Leveraging Langchain to create a quantitative and qualitative GenAI chatbot
This project shows how you can use ChatGPT to query documents for qualitative information, as well as querying databases for quantitative information. Users can interact with a chatbot using natural language to find the information they need.
The bot in this project has been "trained" on a library of documents about the 2023 MLB season to learn qualitative information (MVP, etc.). It can also translate quantitative questions from users into SQL, querying the Postgresql database about batting averages to provide analysis.
Check out the demo recording!
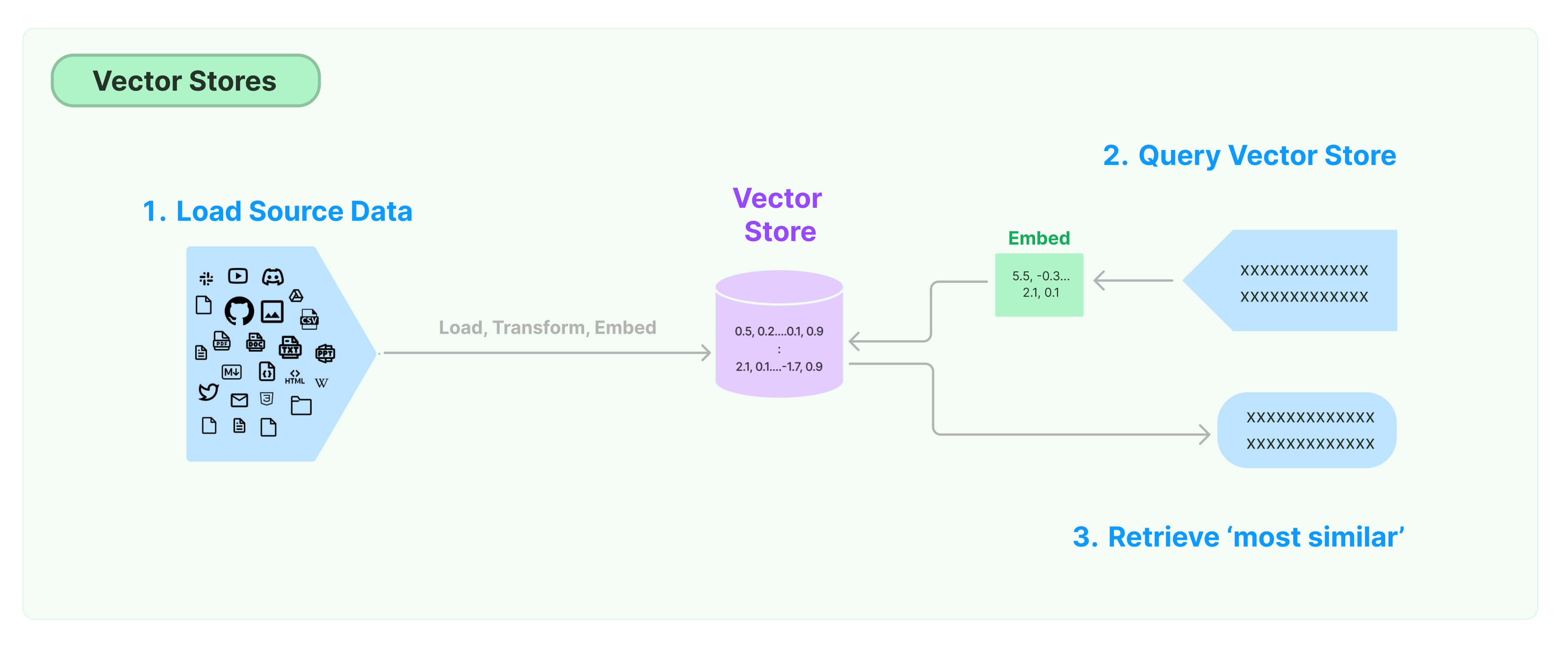
ai-chat-assistant leverages the Langchain library to interact with ChatGPT. To answer qualitative questions, it loads various files (PDF, JSON, etc.) from a local directory. It then chunks and embeds these into a Vector Store database to optimize training and response performance.
Obviously, this simple use case is only for the 2023 MLB season - but it can be easily extended on your own using whatever relevant documents you want to provide.
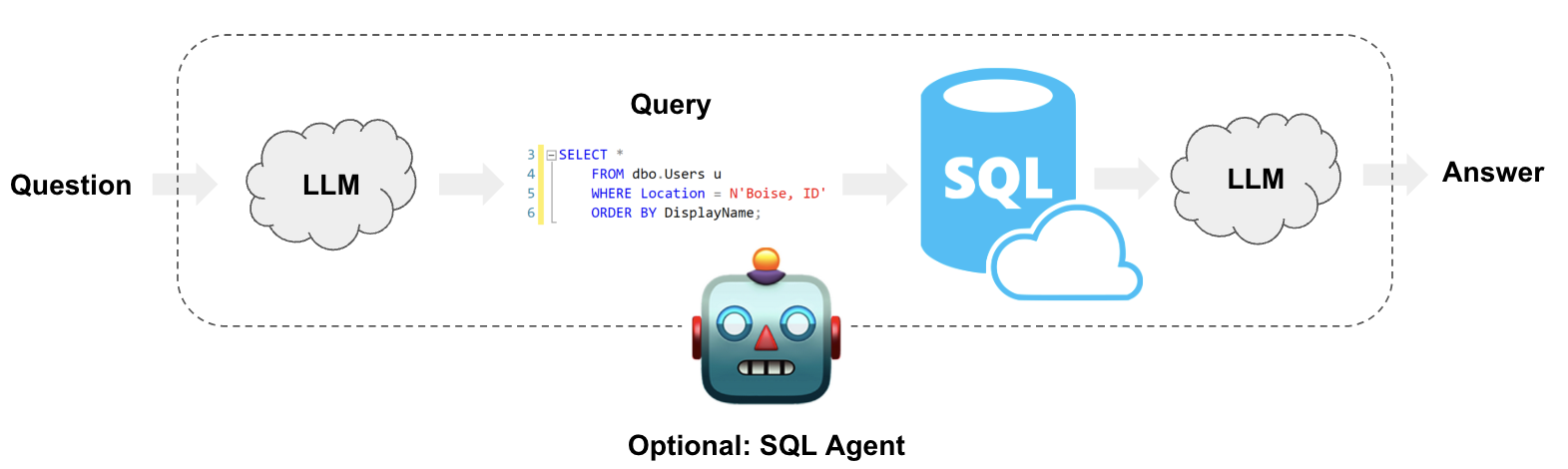
To answer quantitative questions, ai-chat-assistant interprets the user's questions into SQL based on its understanding of select MLB stat tables in Postgres. It then interprets the responses to its queries to provide natural-language analysis based on the user's prompt.
This repository uses a Flask API in order to interact with the OpenAI API. It uses a React app for the user interface and chatbot, and a local Postgres container for the database. The API, UI, and DB are all containerized with Docker, and orchestrated via docker-compose.
The goal of this project is to show how it can be extended for more practical use cases. The UI can be replaced with an integration to Slack or Teams for a chatbot, and the local DB would be replaced with one used for business needs.
Functions to interact with Langchain and the LLM are stored in the langchain_functions folder. Utility functions for connecting to Postgresql and logging errors are stored in the utils folder. MLB information documents are stored in the training_scripts folder. The Postgresql datbase is seeded on start with batting average data, and the table needed for logging ChatGPT messages.
In order to run this project, you will your own OpenAI API Key. If you have not yet created a login and API Key, follow the instructions here.
Additionally, the Free Tier of OpenAI API is too low for this project. This program is still very inexpensive to run (probably will use less than $.10), but without funding your account you will hit the Free Tier API Limits. Please make sure you have funded your OpenAI API account - probably at least $.50 will be sufficient.
- Clone the repository onto your local machine
- Including the following in your
.envfile in the root directory (replacing the OPENAI_API_KEY value):OPENAI_API_KEY=xxx POSTGRES_USER=admin POSTGRES_PASSWORD=admin POSTGRES_DB=postgres POSTGRES_HOST=localhost - From the root directory, run
docker compose up - Navigate to
localhostin your browser URL to access the chatbot
- Clone the repository onto your local machine
- In a terminal window, navigate to the
web-uidirectory and runnpm start - In another terminal window, navigate to the
openai-apidirectory and runflask --app app run - Add a
.envfile to theopenai-apidirectory - Including the following in your
.envfile in the root directory (replacing the OPENAI_API_KEY value):OPENAI_API_KEY=xxx POSTGRES_USER=admin POSTGRES_PASSWORD=admin POSTGRES_DB=postgres POSTGRES_HOST=localhost - In a third terminal window, run
docker compose -f dc-local-db.yml upfrom the root directory to start the database - Navigate to
localhost:3000in your browser URL to access the chatbot