LDM3D model
The LDM3D model was proposed in the paper LDM3D: Latent Diffusion Model for 3D, authored by Gabriela Ben Melech Stan, Diana Wofk, Scottie Fox, Alex Redden, Will Saxton, Jean Yu, Estelle Aflalo, Shao-Yen Tseng, Fabio Nonato, Matthias Muller, and Vasudev Lal.
LDM3D was accepted to the IEEE / CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR) in 2023.
For better results, do not hesitate to use our new checkpoint, ldm3d-4c based on a slighlty different architecture.
The following new LDM3D model checkpoints have been released:
- ldm3d-4c: A new version of LDM3D with higher quality results.
- ldm3d-pano: LDM3D applied to panoramic images.
- ldm3d-sr: Upscaler for LDM3D.
Model details
The abstract from the paper is the following: This research paper proposes a Latent Diffusion Model for 3D (LDM3D) that generates both image and depth map data from a given text prompt, allowing users to generate RGBD images from text prompts. The LDM3D model is fine-tuned on a dataset of tuples containing an RGB image, depth map and caption, and validated through extensive experiments. We also develop an application called DepthFusion, which uses the img2img pipeline to create immersive and interactive 360-degree-view experiences using TouchDesigner. This technology has the potential to transform a wide range of industries, from entertainment and gaming to architecture and design. Overall, this paper presents a significant contribution to the field of generative AI and computer vision, and showcases the potential of LDM3D and DepthFusion to revolutionize content creation and digital experiences.
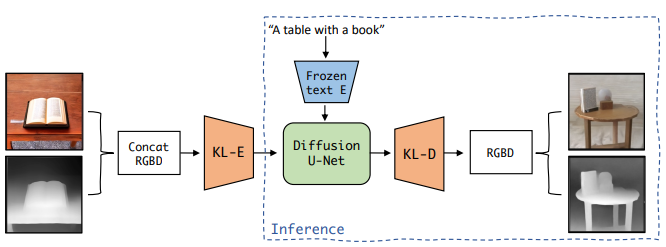 LDM3D overview taken from the LDM3D paper.
LDM3D overview taken from the LDM3D paper.
Usage
You can use this model to generate an RGB image and depth map given a text prompt. A short video summarizing the approach can be found at this url and a VR demo can be found here. A demo is also accessible on Spaces.
Here is how to use this model to get the features of a given text in PyTorch on both a CPU and GPU architecture:
from diffusers import StableDiffusionLDM3DPipeline
pipe = StableDiffusionLDM3DPipeline.from_pretrained("Intel/ldm3d")
# On CPU
pipe.to("cpu")
# On GPU
pipe.to("cuda")
prompt = "A picture of some lemons on a table"
name = "lemons"
output = pipe(prompt)
rgb_image, depth_image = output.rgb, output.depth
rgb_image[0].save(name+"_ldm3d_rgb.jpg")
depth_image[0].save(name+"_ldm3d_depth.png")
This is the result:
Training data
The LDM3D model was finetuned on a dataset constructed from a subset of the LAION-400M dataset, a large-scale image-caption dataset that contains over 400 million image-caption pairs.
Finetuning
The fine-tuning process comprises two stages. In the first stage, we train an autoencoder to generate a lower-dimensional, perceptually equivalent data representation. Subsequently, we fine-tune the diffusion model using the frozen autoencoder
Evaluation results
Quantitative results
The table below shows the quantitative results of text-conditional image synthesis on the 512 x 512-sized MS-COCO dataset with 50 DDIM steps.
| Method | FID ↓ | IS ↑ | CLIP ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| SD v1.4 | 28.08 | 34.17 ± 0.76 | 26.13 ± 2.81 |
| SD v1.5 | 27.39 | 34.02 ± 0.79 | 26.13 ± 2.79 |
| LDM3D (ours) | 27.82 | 28.79 ± 0.49 | 26.61 ± 2.92 |
Our model is on par with the Stable Diffusion models with the same number of parameters (1.06B). IS and CLIP similarity scores are averaged over 30k captions from the MS-COCO dataset.
The following table shows the evaluation results of depth evaluation comparing LDM3D and DPT-Large with respect to ZoeDepth-N that serves as a reference model.
| Method | AbsRel | RMSE [m] |
|---|---|---|
| LDM3D | 0.0911 | 0.334 |
| DPT-Large | 0.0779 | 0.297 |
The results shown above can be referenced in Table 1 and Table 2 of the LDM3D paper.
Qualitative results
The figure below shows some qualitative results comparing our method with Stable Diffusion v1.4 and with DPT-Large for the depth maps  .
.
Ethical Considerations and Limitations
For image generation, the Stable Diffusion limitations and biases apply. For depth map generation, a first limitiation is that we are using DPT-large to produce the ground truth, hence, other limitations and biases from DPT are applicable.
Caveats and Recommendations
Users (both direct and downstream) should be made aware of the risks, biases and limitations of the model.
Here are a couple of useful links to learn more about Intel's AI software:
Disclaimer
The license on this model does not constitute legal advice. We are not responsible for the actions of third parties who use this model. Please cosult an attorney before using this model for commercial purposes.
BibTeX entry and citation info
@misc{stan2023ldm3d,
title={LDM3D: Latent Diffusion Model for 3D},
author={Gabriela Ben Melech Stan and Diana Wofk and Scottie Fox and Alex Redden and Will Saxton and Jean Yu and Estelle Aflalo and Shao-Yen Tseng and Fabio Nonato and Matthias Muller and Vasudev Lal},
year={2023},
eprint={2305.10853},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
- Downloads last month
- 140
Model tree for Intel/ldm3d
Spaces using Intel/ldm3d 2
Collections including Intel/ldm3d
Evaluation results
- FID on LAION-400Mself-reported27.820
- IS on LAION-400Mself-reported28.790
- CLIP on LAION-400Mself-reported26.610
- AbsRel on LAION-400Mself-reported0.091
- RMSE [m] on LAION-400Mself-reported0.334
