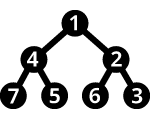
A simple and super efficient priority Queue for .NET that uses a min heap for the underlying data structure.
| Method | Operation | Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Peek() | Find Min | O(1) |
| Offer() | Insert | O(log(n)) |
| Poll() | Dequeue | O(log(n)) |
You can read more about heaps here : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heap_(data_structure)
To install Priority Queue For .Net, run the following command in the Package Manager Console
Install-Package RapidPriorityQueue
IComparer<int> comparer = new IntComparer();
var queue = new PriorityQueue<int>(comparer);
var rando = new Random();
var max = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++)
{
queue.Offer(rando.Next(max));
}
while (queue.Count > 0)
{
var next = queue.Poll();
}Unfortunately int is the only primitive type that I have implemented so far, but it's easy to create your own, see below.
public class Badger
{
public string Color { get; set; }
public double Weight { get; set; }
}public class BadgerComparer : IComparer<Badger>
{
public int Compare(Badger x, Badger y)
{
return x.Weight.CompareTo(y.Weight);
}
}var badgers = new []
{
new Badger { Color = "White", Weight = 20.5 },
new Badger { Color = "Brown", Weight = 53.71 },
new Badger { Color = "Black", Weight = 16.3 },
};
var badgerComparer = new BadgerComparer();
var badgerQueue = new PriorityQueue<Badger>(badgerComparer);
foreach (var badger in badgers)
{
badgerQueue.Offer(badger);
}
while (badgerQueue.Count > 0)
{
var nextBadger = badgerQueue.Poll();
Console.WriteLine("The {0} badger weighs {1} lbs", nextBadger.Color, nextBadger.Weight);
}If you run the program you will see that the badgers are dequeued in the proper order, by ascending weight!
The Black badger weighs 16.3 lbs
The White badger weighs 20.5 lbs
The Brown badger weighs 53.71 lbs