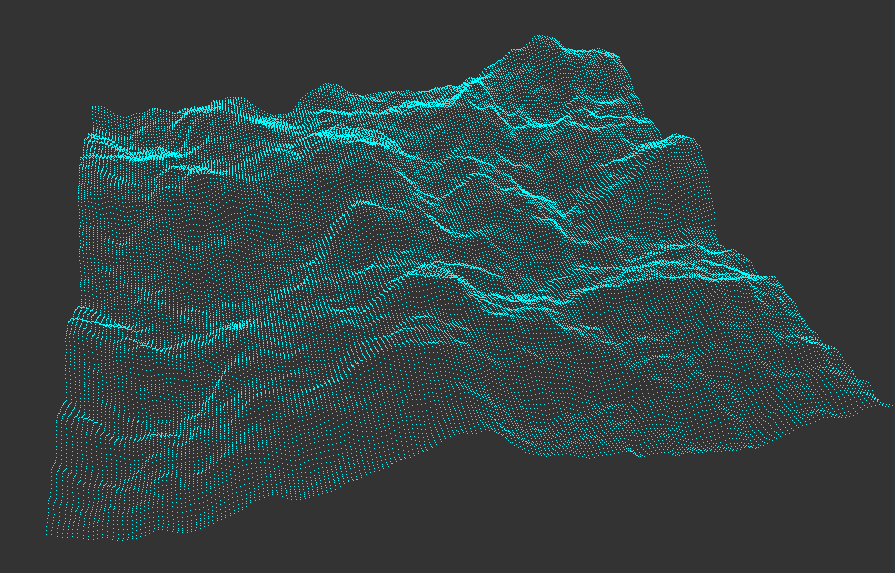
Toy Game Engine implementation for MEGA, M20253-2021/22
It has procedural terrain generation using perlin noise, first person player and .obj file loader. More to come.
- OpenGL
- glut
- Object Collision
- Basic physics simulation
- Procedural terrain destruction with 3D perlin noise
Procedural Terrain
#include <Procedural.h>
ProceduralTerrain(seed, width, length, resolution, flatness,
realistic (true) or smooth (false));
ProceduralTerrain( 6942069, 10, 10, 400, 30, true );
Model Viewer
#include <Visualisation.h>
// generate or load a model of a specific topography type.
viewModel(model, MEGA_QUADS, argc, argv );
viewModel(model, MEGA_TRIANGLES, argc, argv );
// For now, the macros that define what is shown are in the header file
// you can comment out any the top macros : SHOW_VERTICES, SHOW_QUADS,
// SHOW_NORMALS and SHOW_COLLISION
.OBJ Loader
#include <IO.h>
Model a = loadModel("path to model");
// For now this supports only vertices, faces and normals. It also skips comments.
Generate Primitive Geometrical Shapes
#include <GeometricPrimitives.h>
Plane( width, height, step_width, step_height, collision );
Plane( 1, 1, 40, 40, true );
Sphere( radius, sector_resolution, stack_resolution, collision);
Sphere( 1.0f, 36, 18, false);
// This computes the normals for shaders.
Matrix types follow the format:
TYPE (U)nsigned (S)igned (F)loat) + DEPTH (8, 16, 32, 64) + CHANNELS (1, 2, 3)
U8C1 - unsigned integer of 8 bit depth with one channel - uint_t
F32C3 - float value of 32 bit depth with 3 channels.
// Default Constructor
Matrix<F32C1> a;
// Array Constructor
F64C1 array = { 0.3, 0.8451, 0.6598745, 4.126654, 0.25486, 0.789215 };
Matrix<F64C1> b (2, 3, array); // The size of array must not be bigger or smaller than rows*cols
// Fill Constructor
Matrix<U32C1> c (5, 5, (U32C1)value); // It is recomanded to cast the value into the right type.
// Copy Constructor
Matrix<U8C1> d (5, 5, (U8C1)69);
Matrix<U8C1> e (d);
// Identity Constructor
Matrix<F32C1> f;
f.eye(10) // fills f with an identity matrix of size 10Getting values
a.row(index); // returns the row at the specific index
a.col(index); // returns the col at the specific index
a.at(x, y); // returns the specific value at column x and row y
a.data; // returns all the matrix data in the expected type;Helpers
a.cols; // returns the number of columns in a
a.rows; // returns the number of rows in a
a.det(); //returns the determinant
a.inverse(); // returns the inverse of matrix a
std::cout << a << std::endl; // prints the matrix to the console in a readable formatSpecialized matrices
Matrix<F64C1> a;
// Translation Matric
/* 1 0 0 tx
0 1 0 ty
0 0 1 tz
0 0 0 1 */
a.translation( size_t tx, size_t ty, size_t tz);
// Rotation Matrices
a.rotation ( std:vector<F64C1> src );
a.rotationX ( double angle );
a.rotationY ( double angle );
a.rotationZ ( double angle );
/* 1 0 0 cosB 0 -sinB cosY sinY 0 r11 r12 r13
Rx = 0 cos& sin& Ry = 0 1 0 Rz = -sinY cosY 0 R = r21 r22 r23
0 -sin& cos& sinB 0 cosB 0 0 1 r31 r32 r33 */
// Scaling Matrix
/* sx 0 0 0
0 sy 0 0
0 0 sz 0
0 0 0 1 */
a.scaling ( size_t x, size_t y, size_t z );
// Rotation and Translation Matrix
/* r11 r12 r13 tx
r21 r22 r23 ty
r31 r32 r33 tz
0 0 0 1 */
a.Rt( size_t x, size_t y, size_t z );
The vector follows the same types as the Matrix class.
// Default Constructor
Vector<F32C1> a;
// Array Constructor
// The size of the array should not be bigger or smaller than rows*cols.
F64C1 array = { 0.3, 0.8451, 0.6598745, 4.126654, 0.25486, 0.789215 };
Vector<F64C1> b (2, 3, array);
// std::vector Constructor
// The size of the array should not be bigger or smaller than rows*cols.
std::vector<F64C1> val { 0.3, 0.8451, 0.6598745, 4.126654, 0.25486, 0.789215 };
Vector<F64C1> b (2, 3, val);
// Copy Constructor
Vector<U8C1> c (b);Manipulate values
a[ index ] // Use the operator[] to get item at index.
a.push_back( item ) // Add another item into the vector. Must be of same type as the vector.
a.push_back( std::vector<type> ) // You can also add vectors
a.push_back( Vector<type> )
a.data; // returns all the vector data in the expected type;Arithmatic
a.dot( b ) // dot product of a and b
a == b // compare a and b
a (operator) b // any operator works, +, -, *, /, etc.Helpers
a.size // returns the size of the vector
a.L // length of the vector
a.T() // transpose vector
std::cout << a << std::endl; // prints the matrix to the console in a readable format
We make use of Quaternions, Euler Angles and Rotation Matrices. Quaternions and Euler Angles have their own classes, while Rotation matrices can easily be formed using the standard matrix class.
// Creating Quanternions
Quaternion a;
Quaternion b( 0.19701792944740, -0.003000273037276, -0.930084641554, 0.3100282138517);
Quaternion c( Matrix<F64C1>& src ); // Rotation Matrix -> Quaternion
Quaternion d( EulerAngle& src); // Euler Angles -> Quaternion// Creating Euler Angles
EulerAngle a;
EulerAngle b( 0.13762212611904287, 0.3732315081176748, -2.472067119945251 );
EulerAngle d( Matrix<F64C1>& src); // Rotation Matrix -> Euler Angles
EulerAngle c( Quaternion& src ); // Quaternion -> Euler Angles// Creating a Rotation Matrix;
Matrix<F64C1> a;
a.rotation( std::vector<F64C1> src ); // full rotation matrix
a.rotationX( std::vector<F64C1> src ); // rotation around the X axis;
a.rotationY( std::vector<F64C1> src ); // rotation around the Y axis;
a.rotationZ( std::vector<F64C1> src ); // rotation around the Z axis;
// Quanternion -> Rotation Matrix
Quaternion quat( 0.19701792944740, -0.003000273037276, -0.930084641554, 0.3100282138517);
Matrix<F64C1> b = quat.toRotMat();
// Euler Angles -> Rotation Matrix
EulerAngle eul( 0.13762212611904287, 0.3732315081176748, -2.472067119945251 );
Matrix<F64C1> c = eul.toRotMat();Arithmetic
// Quaternions
Quaternion a( 0.19701792944740, -0.003000273037276, -0.930084641554, 0.3100282138517);
Quaternion b( 0.19701792944740, -0.003000273037276, -0.930084641554, 0.3100282138517);
a + b;
a - b;
a * b;
a / b;
Quaternion.innerProduct( a, b );Euler Angles don't have arithmatic functions. Rotation Matrices inherit all the arithmatic operations from the Matrix class.
Helpers
// Quaternions
Quaternion a;
a.normalize() // normalise the values
a.invert() // invert the values
std::cout << a << std::endl; // display the quat in a readable format in the console.// Euler Angles
EulerAngle a;
std::cout << a << std::endl; // display the angles in a readable format in the console.
All of the game meshes are derived from the parent Object class.
class Object {
protected:
Model Model;
Material Material;
Matrix<F32C1> t;
Quaternion Direction;
public:
virtual Object(); // Default Constructor
virtual Object( const Object& obj ); // Copy constructor
virtual Object( Model model, Material material, Vector& coordinates); // Create new object
virtual ~Object(); // Destructor
virtual void render();
virtual void move(Matrix& Rt);
virtual void setStatic( bool set) const;
// OpenGL functions
void Draw( Shader &shader );
bool changedSinceLastFrame = false; // only objects that have changed will be re-rendered for the next frame
mutable bool Static = false; // only non-static objects will be rendered every frame
private:
// OpenGL functions
unsigned int VAO, VBO, EBO;
void setupMesh();
const uint16_t world_id;
static uint32_t next_id;
};