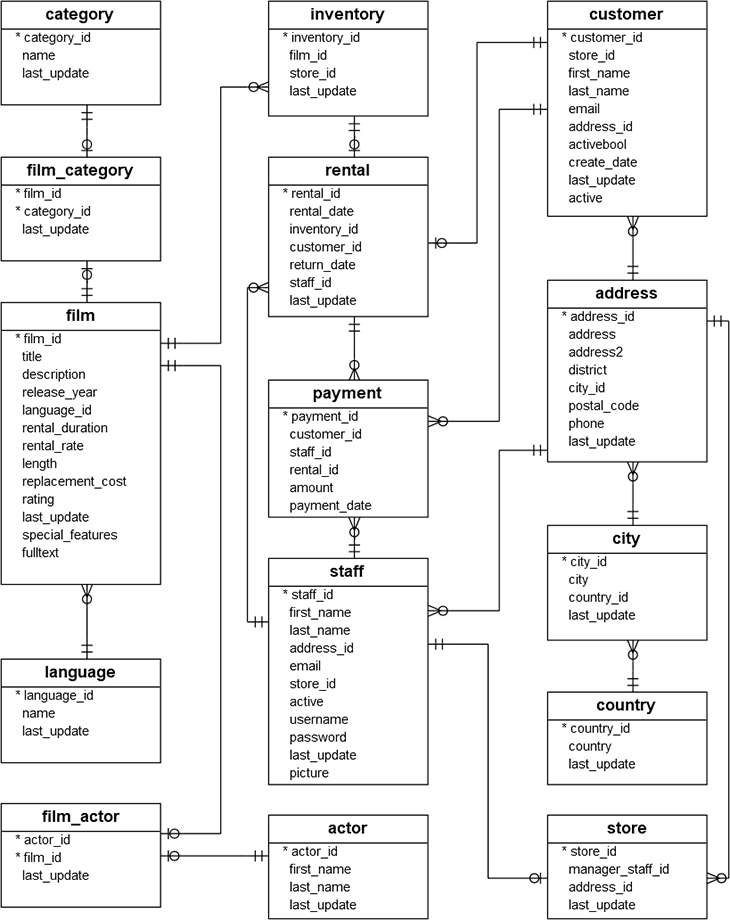
The DVD rental database is the PostgreSQL sample database which is used for learning and practicing PostgreSQL. In this repo, a total of 10 queries are written in order to analyze different business-like questions which can let the students practice how to manipulate with PostgreSQL by pgAdmin 4. The DVD rental database dataset can be downloaded from this link
- PostgreSQL (version 16)
- pgAdmin 4 (version 7.3)
- Git (version 2.37.1)
There are 15 tables in the DVD Rental database:
- actor – stores actors data including first name and last name.
- film – stores film data such as title, release year, length, rating, etc.
- film_actor – stores the relationships between films and actors.
- category – stores film’s categories data.
- film_category- stores the relationships between films and categories.
- store – contains the store data including manager staff and address.
- inventory – stores inventory data.
- rental – stores rental data.
- payment – stores customer’s payments.
- staff – stores staff data.
- customer – stores customer data.
- address – stores address data for staff and customers
- city – stores city names.
- country – stores country names.
- language – stores language data
According to the project goal, the skills demonstrated in the lessons are going to be applied in the analysis. The following 10 queries are the combination of different skills and functions that help the analysis of the DVD rental database.
Query_01: Comparison Operator
SELECT film_id, title, replacement_cost
FROM film
WHERE replacement_cost > 20
ORDER BY replacement_cost DESC
This query retrieved which film's replacement cost was larger than $20 with the film ID, film title, and the replacement cost. The table is in descending order by the replacement cost of the film. In this query, comparison operator '>' is used to compare the replacement cost of each film which larger than $20.
Query_02: Logical operator
SELECT staff_id, first_name, last_name, active
FROM staff
WHERE active in (true)
This query retrieved which staff is currently working in the DVD store with the staff ID, staff's first name, last name, and their active status. In this query, the logical operator "IN" is used to check whether the staff's active status is true or not.
Query_03: Wildcard
SELECT city_id, city
FROM city
WHERE city ILIKE '%c%'
This query retrieved which city contains the letter 'c' in their city name with their city ID. The wildcard "ILIKE" is used to check which city contains the letter 'c' in it.
Query_04: Inner join
SELECT a.actor_id, a.first_name, a.last_name, SUM(amount) AS total_amount
FROM payment p
JOIN rental r ON p.rental_id = r.rental_id
JOIN inventory i ON r.inventory_id = i.inventory_id
JOIN film f ON i.film_id = f.film_id
JOIN film_actor fc ON f.film_id = fc.film_id
JOIN actor a ON fc.actor_id = a.actor_id
GROUP BY a.actor_id
ORDER BY total_amount DESC
This query retrieved which actor earns the most revenue in DVD rental. The query joined tables payment, rental, film, film_actor, actor, and the total amount of revenue generated by actors. The table is in descending order by the total amount of revenue.
Query_05: Outer Join
SELECT f.film_id, f.title
FROM film f
JOIN inventory i ON f.film_id = i.film_id
FULL JOIN rental r ON i.inventory_id = r.inventory_id
WHERE rental_id is NULL
This query retrieved which films in inventory have never been rented with their film ID and film title. The outer join lets the query select those films that have no rental ID.
Query_06: Group BY
SELECT co.country_id, co.country, COUNT(*) as rental_count
FROM rental r
FULL JOIN customer c ON r.customer_id = c.customer_id
FULL JOIN address ad ON c.address_id = ad.address_id
FULL JOIN city ci ON ad.city_id = ci.city_id
FULL JOIN country co ON ci.country_id = co.country_id
GROUP BY co.country_id
ORDER BY rental_count DESC
This query counts the rental number in each country. The rental number of each country is counted with the group by country ID.
Query_07: Except
SELECT f.film_id, f.title
FROM film f
FULL JOIN film_actor fc ON f.film_id = fc.film_id
FULL JOIN actor a ON fc.actor_id = a.actor_id
EXCEPT
SELECT f.film_id, f.title
FROM film f
JOIN film_actor fc ON f.film_id = fc.film_id
JOIN actor a ON fc.actor_id = a.actor_id
This query retrieved the films without any actors on it. The expect operator is used to eliminate the film containing any actor.
Query_08: Sub-query
SELECT rental_id FROM rental
WHERE rental_id IN (
SELECT rental_id
FROM payment
WHERE amount = 0
)
This query retrieved the rentals that have been paid $0. The sub-query retrieved the rental ID which has a $0 amount in payment.
Query_09: CTE's
WITH max_rental_duration AS (
SELECT c.customer_id, c.first_name, c.last_name, SUM(rental_duration) AS total_rental_duration
FROM film f
JOIN inventory i ON f.film_id = i.film_id
JOIN rental r ON i.inventory_id = r.inventory_id
JOIN customer c ON r.customer_id = c.customer_id
GROUP BY c.customer_id
)
SELECT customer_id, first_name, last_name, total_rental_duration
FROM max_rental_duration
WHERE total_rental_duration = (SELECT max(total_rental_duration) FROM max_rental_duration)
This query retrieved the customer(s) who have the longest film rental duration. The CTE saves the maximum number of rental duration temporarily. After that, the query selects the total rental duration of customers who are equal to the max number of rental duration.
Query_10: Unnest
SELECT unnest(special_features) AS special_features,COUNT(1) FROM film
GROUP BY unnest(special_features)
This query counts the number of the film according to the special features. The unnest function extracted each element from the special features column.
The results of all queries have been saved in the corresponding folder of each query. The results are stored in csv files.