EvilWorker is a new Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) attack framework — based on leveraging service workers — designed to conduct credential phishing campaigns.
Full article: https://medium.com/@ahaz1701/evilworker-da94ae171249.
Evilginx2 has established itself as the indispensable reference in the field of AiTM attacks. Thanks to its modular architecture, this solution can easily adapt to any platform, such as mainstream services (like Microsoft Office 365 or Google) or internal web applications, and dynamically bypass advanced security mechanisms including MFA.
Despite its effectiveness, Evilginx2 faces certain technical limitations inherent to its architecture:
- Its use relies heavily on the development and maintenance of configuration files for each legitimate service.
- The systematic substitution of legitimate domain names with a malicious one — within HTTP responses relayed by the proxy server — may disrupt the proper rendering and operation of the service. Furthermore, this strategy can be easily neutralized by using a code obfuscation engine or by implementing a dynamic domain name generation process for critical resources.
- The acquisition and configuration of new domains and subdomains capable of bypassing modern security filters are necessary for each Red Teaming engagement.
In response to the identified limitations, I have developed an innovative approach aimed at contributing to the evolution of AiTM techniques, both on an operational and strategic level.
Unlike the Evilginx2 method — which requires manual configuration steps and the development of phishlets — my goal was to design a fully autonomous and dynamic solution, capable of adapting in real time to any legitimate service.
To develop this solution, I leveraged service workers — a native technology in modern browsers originally designed to enhance the user experience.
When a victim clicks on a phishing link, a service worker is immediately registered within their browser and acts as a malicious proxy. Nearly all requests made within the context of the web application are redirected to a remote proxy server — controlled by the attacker — which forwards them to the legitimate service and then relays the responses back to the victim.
This innovative approach offers a proxying mechanism that is far more efficient than Evilginx2, while overcoming the technical limitations inherent to its architecture — namely, the need to develop and maintain configuration files for each service, as well as the issues related to the systematic substitution of legitimate domain names.
Additionally, the malicious proxy server requires only the use of a primary domain and a subdomain to operate, and it is compatible with PaaS (unlike Evilginx2), such as Azure Web Apps Service. The shared nature of this type of platform makes any degradation of the main domain's reputation virtually impossible — such an action would affect the entire ecosystem, thereby offering implicit protection against blocking or negative categorization mechanisms used by traditional security solutions.
Note
EvilWorker relies exclusively on standard Node.js libraries, thereby avoiding any external dependencies that could potentially compromise its long-term reliability.
It is strongly recommended to use Node.js version 22.15.0 or higher to ensure support for zstd compression and decompression algorithms by the malicious proxy server.
git clone https://github.com/Ahaz1701/EvilWorker.gitNote
It is strongly recommended to host EvilWorker on a PaaS such as Azure Web Apps Service.
EvilWorker can be quickly deployed for testing or development purposes using Ngrok or similar tools:
node proxy_server.js
ngrok http 3000Note
EvilWorker is an autonomous and dynamic solution that does not require the development of specific configuration files to adapt in real time to the targeted legitimate service.
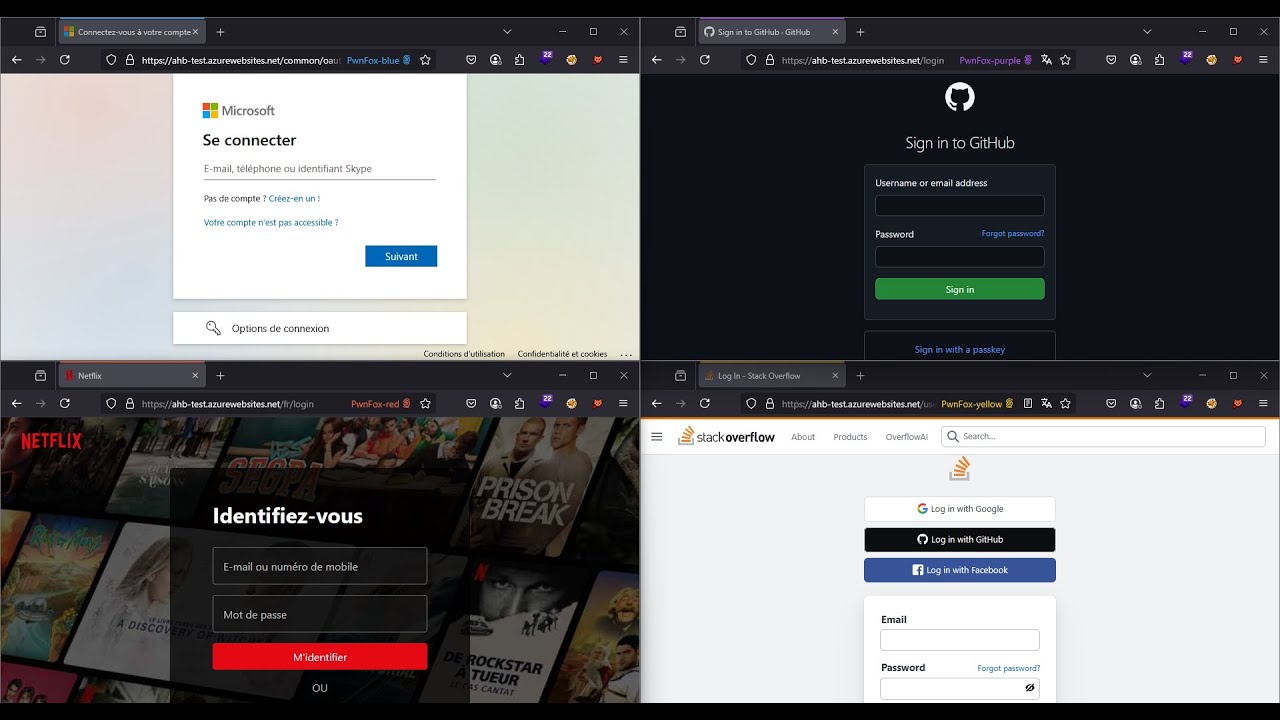
A real-time proxying of legitimate Microsoft Office 365, Stack Overflow, Netflix, and GitHub services, centralized on a single domain and subdomain provisioned by Azure Web Apps:
To create a valid phishing link, you simply need to follow the pattern below:
// Pattern to follow to create a valid phishing link
http(s)://$PHISHING_DOMAIN_NAME$PROXY_ENTRY_POINT&$PHISHED_URL_PARAMETER=$LEGITIMATE_LOGIN_PAGE_URL
// A concrete example of a valid phishing link
https://ahb-test.azurewebsites.net/login?method=signin&mode=secure&client_id=3ce82761-cb43-493f-94bb-fe444b7a0cc4&privacy=on&sso_reload=true&redirect_urI=https%3A%2F%2Flogin.microsoftonline.com%2F
If the malicious proxy server fails to proxy the victim’s HTTP traffic, it is recommended to read the full article to understand the specific cases that may cause issues and how to resolve them.
To minimize EvilWorker's indicators of compromise (IOCs), it is recommended to modify:
- The value of the
PROXY_ENTRY_POINTvariable:
const PROXY_ENTRY_POINT = "/login?method=signin&mode=secure&client_id=3ce82761-cb43-493f-94bb-fe444b7a0cc4&privacy=on&sso_reload=true";- The value of the
PHISHED_URL_PARAMETERvariable in all project files:
const PHISHED_URL_PARAMETER = "redirect_urI";- The names of the following files and paths in all project files:
const PROXY_FILES = {
index: "index_smQGUDpTF7PN.html",
notFound: "404_not_found_lk48ZVr32WvU.html",
script: "script_Vx9Z6XN5uC3k.js"
};
const PROXY_PATHNAMES = {
proxy: "/lNv1pC9AWPUY4gbidyBO",
serviceWorker: "/service_worker_Mz8XO2ny1Pg5.js",
script: "/@",
mutation: "/Mutation_o5y3f4O7jMGW",
jsCookie: "/JSCookie_6X7dRqLg90mH",
favicon: "/favicon.ico"
};Note
EvilWorker includes a logging system for intercepted communications, which are systematically encrypted using the AES-256 algorithm in CTR mode.
It is strongly recommended to modify the encryption key and store it more securely for real engagements.
const ENCRYPTION_KEY = "HyP3r-M3g4_S3cURe-EnC4YpT10n_k3Y";Intercepted communications are automatically stored in the phishing_logs directory at the root of the project.
To decrypt them, simply run the following command:
node decrypt_log_file.js $ENCRYPTED_LOG_FILE_PATHNote
EvilWorker includes a JavaScript code injection module specifically designed to bypass advanced security mechanisms implemented by the targeted services.
The script_Vx9Z6XN5uC3k.js file is automatically added to all HTML pages relayed by the malicious proxy server, so feel free to add your own JavaScript code to it.
Distributed under the BSD-2-Clause License. See LICENSE for more information.
LinkedIn: Antoine HAZEBROUCK
Email address: [email protected]