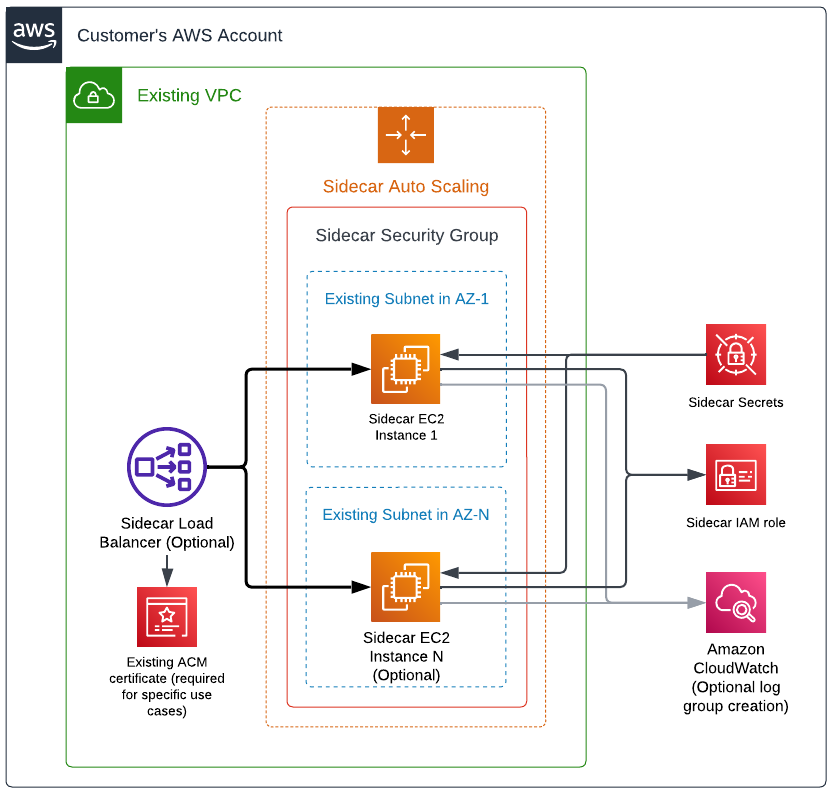
A quick start to deploy a sidecar to AWS EC2 using Terraform!
This quick start guide uses our Terraform module for AWS EC2. The source code for this module is available in the public GitHub repository terraform-aws-sidecar-ec2.
- Make sure you have access to your AWS environment with an account that has sufficient permissions to deploy the sidecar. The minimum permissions must allow for the creation of the elements listed previously. We recommend Administrator permissions (
AdministratorAccesspolicy) as the module creates an IAM role. - Install and configure the AWS CLI.
- Install Terraform.
See the Terraform module's requirements in file versions.tf.
-
Save the code below in a
.tffile (exsidecar.tf) in a new folder.- Fill the parameters
sidecar_id,control_plane,client_idandclient_secretwith the information from theCyral Templatesoption in theDeploymenttab of your sidecar details. - Fill the parameters
vpc_idandsubnetswith an existing VPC and subnets that allows network connectivity to the Cyral control plane (outbound HTTPS and gRPC traffic using port443) and to the database you plan to protect with this sidecar.
- Fill the parameters
-
Open a command line terminal in the new folder.
-
Configure the AWS CLI credentials or provide them through environment variables.
-
Run
terraform initfollowed byterraform apply.
provider "aws" {
# Define the target AWS region
region = "us-east-1"
}
module "cyral_sidecar" {
source = "cyralinc/sidecar-ec2/aws"
version = "~> 5.0" # terraform module version
sidecar_id = ""
control_plane = ""
client_id = ""
client_secret = ""
# The ports that the sidecar will allow for incoming connections.
# The set of ports below includes the default ports for all of
# our currently supported repositories and considers MongoDB
# ports in the range from 27017 to 27019.
sidecar_ports = [
443, 453, 1433, 1521, 3306, 5432, 5439, 9996, 9999,
27017, 27018, 27019, 31010
]
vpc_id = "<vpc-id>"
subnets = ["<subnet-id>"]
#############################################################
# DANGER ZONE
# The following parameters will expose your sidecar to the
# internet. This is a quick set up to test with databases
# containing dummy data. Never use this configuration if you
# are binding your sidecar to a database that contains any
# production/real data unless you understand all the
# implications and risks involved.
# If you provided private subnets, set this to `false`
associate_public_ip_address = true
# Do not deploy a load balancer, meaning it will also use
# a single EC2 instance for this sidecar
deploy_load_balancer = false
# Unrestricted inbound to SSH into EC2 instances
ssh_inbound_cidr = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
# Unrestricted inbound to ports defined in `sidecar_ports`
db_inbound_cidr = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
# Unrestricted inbound to monitor EC2 instances (port 9000)
monitoring_inbound_cidr = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
#############################################################
}The quick start example above will create the simplest configuration possible on your AWS account and deploy a single sidecar instance without a load balancer.
Deploying a test sidecar is the easiest way to have a sidecar up and running to understand the basic concepts of our product.
In case the databases you are protecting with the Cyral sidecar also live on AWS, make sure to
add the sidecar security group (see output parameter aws_security_group_id) to the list of
allowed inbound rules in the databases' security groups. If the databases do not live on AWS,
analyze what is the proper networking configuration to allow connectivity from the EC2
instances to the protected databases.
- Save the code below in a
.tffile (exsidecar.tf) in a new folder.- Fill the parameters
sidecar_id,control_plane,client_idandclient_secretwith the information from theCyral Templatesoption in theDeploymenttab of your sidecar details. - Fill the parameters
vpc_idandsubnetswith an existing VPC and subnets that allows network connectivity to the Cyral control plane (outbound HTTPS and gRPC traffic using port443) and to the database you plan to protect with this sidecar. - Fill the remaining parameters as intructed in the comments.
- Fill the parameters
- Open a command line terminal in this new folder.
- Configure the AWS CLI credentials or provide them through environment variables.
- Run
terraform initfollowed byterraform apply.
provider "aws" {
# Define the target AWS region
region = "us-east-1"
}
module "cyral_sidecar" {
source = "cyralinc/sidecar-ec2/aws"
version = "~> 5.0" # terraform module version
sidecar_id = ""
control_plane = ""
client_id = ""
client_secret = ""
# Assign the version that will be used by the sidecar instances.
# Remove the parameter or leave it empty should you prefer to
# perform upgrades directly from the control plane using the
# 1-click upgrade.
sidecar_version = ""
# The ports that the sidecar will allow for incoming connections.
# The set of ports below includes the default ports for all of
# our currently supported repositories and considers MongoDB
# ports in the range from 27017 to 27019.
sidecar_ports = [
443, 453, 1433, 1521, 3306, 5432, 5439, 9996, 9999,
27017, 27018, 27019, 31010
]
# Use 2 instances `m5.large`
instance_type = "m5.large"
asg_min = 1
asg_desired = 2
asg_max = 4
vpc_id = "<vpc-id>"
# For production use cases, provide multiple subnets in
# different availability zones.
subnets = [
"<subnet-az1-id>",
"<subnet-az2-id>",
"<subnet-azN-id>"
]
associate_public_ip_address = false
load_balancer_scheme = "internal"
enable_cross_zone_load_balancing = true
# Restrict the inbound to SSH into the EC2 instances
ssh_inbound_cidr = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
# Restrict the inbound to ports defined in `sidecar_ports`
db_inbound_cidr = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
# Restrict the inbound to monitor the EC2 instances (port 9000)
monitoring_inbound_cidr = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}The example above will create a production-grade configuration and assumes you understand the basic concepts of a Cyral sidecar.
For a production configuration, we recommend that you provide multiple subnets in different availability zones and properly assess the dimensions and number of EC2 instances required for your production workload.
In order to properly secure your sidecar, define appropriate inbound CIDRs using variables
ssh_inbound_cidr, db_inbound_cidr and monitoring_inbound_cidr or define inbound
rules using variables ssh_inbound_security_group and db_inbound_security_group. Beware
that defining CIDR and security group rules at the same time is not allowed. See the
input variables documentation in the module's input section
for more information.
In case the databases you are protecting with the Cyral sidecar also live on AWS, make sure to
add the sidecar security group (see output parameter aws_security_group_id) to the list of
allowed inbound rules in the databases' security groups. If the databases do not live on AWS,
analyze what is the proper networking configuration to allow connectivity from the EC2
instances to the protected databases.
See the full list of parameters in the module's docs.
This quick start supports 1-click upgrade.
Instructions for sidecar upgrade are available in the module's docs.
Instructions for advanced configurations are available in the module's docs.